(Press-News.org) TORONTO, September 17, 2010 – Nearly half of women with diabetes prior to pregnancy have a potentially-avoidable C-section and their babies are twice as likely to die as those born to women without diabetes, according to the POWER study.
Researchers from St. Michael's Hospital, the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES) and Women's College Hospital say rates of diabetes in Ontario have doubled in the last 12 years. Nearly one in 10 Ontario adults has been diagnosed with diabetes, including more women than ever before.
As women develop type 2 diabetes (adult onset) during childbearing age, complications during pregnancy are becoming increasingly common.
"We are seeing more younger women living with diabetes. In fact, while older men still have higher rates than older women, women under 45 are getting diagnosed at the same rate as men in that age group," says Dr. Lorraine Lipscombe, a scientist at the Women's College Research Institute at Women's College Hospital and ICES. "This trend is having increasing implications for younger women. With more women having babies later in life, we are seeing a greater number of women getting pregnant with diabetes. The POWER Study found that having diabetes before pregnancy significantly increases the risk of pregnancy and fetal complications."
The POWER (Project for an Ontario Women's Health Evidence-Based Report) Study — a joint study from St. Michael's Hospital and ICES — is the first in the province to provide a comprehensive overview of women's health in relation to income, education, ethnicity and geography. The findings are detailed in the report titled Diabetes-the ninth chapter to be released as part of the study. Findings can be used by policymakers and health-care providers to improve access, quality and outcomes of care for Ontario women. The POWER Study was funded by Echo: Improving Women's Health in Ontario, an agency of the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care.
"By identifying the provincial variations in diabetes care, the Local Health Integration Networks can now use this data for priority setting, planning and quality improvement activities," says Pat Campbell, CEO, Echo. "By implementing interventions at the policy, population health and practice levels we can reduce these regional inequities and improve the health of both men and women with diabetes."
The POWER study, released today, examined the impact of diabetes on Ontarians. Key findings include:
45 per cent of women with pre-gestational diabetes are having C-sections compared with 37 per cent of women with gestational diabetes and 27 percent of women without diabetes.
Babies born to women with pre-pregnancy diabetes have twice as many fetal complications as those born to women without diabetes.
The rate of stillbirth/in-hospital mortality in women with pre-pregnancy diabetes is twice the rate in women with diabetes (5.2 per 1,000 vs 2.5 per 1,000) than women without diabetes.
Rates of major and minor congenital anomalies were 60 per cent higher among women with pre-pregnancy diabetes than women without diabetes.
More than 50 per cent of people who don't yet have diabetes have risk factors for the disease.
One in four adults aged 65 and older have been diagnosed with diabetes.
"Infants born to women with diabetes are at much higher risk for serious complications –which can be prevented by controlling glucose and blood pressure levels at the time of conception and during pregnancy," says Dr. Gillian Booth, scientist at St. Michael's Hospital and scientist at ICES. "This reflects a need for more targeted pre-pregnancy counselling and better pregnancy care for this group of women."
"Diabetes is quickly becoming a worldwide epidemic, owing to a dramatic rise in type 2 diabetes – but most diabetes can be prevented," says Arlene Bierman, a physician at St. Michael's Hospital and principal investigator of the study. "We need to focus on preventing or reducing rates of diabetes among young women, one of the most vulnerable groups, and ensure that women who have diabetes get effective treatment," adds Dr. Bierman, also an ICES investigator.
###
For more information on the POWER Study and its partners, visit www.powerstudy.ca. Other findings from the study will be released later this year.
END
Global efforts to tackle millions of preventable child and maternal deaths will fail to extend gains unless world leaders act now to pour more healthcare resources directly into families and communities, according to a new World Vision report launched today.
"The Missing Link: Saving children's lives through family care" examines how the resources invested to achieve Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) 4 and 5 can go further toward saving the more than 8 million children under the age of five and 350,000 mothers who die each year, mostly from preventable causes. Undertaken ...
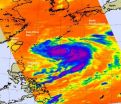
Infrared satellite data from NASA's Aqua satellite revealed strong convection and a tight circulation center within Typhoon Fanapi as it heads for a landfall in Taiwan this weekend.
