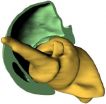
(Press-News.org) A musculoskeletal system so far unknown in the animal world was recently discovered in weevils. The hip of Trigonopterus oblongus does not consist of the usual hinges, but of joints based on a screw-and-nut system. This first biological screw thread is about half a millimeter in size and was studied in detail using synchrotron radiation. The discovery is reported by the current issue of the Science magazine. (DOI:10.1126/science.1204245)
"Such a construction for animal leg movement is quite unusual, as large areas of skeletal parts move on top of each other. Supply of the leg takes place via a very small opening in the center of the screw," Thomas van de Kamp from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology says. In nature, hips and shoulders usually are based on ball-and-socket systems or hinges that can be operated more easily by organisms. Screws and nuts are known from engineering and used for the fixed connection of components. "Now, we found that nature was first in inventing screws and nuts, because weevils have been using this construction for about 100 million years already," Alexander Riedel from the Karlsruhe State Museum of Natural History says. This museum supplied the weevil samples studied. The detailed three-dimensional images of the joints were made at the national ANKA synchrotron radiation source of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology.
As a rule, weevils are clumsier than many other beetles, e.g. cara-bidae. Transformation of a hinge joint into a screw joint, however, allowed them to move their legs further down, which made them better climbers. The Trigonopterus oblongus weevil analyzed here lives on twigs and foliage in the jungle of Papua New Guinea. For feeding, the thorn is pushed into the plant tissue, while the hind legs provide strong foothold. Presumably, the screw joint also is advan-tageous in this respect.
"Meanwhile, we have also studied other weevil species and always found screw joints," explain Riedel and van de Kamp. "Obviously, this joint exists in all weevils, of which more than 50,000 species exist worldwide." In this case, the researchers would have identified the screw joint to be a so far unknown basic feature of the weevil family. The best known species in Germany are curculio nucum and curculio glandium as well as the corn weevil, a grain pest.
The three-dimensional image reconstructions of the joint of Trigonopterus oblongus of half a millimeter in size were made by means of the newly installed microtomograph of the ANKA synchrotron radiation source. "It extends the existing ensemble of synchrotron imaging techniques for wide application in life sciences," says Tilo Baumbach, Head of the ANKA synchrotron radiation source. "External users can now apply modern systems, from long-wave terahertz radiation to the highly brilliant X-radiation used in this case."
INFORMATION:
The studies of the Trigonopterus species are funded by the DFG.
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) is a public corporation according to the legislation of the state of Baden-Württemberg. It fulfills the mission of a university and the mission of a national research center of the Helmholtz Association. KIT focuses on a knowledge triangle that links the tasks of research, teaching, and innovation.
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology: Nature uses screws and nuts
With a screw thread as joint, weevils move in nature; scientists from Karlsruhe revealed anatomy using synchrotron computer tomography
2011-07-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Canvas Prints Made Even Easier with Photo Montage Service at PhotoInCanvas
2011-07-02
Canvas prints specialists PhotoInCanvas has implemented a superb new feature at the site which helps customers that just can't choose which image to use. If people have too many great shots of a similar theme to choose from, then the team at PhotoInCanvas can put all of them into a fantastic photo canvas.
This feature may be perfect for individuals that have been to an event such as festival where an abundance of photographs are taken. PhotoInCanvas is urging customers to send them all in so they can group them together to create a stunning image.
The PhotoInCanvas ...
Star Partner Receives The GPWA Seal Of Approval
2011-07-02
On the 22 June 2011 Star Partner received their GPWA sponsorship. Having the Seal of Approval from the GPWA signifies that Star Partner is of a professional standard.
GPWA has over 10,000 public and private registered members and is the only professional organisation of its kind. The GPWA Seal of Approval is awarded to gambling portal websites that meet certain standards and the GPWA code of conduct. Being part of the GPWA enables public and private members to be part of online forums with in-depth news and advice about new industry developments, online gaming law, ...
