(Press-News.org) Scientists have discovered fundamental steps of charging of nano-sized water droplets and unveiled the long-sought-after mechanism of hydrogen emission from irradiated water. Working together at the Georgia Institute of Technology and Tel Aviv University, scientists have discovered when the number of water molecules in a cluster exceeds 83, two excess electrons may attach to it — forming dielectrons — making it a doubly negatively charged nano droplet. Furthermore, the scientists found experimental and theoretical evidence that in droplets comprised of 105 molecules or more, the excess dielectrons participate in a water-splitting process resulting in the liberation of molecular hydrogen and formation of two solvated hydroxide anions. The results appear in the June 30 issue of the Journal of Physical Chemistry A.
It has been known since the early 1980s that while single electrons may attach to small water clusters containing as few as two molecules, only much larger clusters may attach more than single electrons. Size-selected, multiple-electron, negatively-charged water clusters have not been observed — until now.
Understanding the nature of excess electrons in water has captured the attention of scientists for more than half a century, and the hydrated electrons are known to appear as important reagents in charge-induced aqueous reactions and molecular biological processes. Moreover, since the discovery in the early 1960s that the exposure of water to ionizing radiation causes the emission of gaseous molecular hydrogen, scientists have been puzzled by the mechanism underlying this process. After all, the bonds in the water molecules that hold the hydrogen atoms to the oxygen atoms are very strong. The dielectron hydrogen-evolution (DEHE) reaction, which produces hydrogen gas and hydroxide anions, may play a role in radiation-induced reactions with oxidized DNA that have been shown to underlie mutagenesis, cancer and other diseases.
"The attachment of multiple electrons to water droplets is controlled by a fine balancing act between the forces that bind the electrons to the polar water molecules and the strong repulsion between the negatively charged electrons," said Uzi Landman, Regents' and Institute Professor of Physics, F.E. Callaway Chair and director of the Center for Computational Materials Science (CCMS) at Georgia Tech.
"Additionally, the binding of an electron to the cluster disturbs the equilibrium arrangements between the hydrogen-bonded water molecules and this too has to be counterbalanced by the attractive binding forces. To calculate the pattern and strength of single and two-electron charging of nano-size water droplets, we developed and employed first-principles quantum mechanical molecular dynamics simulations that go well beyond any ones that have been used in this field," he added.
Investigations on controlled size-selected clusters allow explorations of intrinsic properties of finite-sized material aggregates, as well as probing of the size-dependent evolution of materials properties from the molecular nano-scale to the condensed phase regime.
In the 1980s Landman, together with senior research scientists in the CCMS Robert Barnett, the late Charles Cleveland and Joshua Jortner, professor of chemistry at Tel Aviv University, discovered that there are two ways that single excess electrons can attach to water clusters – one in which they bind to the surface of the water droplet, and the other where they localize in a cavity in the interior of the droplet, as in the case of bulk water. Subsequently, Landman, Barnett and graduate student Harri-Pekka Kaukonen reported in 1992 on theoretical investigations concerning the attachment of two excess electrons to water clusters. They predicted that such double charging would occur only for sufficiently large nano-droplets. They also commented on the possible hydrogen evolution reaction. No other work on dielectron charging of water droplets has followed since.
That is until recently, when Landman, now one of the world leaders in the area of cluster and nano science, and Barnett teamed up with Ori Chesnovsky, professor of chemistry, and research associate Rina Giniger at Tel Aviv University, in a joint project aimed at understanding the process of dielectron charging of water clusters and the mechanism of the ensuing reaction - which has not been observed previously in experiments on water droplets. Using large-scale, state-of-the-art first-principles dynamic simulations, developed at the CCMS, with all valence and excess electrons treated quantum mechanically and equipped with a newly constructed high-resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometer, the researchers unveiled the intricate physical processes that govern the fundamental dielectron charging processes of microscopic water droplets and the detailed mechanism of the water-splitting reaction induced by double charging.
