(Press-News.org) Results from the longest running breast screening trial show that screening with mammography reduces the number of deaths from breast cancer.
The study*, by researchers at Queen Mary, University of London, shows that the number of deaths that are prevented goes up year after year.
The results are new evidence of the long-term benefits of regular breast screening.
Senior author, Professor Stephen Duffy explained: "Breast cancer can take many years to develop so to tell if screening is effective, we need to see how women fair in the long-term.
"In this study, we've continued to monitor women for nearly three decades and we've found that the longer we look, the more lives are saved."
The study included over 130,000 women and was the first to show that screening, with mammography only, led to fewer deaths from breast cancer. It compared a group of women who were invited for regular mammograms with a group who were not. The women have now been followed up for 29 years to see how many died of the disease.
The results showed that 30 per cent fewer women in the screening group died of breast cancer and that this effect persisted year after year.
The study also showed that one cancer death is prevented for approximately every 400 to 500 women in the screening group.
Professor Duffy added: "This suggests that the long-term benefits of screening, in terms of deaths prevented, are more than double those often quoted for short-term follow-up.
"Unfortunately, we cannot know for certain who will and who won't develop breast cancer. But if you take part in screening and you are diagnosed with breast cancer at an early stage, the chances that it will be successfully treated are very good."
###
* Swedish Two-County Trial: Impact of Mammographic Screening on Breast Cancer Mortality during 3 Decades, Tabár et al, Radiology
Study shows long-term benefits of breast screening
2011-06-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Team approach reduces urinary tract infections in rehab patients
2011-06-28
Baltimore, Maryland, June 28, 2011 – Nurses, occupational and physical therapists, case managers and education staff, all working together at a 300-bed Nebraska rehabilitation hospital, have successfully implemented a team approach to dramatically reduce infections from urinary catheters, the most prevalent type of infection acquired in healthcare settings.
The interdisciplinary team at Madonna Rehabilitation Hospital in Lincoln, one of the largest free-standing rehabilitation hospitals in the country, reduced catheter associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) by 89 ...
triCerat Takes On IT Decisions 2011 in London
2011-06-28
triCerat is excited to announce its debut at IT decisions in London, June 28-29 at the QEII Conference Centre in Westminster, London.
IT decisions addresses the current, significant developments affecting IT systems in the real world. The two-day program includes sessions on virtualization, storage, cloud computing, software-as-a-service (SaaS), mobile and wireless accessibility, security, green IT, and more. The 30-minute sessions and roundtable discussions were designed with time-efficiency in mind for the busy IT executive. Keynote speaker Tim Jennings, Research Fellow ...
Intensive, hands-on effort reduces bloodstream infections in critically ill patients
2011-06-28
Baltimore, Maryland, June 28, 2011 – Nurses on a surgical intensive care unit (SICU) at a large academic medical center cut bloodstream infections to zero and saved more than $200,000 during a six-month period.
The University of Maryland Medical Center SICU sustained a rate of zero central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLABSIs) for a 25-week period, eliminating 14 CLABSIs and saving 2-3 lives when compared to the same time period in the previous year, according to results of an intensive, six-month nursing initiative presented today at the 38th Annual Educational ...
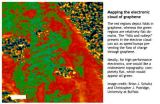
Researchers image graphene electron clouds, revealing how folds can harm conductivity
2011-06-28
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- A research team led by University at Buffalo chemists has used synchrotron light sources to observe the electron clouds on the surface of graphene, producing a series of images that reveal how folds and ripples in the remarkable material can harm its conductivity.
The research, scheduled to appear June 28 in Nature Communications, was conducted by UB, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the Molecular Foundry at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), and SEMATECH, a global consortium of semiconductor manufacturers.
Graphene, ...
Gothic Cabinet Craft Releases iPhone App for Furniture Shoppers
2011-06-28
Gothic Cabinet Craft (http://www.gothiccabinetcraft.com), one of the largest manufacturers and retailers of real wood furniture in the North Eastern United States, today announces the release of their new iPhone app for furniture shoppers, ShopGothic. A free app, ShopGothic was designed to aid in the furniture shopping process of Gothic Cabinet Craft's customers.
"No more guessing what color will best match existing furniture," says Aristidis Zaharopoulos, President of Gothic Cabinet Craft, Inc. "We found that to be a problem for many of our customers. ...
First joint ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias
2011-06-28
Cardiovascular disease (CVD), driven by the global pandemics of obesity and diabetes, poses a daunting challenge to clinicians in the 21st century. Despite progress, there is still much to be done to improve the control of dyslipidaemia, a key risk factor. In Europe, as many as one-half of patients are inadequately treated.1,2 The first European guidelines specifically focused on managing dyslipidaemias offer new hope.3,4 Experts from the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) and the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) worked together to develop these guidelines. The ...
Religion benefits traumatic brain injury victims, Wayne State University research finds
2011-06-28
DETROIT – Brigid Waldron-Perrine, Ph.D., a recent graduate from Wayne State University, and her mentor, Lisa J. Rapport, Ph.D., professor of psychology at Wayne State University's College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, found that if traumatic brain injury (TBI) victims feel close to a higher power, it can help them rehabilitate. The study was recently published in Rehabilitation Psychology.
Traumatic brain injury is a disruption of normal brain function after a head injury and affects 1.7 million Americans annually, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. ...
Stepped-up vaccine series for hepatitis B is effective during pregnancy
2011-06-28
DALLAS – June 28, 2011 – UT Southwestern Medical Center maternal-fetal specialists have confirmed a potential new protocol to protect pregnant women who are at risk for hepatitis B, a health problem that affects 2 billion people worldwide.
An accelerated hepatitis B vaccination schedule for high-risk pregnant women was found effective and well-tolerated. The findings appear in the journal Obstetrics & Gynecology.
While the normal three-shot regimen of hepatitis B vaccine for adults – given over a six-month period – has long been recommended for pregnant women, that ...
The good, the bad and the ugly: The many roles of c-JUN in cancer
2011-06-28
The c-JUN protein was initially described in the late 1980s as the mammalian equivalent of a protein responsible for causing cancer in birds. Intense research in a number of labs has subsequently led to a basic understanding of how the protein works. c-JUN is a transcription factor that modifies (phosphorylates) key regulatory proteins in the cell, thereby activating or deactivating them and leading to unregulated cell division and hence cancer. It has also become clear that c-JUN acts not on its own but in conjunction with an array of further proteins that modulate ...
Rockin' tortoises: A 150-year-old new species
2011-06-28
A team of researchers investigated a desert tortoise from the Southwest USA and northwestern Mexico. What was thought to be a simple problem in species identification turned out to be a very complex matter. Their investigations required forensic genetics and several other methods. In the end, they found it necessary to describe a new species. More than that, the discovery has very important implications for conservation and the development of the deserts of southern California.
Since the original description of Agassiz's Land Tortoise, scientifically called Gopherus agassizii, ...