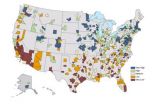
(Press-News.org) BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Which U.S. metro region is most likely to come out of the next recession, natural disaster or other regional "shock" relatively unscathed? Rochester, Minn. A little more battered might be College Station-Bryan, Texas.
These two regions are ranked first and last, respectively, by a new online tool measuring more than 360 U.S. metros for their "regional resilience," or capacity to weather acute and chronic stresses ranging from gradual economic decline to rapid population gains to earthquakes and floods.
The Resilience Capacity Index (RCI), developed by Kathryn A. Foster, director of the Regional Institute, a research and public policy center of the University at Buffalo, produces a single statistic for each region based on its performance across 12 economic, socio-demographic and community connectivity indicators, ranging from income equality and business environment to voter participation and the population of health-insured.
As a gauge for how well a region is positioned to adapt to stress, the index can help regional leaders identify strengths and weaknesses and target related policy changes toward building their resilience capacity.
"Conceiving of regions as capable of adapting and transforming in response to challenges allows researchers and practitioners to understand the conditions and interventions that may make one place more or less resilient and why," said Foster, also a professor of urban and regional planning with UB's School of Architecture and Planning.
Foster developed the index as part of Building Resilient Regions, a national network of experts on metropolitan regions funded by the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation and administered by the University of California, Berkeley. Online at http://brr.berkeley.edu, the index features maps revealing geographic patterns in resilience capacity, detailed data profiles for each metro and a "compare metros" tool.
Overall, Northeastern and Midwestern regions tend to be more resilient than those in the South or West, largely because these regions earn high scores for affordability, the size of their health-insured population, rates of homeownership and metropolitan stability, as measured by recent population change.
For instance, the Buffalo Niagara metro region ranks among the nation's top regions for its metropolitan stability and health-insured population. However, lower rankings on indicators such as income equality, business environment and population without disabilities to some degree offset its assets. This gives the Buffalo Niagara metro region an overall RCI rank of 86, still categorized as high.
Across the three categories of regional capacity, the top-scoring metros are geographically diverse. Raleigh, N.C., with leading technology firms, medical centers and universities, heads the economic category. Ames, Iowa, ranks first for socio-demographic capacity due to its exceptionally high level of educational attainment (Iowa State University is located there). For community connectivity, Bismarck, N.D., scores highest given its critical mass of civic institutions as the state capital.
Metropolitan areas with populations over 1 million vary widely in their resilience capacity. The top-ranking large metropolitan area, Minneapolis-St. Paul, achieves its status with very high socio-demographic capacity and levels of community connection, the latter reflecting the region's No. 1 rank for voter participation. The lowest-ranking large metropolitan area is Miami, Fla., a region with very low regional affordability and income equality.
Foster points out that a region's RCI score is not necessarily a sentence for success or failure in the face of the next population boom, economic recession or industry shutdown.
"What it does tell us is that some regions are structurally more prepared than others, and thus have greater capacity to bounce back in the wake of stress," she said. "Still, regions with a high capacity for resilience can squander their strengths just as those ranked low can rise to the occasion and perform above expectations."
Additional research efforts, a number of which are highlighted on the Building Resilient Regions site, are under way to measure how regions actually respond to stress. Future studies will explore which resilience capacity measures matter most for different kinds of stresses as well as the significance of key governance and environmental factors not captured by the RCI.
INFORMATION:
A major research and public policy center of UB, the Regional Institute plays a vital role in addressing key policy and governance issues for regions, with focused analysis of the Buffalo Niagara region. The institute leverages the resources of the university and binational community to pursue a wide range of scholarship, projects and initiatives that frame issues, inform decisions and guide change.
The University at Buffalo is a premier research-intensive public university, a flagship institution in the State University of New York system and its largest and most comprehensive campus. UB's more than 28,000 students pursue their academic interests through more than 300 undergraduate, graduate and professional degree programs. Founded in 1846, the University at Buffalo is a member of the Association of American Universities.
'Resilience' of US metros measured by online index developed by UB researchers
2011-07-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Amazing Hand-Crafted Polymer Clay Switch Plates 50% Off Clearance At Habitatter.com!
2011-07-12
Since 2008, Habitatter.com has been offering the highest quality in home decorating accessories, and Good Night Irene! has been with them since the beginning.
Good Night Irene! is a one-woman studio in beautiful Asheville, North Carolina who has been creating imaginative switch plates since 1992. Her designs reflect nature and all have texture to thrill your hands as well as your eyes. These light switch plates are made with polymer clay, a versatile and durable synthetic material, and cured directly onto plastic switch plates to ensure a perfect fit.
All good things ...