The mass spectrometric measurements, performed at Tel Aviv, revealed that singly charged clusters were formed in the size range of six to more than a couple of hundred water molecules. However, for clusters containing more than a critical size of 83 molecules, doubly charged clusters with two attached excess electrons were detected for the first time. Most significantly, for clusters with 105 or more water molecules, the mass spectra provided direct evidence for the loss of a single hydrogen molecule from the doubly charged clusters.
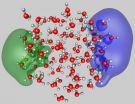
The theoretical analysis demonstrated two dominant attachment modes of dielectrons to water clusters. The first is a surface mode (SS'), where the two repelling electrons reside in antipodal sites on the surface of the cluster (see the two wave functions, depicted in green and blue, in Figure 1). The second is another attachment mode with both electrons occupying a wave function localized in a hydration cavity in the interior of the cluster — the so-called II binding mode (see wave function depicted in pink in Figure 2). While both dielectron attachment modes may be found for clusters with 105 molecules and larger ones, only the SS' mode is stable for doubly charged smaller clusters.
"Moreover, starting from the II, internal cavity attachment mode in a cluster comprised of 105 water molecules, our quantum dynamical simulations showed that the concerted approach of two protons from two neighboring water molecules located on the first shell of the internal hydration cavity, leads, in association with the cavity-localized excess dielectron (see Figure 2), to the formation of a hydrogen molecule. The two remnant hydroxide anions diffuse away via a sequence of proton shuttle processes, ultimately solvating near the surface region of the cluster, while the hydrogen molecule evaporates," said Landman.
"What's more, in addition to uncovering the microscopic reaction pathway, the mechanism which we discovered requires initial proximity of the two reacting water molecules and the excess dielectron. This can happen only for the II internal cavity attachment mode. Consequently, the theory predicts, in agreement with the experiments, that the reaction would be impeded in clusters with less than 105 molecules where the II mode is energetically highly improbable. Now, that's a nice consistency check on the theory," he added.
As for future plans, Landman remarked, "While I believe that our work sets methodological and conceptual benchmarks for studies in this area, there is a lot left to be done. For example, while our calculated values for the excess single electron detachment energies are found to be in quantitative agreement with photoelectron measurements in a broad range of water cluster sizes — containing from 15 to 105 molecules — providing a consistent interpretation of these measurements, we would like to obtain experimental data on excess dielectron detachment energies to compare with our predicted values," he said.
"Additionally, we would like to know more about the effects of preparation conditions on the properties of multiply charged water clusters. We also need to understand the temperature dependence of the dielectron attachment modes, the influence of metal impurities, and possibly get data from time-resolved measurements. The understanding that we gained in this experiment about charge-induced water splitting may guide our research into artificial photosynthetic systems, as well as the mechanisms of certain bio-molecular processes and perhaps some atmospheric phenomena."
"You know," he added. "We started working on excess electrons in water clusters quite early, in the 1980s — close to 25 years ago. If we are to make future progress in this area, it will have to happen faster than that."
INFORMATION:
Scientists discover dielectron charging of water nano-droplet
2011-06-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
International team demonstrates subatomic quantum memory in diamond
2011-06-28
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) –– Physicists working at the University of California, Santa Barbara and the University of Konstanz in Germany have developed a breakthrough in the use of diamond in quantum physics, marking an important step toward quantum computing. The results are reported in this week's online edition of Nature Physics.
The physicists were able to coax the fragile quantum information contained within a single electron in diamond to move into an adjacent single nitrogen nucleus, and then back again using on-chip wiring.
"This ability is potentially useful ...
Female mate choice enhances offspring fitness in an annual herb
2011-06-28
In many organisms females directly or indirectly select mates (or sperm) and potentially influence the fitness of their offspring. Mate choice and sexual selection in plants is more complex in some ways than in animals because plants are sessile organisms and often have to rely on external vectors, such as animals, for pollen transport. As such, there is only so much a plant can do to affect the timing of pollen arrival, or the size and diversity of deposited pollen. But can a plant control which pollen grains, of the hundreds that land on their stigmas, make it to the ...