Earlier exit from hospital after hip operation
2011-07-02
Discharged from the hospital within two days of a total hip replacement operation? It's possible, thanks to the new 'Fast Track' protocol that underwent testing in the U.S., in response to both patient requests for shorter hospital stays and economic realities of providing medical care. According to Dr. Lawrence Gulotta and colleagues, from Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, a carefully screened group of patients undergoing total hip replacement can be discharged from the hospital two days after surgery, without any increase in complications or adverse effects compared ...
Research examines dentists' role in painkiller abuse
2011-07-02
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — The Obama administration turned a bright spotlight on prescription painkiller abuse in April when the Office of National Drug Control Policy released a national action plan and a statement from Vice President Joe Biden. With a cover article in the July edition of the Journal of the American Dental Association (JADA), dentists focus that spotlight on themselves both as major sources of opioid drugs and as professionals with largely untapped power to recognize and reduce abuse.
"Many dentists really haven't even perceived there to be ...
Grand Rapids Dentist Keeps Patients In The Know With Smile Update
2011-07-02
Recognized as an expert in the field of cosmetics and technology in dentistry, Dr. Lambert, Grand Rapids dentist, is pleased to offer patients ongoing valuable insight to dentistry with his practice newsletter, Smile Update. These updates were created to offer patients a way to remain up-to-date with not only the office, but current dental health issues as well, and can be accessed via the practice's website.
The Smile Update, by Dr. Thomas Lambert, was created to improve patient's' dental health and awareness. Patients can visit the practice's website to access this ...
Mutations can spur dangerous identity crisis in cells
2011-07-02
As our bodies first form, developing cells are a lot like children put on the school bus with their names and addresses pinned to their shirts.
The notes identify one as a future heart cell, another as a liver cell, a third as a neuron. And that's what they each grow up to be.
But once those cells reach adulthood, changes to those original marching orders caused by aging, disease and other stressors like smoking can precipitate a kind of identity crisis, researchers at the University of Michigan Health System have found.
The cells start to forget things like which ...
Treatment approach to human Usher syndrome: Small molecules ignore stop signals
2011-07-02
Usher syndrome is the most common form of combined congenital deaf-blindness in humans and affects 1 in 6,000 of the population. It is a recessive inherited disease that is both clinically and genetically heterogeneous. In the most severe cases, patients are born deaf and begin to suffer from a degeneration of the retina in puberty, ultimately resulting in complete blindness. These patients experience major problems in their day-to-day life. While hearing loss can be compensated for with hearing aids and cochlea implants, it has not proven possible to develop a treatment ...
Global plant database set to promote biodiversity research and Earth-system sciences
2011-07-02
The world's largest database on plants' functional properties, or traits, has been pub-lished. Scientists compiled three million traits for 69,000 out of the world's ~300,000 plant species. The achievement rests on a worldwide collaboration of scientists from 106 re-search institutions. The initiative, known as TRY, is hosted at the Max Planck Institute for Biogeochemistry in Jena (Germany). Jointly coordinated with the University of Leipzig (Germany), IMBIV-CONICET (Argentina), Macquarie University (Australia), CNRS and University of Paris-Sud (France), TRY promises to ...
Evolution of sport performances follows a physiological law
2011-07-02
Geoffroy Berthelot and Stephane Len, both researchers at the IRMES (Institut de Recherche bioMédicale et d'Epidemiologie du Sport at INSEP, Paris, France), have published their findings in Age, the official journal of the American Aging Association, describing the evolution of performances in elite athletes and chess grandmasters. This article is congruous with the epidemiological approaches developed by the laboratory, and suggests that changes in individual performance are linked to physiological laws structuring the living world.
Physiological parameters that characterize ...
New study documents first cookiecutter shark attack on a live human
2011-07-02
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- A new study co-authored by University of Florida researchers provides details on the first cookiecutter shark attack on a live human, a concern as warm summer waters attract more people to the ocean.
The study currently online and appearing in the July print edition of Pacific Science warns that swimmers entering the cookiecutter's range of open ocean tropical waters may be considered prey.
The sharks feed near the surface at night, meaning daytime swimmers are less likely to encounter them. The species is small, with adults reaching about 2 feet, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
[Press-News.org] Karlsruhe Institute of Technology: Nature uses screws and nutsWith a screw thread as joint, weevils move in nature; scientists from Karlsruhe revealed anatomy using synchrotron computer tomography