Epigenetic pathway and new drug show promise in reversing a hard-to-treat childhood cancer
2011-07-12
A difficult-to-treat form of childhood leukemia relies on changes in the structure of DNA – so-called epigenetic changes – to wreak genomic havoc within white blood cells, according to one of two studies conducted by a research team at Children's Hospital Boston and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. Together with collaborators from a biotechnology company, the same team also showed that a new drug that blocks these changes could deactivate cancer-promoting genes and halt the growth of this cancer.
These studies, reported in a pair of papers in the July 11, 2011 issue of Cancer ...
Neural stem progenitor cell transplantation’s potential to aid spinal cord injury tested
2011-07-12
Tampa, Fla. (July. 11, 2011) – A study published in the current issue of Cell Transplantation (20:5) investigating optimal routes for transplanting neural stem/progenitor cells (NS/PCs) in animal models of spinal cord injury (SCI) has demonstrated that intralesional (IL) injection conferred benefits over intravenous injection (IV) and intrathecal (IT) injection. The study, by a team of Keio University (Japan) researchers, is now freely available on-line at http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/cog/ct/ .
"Spinal cord injury usually results in severe, paralytic damage ...
Just like teens, parents get personal on Facebook
2011-07-12
They may not dress like Justin Bieber or Selena Gomez, but parents are a whole lot like their teenagers when it comes to their behaviour on Facebook. That's the finding of a new study by University of Guelph researchers.
Parents are just as likely as their kids to disclose personal information on the social networking site, according to the research, which will be published in the journal Social Psychological and Personality Science and is available online now.
And (gasp!) mom and dad are just as susceptible to the need for popularity.
"Facebook is not just a phenomenon ...
Sertoli cells show promise for therapeutics
2011-07-12
Tampa, Fla. (July 11, 2011) – Two papers published in the current issue of Cell Transplantation (20:5), now freely available on-line at http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/cog/ct/, highlight the therapeutic potential of human Sertoli cells that are present in the testes and are also called "nurse" or "mother" cells because they nurture the developing sperm cells. Sertoli cells form the blood-testes barrier that separates the blood compartment of the testes from the compartment of the seminiferous tubules. Once differentiated to form the blood-testes barrier, Sertoli cells ...
The truth about cats and dogs: Pets are good for mental health of 'everyday people'
2011-07-12
WASHINGTON – Pets can serve as important sources of social and emotional support for "everyday people," not just individuals facing significant health challenges, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
And, the study found, pet owners were just as close to key people in their lives as to their animals, indicating no evidence that relationships with pets came at the expense of relationships with other people, or that people relied more on pets when their human social support was poorer.
Psychologists at Miami University and Saint ...
Writing DNR orders takes longer, death more likely when surrogate decision-maker involved
2011-07-12
INDIANAPOLIS – Indiana University and Regenstrief Institute researchers report that it takes significantly longer for orders to forgo resuscitation in the event of cardiac arrest to be written for patients who had that decision made for them by a surrogate decision-maker compared to patients who made their own decisions, even though patients with a surrogate were sicker and the resuscitation issue might arise sooner. Among patients who died, patients with a surrogate had a shorter time frame between writing the DNR order and time of death compared to patients who made ...
Biofilters reduce carbon footprint of old landfill sites
2011-07-12
Researchers in the US are testing biofilter systems as a viable alternative to releasing methane from passive landfill vents into the atmosphere. The technology could reduce the overall impact of old landfills on global warming. Details are reported in the current issue of the International Journal of Environmental Engineering.
Organic matter rotting in smaller, old landfill sites generates a slow trickle of the potent greenhouse gas, methane, into the atmosphere, amounting to just 2 or 3 kilograms per day per vent. In contrast to controlled methane generate for biofuel ...
Aerospace Manufacturing in Mexico is the Subject of Offshore Group Podcast
2011-07-12
Carlos Bello, executive director of the Mexican Federation of Aerospace Industries, recently sat down with The Offshore Group to discuss the current state of affairs in Mexico's rapidly developing aerospace sector.
During the session, Bello informed that Mexico is currently home to 232 aerospace and aerospace industry related companies that employ a combined 29,000 workers. According to Bello, "In recent years, aerospace manufacturing in Mexico has been "experiencing a growth rate of about 20% annually, with the exception of 2009, which was a difficult year ...
EARTH: Is there really a minerals crisis?
2011-07-12
Alexandria, VA – China sent the high-tech industry and markets reeling last fall when it blocked exports of raw rare earth minerals to Japan, Europe and the U.S. The sudden severing of rare earths supply was a frightening prospect as the minerals are key ingredients in a broad range of high-tech products, from smartphones to wind turbines and hybrid cars. Although the bans have since been lifted, governments around the world saw the ban as a kind of wake-up call and started looking at ways to develop their own mineral resources — for rare earths as well as basic industry ...