Studies examine impact of media use among youth, recommend preventative measures
2011-06-28
SEATTLE – June 27, 2011 – In today's society where access to media is ever present, many parents worry about what is appropriate media usage for their children and how media consumption can potentially affect them. Two new studies led by Dr. Dimitri A. Christakis, MD, MPH and Dr. Michelle M. Garrison, PhD of Seattle Children's Research Institute, focus on different uses of media and assess how media usage can lead to depression in college students and disrupt sleep patterns in preschool aged children. The results of Dr. Christakis' study, "Problematic Internet Usage in ...
Fossilized pollen reveals climate history of northern Antarctica
2011-06-28
VIDEO:
Rice University scientist John Anderson discusses what researchers have learned from studying the first direct and detailed climate record from the continental shelves surrounding Antarctica, and he describes the years...
Click here for more information.
HOUSTON -- (June 27, 2011) -- A painstaking examination of the first direct and detailed climate record from the continental shelves surrounding Antarctica reveals that the last remnant of Antarctic vegetation ...
UCLA stem cell scientists discover new airway stem cell
2011-06-28
Researchers at UCLA have identified a new stem cell that participates in the repair of the large airways of the lungs, which play a vital role in protecting the body from infectious agents and toxins in the environment.
The airways protect the body by producing and clearing mucus from the airways. The mucus is largely produced by specialized mucus glands in the airway and the mechanisms of normal and excessive mucus production are not well understood. However, this newly discovered lung stem cell for the mucus glands will likely yield new insights into this critical ...
Childhood cancer survivors are at high risk for multiple tumors as they age
2011-06-28
The largest study yet of adult childhood cancer survivors found that the first cancer is just the beginning of a lifelong battle against different forms of the disease for about 10 percent of these survivors.
The research involved 14,358 individuals enrolled in the federally funded Childhood Cancer Survivor Study (CCSS). St. Jude Children's Research Hospital investigators leading the effort reported that 1,382, or 9.6 percent, of survivors developed new tumors unrelated to their original cancers. About 30 percent of those survivors, 386 individuals, developed third tumors. ...
Surprising drop in physicians' willingness to accept patients with insurance
2011-06-28
NEW YORK (June 27, 2011) -- As required under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010, millions of people will soon be added to the ranks of the insured. However, this rapid expansion of coverage is colliding with a different, potentially problematic trend that could end up hampering access to health care.
Since 2005, doctors have been accepting fewer and fewer patients with health insurance, according to a new study published in the June 27th issue of Archives of Internal Medicine. As a result, says Dr. Tara Bishop, assistant professor of public health ...
Landsat Satellite images reveal extent of historic North Dakota flooding
2011-06-28
Heavy rains in Canada caused historic flooding in Minot, N.D. Landsat satellite images taken before and during the flooding reveal the water's extent.
The Souris River finally crested on June 26, but not before more than 4,000 homes and hundreds of businesses were flooded. About one-fourth of Minot's 40,000 residents evacuated the city. Residents expect a long recovery as the river slowly retreats.
The Souris River reading at Minot's Broadway Bridge around 11:00 p.m. on June 25 reached nearly four feet higher than the all-time high set in 1881.
The Landsat Program ...
Study finds peat wildfire smoke linked to heart failure risk
2011-06-28
An EPA study published online Monday in Environmental Health Perspectives finds that the 2008 peat bog wildfires in NC led to an increase in emergency room visits for respiratory and cardiovascular effects.
The study found a 37 percent increase in ER visits for people with symptoms of heart failure during a three day period of dense smoke exposure and the following five days.
Other findings include a 65 percent increase in visits for asthma, 73 percent increase in visits for COPD and 59 percent increase in visits for pneumonia and bronchitis.
This is the first ...
Related studies point to the illusion of the artificial
2011-06-28
SAN ANTONIO (June 27, 2011) — In the constant battle to lose inches or at least stay the same, we reach for the diet soda. Two studies presented June 25 and 27 at the American Diabetes Association's Scientific Sessions in San Diego suggest this might be self-defeating behavior.
Epidemiologists from the School of Medicine at The University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio reported data showing that diet soft drink consumption is associated with increased waist circumference in humans, and a second study that found aspartame raised fasting glucose (blood sugar) ...