At 1500 UTC (10 a.m. EDT) on Sept. 17, Typhoon Fanapi's maximum sustained winds were near 85 knots (97 mph). It was centered about 360 nautical miles east-southeast of Taipei, Taiwan near 23.2 North and 127.4 East. It is churning up high seas up to 22 feet.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Typhoon Fanapi on September 17 at 04:45 UTC (12:45 a.m. EDT) and captured an infrared image of its ...
We run our modern lives largely by the clock, from the alarms that startle us out of our slumbers and herald each new workday to the watches and clocks that remind us when it's time for meals, after-school pick-up and the like.
In addition to those ubiquitous timekeepers, though, we have internal "clocks" that are part of our biological machinery and which help set our circadian rhythms, regulating everything from our sleep-wake cycles to our appetites and hormone levels. Light coming into our brains via our eyes set those clocks, though no one is sure exactly how this ...
NASA's CloudSat satellite captured a profile of Hurricane Karl as it began making landfall in Mexico today. The satellite data revealed very high, icy cloud tops in Karl's powerful thunderstorms, and moderate to heavy rainfall from the storm. Meanwhile, NASA's "GRIP" mission was also underway as aircraft were gathering valuable data about Hurricane Karl as he moves inland.
NASA's Genesis and Rapid Intensification Processes mission (known as GRIP) is still underway and is studying the rapid intensification of storms, and that's exactly what Karl did on Thursday Sept. ...
Julia is waning in the eastern Atlantic Ocean because of outflow from massive Hurricane Igor, despite his distance far to the west. Satellite imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite showed that Julia's eye was no longer visible, a sign that she's weakening.
As NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Hurricane Julia from space on Sept. 16 at 1:35 p.m. EDT, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument captured a visible image of the storm. In the MODIS image, Julia's eye was no longer visible and its center was cloud-filled.
Although Julia is weakening from ...
Spoilage bacteria that can cause red coloration of pickles' skin during fermentation may actually help clean up dyes in textile industry wastewater, according to a U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) study.
Some species of Lactobacilli-food-related microorganisms-can cause red coloring when combined with tartrazine, a yellow food-coloring agent used in the manufacture of dill pickles. Now Agricultural Research Service (ARS) microbiologist Ilenys Pérez-Díaz and her colleagues have found that these spoilage Lactobacilli also may have environmental benefits. ARS is ...
Deleting a certain gene in mice can make them smarter by unlocking a mysterious region of the brain considered to be relatively inflexible, scientists at Emory University School of Medicine have found.
Mice with a disabled RGS14 gene are able to remember objects they'd explored and learn to navigate mazes better than regular mice, suggesting that RGS14's presence limits some forms of learning and memory.
The results were published online this week in the Early Edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Since RGS14 appears to hold mice back mentally, ...
Solar energy could be a central alternative to petroleum-based energy production. However, current solar-cell technology often does not produce the same energy yield and is more expensive to mass-produce. In addition, information on the total effect of solar energy production on the environment is incomplete, experts say.
To better understand the energy and environmental benefits and detriments of solar power, a research team from Rochester Institute of Technology has conducted one of the first life-cycle assessments of organic solar cells. The study found that the embodied ...
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a serious public health problem in the United States. Recent data show that approximately 1.7 million people sustain a traumatic brain injury annually. While the majority of TBIs are concussions or other mild forms, traumatic brain injuries contribute to a substantial number of deaths and cases of permanent disability.
Currently, there are no drugs available to treat TBI: a variety of single drugs have failed clinical trials, suggesting a possible role for drug combinations. Testing this hypothesis in an animal model, researchers at SUNY ...
Salt Lake City, September 17, 2010—Colon cancer is the second most common cancer in the United States and causes more than 50,000 deaths each year. It has been known for some time that mutations in the APC gene occur in more than 85 percent of all sporadic colon cancers. Now researchers at Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah demonstrate in a study featured today in Cell the mechanism by which mutation of the APC gene affects a cellular process known as DNA methylation. DNA methylation is a chemical modification made to DNA that plays an important role in ...