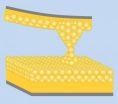
(Press-News.org) BUFFALO, N.Y. -- At an atomic scale, the tiniest bridge of gold -- that made of a single atom -- is actually the strongest, according to new research by engineers at the University at Buffalo's Laboratory for Quantum Devices.
The counterintuitive finding is the result of experiments probing the characteristics of atomic-scale necks of gold that formed when the pointed, gold tip of a cantilever was pushed into a flat, gold surface. An examination of these tiny, gold bridges revealed that they were stiffest when they comprised just a single atom.
The study was published in June in Physical Review B by a trio of UB researchers: postdoctoral fellow Jason Armstrong and professors Susan Hua and Harsh Deep Chopra, all in UB's Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. Support for the work came from National Science Foundation grants No. DMR-0706074 and No. DMR-0964830.
As engineers look to build devices such as computer circuits with ever-smaller parts, it is critical to learn more about how tiny components comprising a single atom or a few atoms might behave. The physical properties of atomic-scale gadgets differ from those of larger, "bulk" counterparts.
"Everyday intuition would suggest that devices made of just a few atoms would be highly susceptible to mechanical forces," the team said. "This study finds, however, that the ability of the material to resist elastic deformation actually increases with decreasing size."
Another observation the team made while studying the tiny gold necks: abrupt atomic displacements that occur as the gold tip and surface are drawn apart are not arbitrary, but follow well-defined rules of crystallography. More scientific highlights of the work are summarized in the Physical Review Focus of the American Physical Society at http://focus.aps.org/story/v27/st24.
UB's Laboratory for Quantum Devices, led by Chopra and Hua, works on mapping the evolution of various physical properties of materials -- including mechanical, magnetic and magneto-transport behavior -- as sample sizes grow from a single atom to bulk.
This complicated task requires technology capable of capturing a single or few atoms between probes, and further pushing and pulling on the atoms to study their response.
The sophisticated technology that Armstrong, Hua and Chopra invented and built to accomplish the research was recently licensed to Precision Scientific Instruments Inc., a Western New York start-up company founded by the leaders of Murak & Associates LLC, a management consulting practice; SoPark Corporation, an electronics service manufacturer (ESM); and The PCA Group, Inc., a consulting firm that offers total technology solutions.
"The instruments and methods are incredibly precise and capable of deforming the sample at the picometer scale (about 100 times smaller than an atom), which means literally stretching the bond lengths, and simultaneously measuring the forces at the piconewton level, as well as various other properties. As a very broad perspective, by enabling researchers to probe the very small, the technology could speed advances in fields ranging from satellite communications to health care," said Gerry Murak, president and cofounder of Precision Scientific Instruments, Inc.
"Small is exciting, and atomic scale devices are the new frontier of technology. Metrology systems capable of probing the behavior of atomic-scale devices are sorely needed, and this technology gives us a unique platform," Murak said.
INFORMATION:
The University at Buffalo is a premier research-intensive public university, a flagship institution in the State University of New York system and its largest and most comprehensive campus. UB's more than 28,000 students pursue their academic interests through more than 300 undergraduate, graduate and professional degree programs. Founded in 1846, the University at Buffalo is a member of the Association of American Universities.
Narrowest bridges of gold are also the strongest, study finds
Technology used to probe tiny samples is licensed to Western New York firm
2011-07-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Common Injuries from Motorcycle Accidents
2011-07-14
According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), motorcyclists should wear helmets and protective clothing whenever operating their bikes. Motorcycles require more skill and attention to drive than passenger vehicles, which is why the NHTSA also recommends bikers take special courses to learn defensive driving and proper operation of their vehicles.
However, even the safest biker cannot always avoid a motorcycle accident, and despite protective clothing and helmets, bikers run a much higher risk of sustaining serious injury in an accident. When ...
Health care in the home – new report July 18
2011-07-14
For many reasons -- including the rising cost of health care and aging of the U.S. population -- health care is increasingly moving from formal medical facilities into patients' homes. A wide range of procedures and therapies are now carried out far from any hospital or clinic, often with no health care professional on site.
HEALTH CARE COMES HOME: THE HUMAN FACTORS, a new report from the National Research Council, recommends steps the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and other agencies and groups can take to ensure that the medical devices used in home care are easy ...
Hip Fractures Among the Elderly
2011-07-14
Health issues intensify when an elderly person fractures a hip. In fact, 29 percent of older people who break a hip will die within one year; that's according to the University of Maryland School of Medicine. Combine a hip fracture with another chronic disease and morbidity can rise to 75 percent of those cases.
Unfortunately, hip fractures are on the rise. Approximately 300,000 Americans over the age of 64 break their hips annually. And, The large majority of those are women. Considering that millions of boomers will hit retirement age over the next few years, fractures ...
Biologists discover an 'evening' protein complex that regulates plant growth
2011-07-14
Farmers and other astute observers of nature have long known that crops like corn and sorghum grow taller at night. But the biochemical mechanisms that control this nightly stem elongation, common to most plants, have been something of a mystery to biologists—until now.
In this week's early online publication of the journal Nature, biologists at the University of California, San Diego report their discovery of a protein complex they call the "evening complex" that regulates the rhythmic growth of plants during the night. More importantly, the biologists show how this ...
Legislators Contemplate Bills Protecting Hotel Maids
2011-07-14
In the wake of the sexual assault allegations against International Monetary Fund Chief Dominique Strauss-Kahn, New York legislators are contemplating new proposals that would offer further protections to hotel maids. In May, Strauss-Kahn was arrested on suspicion of sexual assault stemming from an encounter with a hotel maid at the Sofitel Hotel near Times Square.
On May 23rd, Assemblyman Rory Lancman introduced the Hotel Worker Protection Act, which would add a new provision to Section 202 of the Labor Code. Essentially, the bill would allow hotel employees (specifically ...
Pitt, Wake Forest team finds why stored transfusion blood may become less safe with age
2011-07-14
PITTSBURGH, July 13 – Transfused blood may need to be stored in a different way to prevent the breakdown of red blood cells that can lead to complications including infection, organ failure and death, say researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and Wake Forest University. This week in the early online version of Circulation, the team reports the latest findings from its ongoing exploration of the interaction between red blood cell breakdown products and nitric oxide (NO), revealing new biological mechanisms that can reduce blood flow and possibly ...
With Resources, Children with Cerebral Palsy Can Succeed
2011-07-14
Maybe you've had concerns for your child's well-being since the day of his or her birth because your labor was mismanaged, delivery was delayed, too much Pitocin was used or your baby was in fetal distress.
Maybe you suspected there was a problem when you noticed your infant didn't reach for you with two hands or seemed excessively stiff or floppy. He or she just didn't move like other babies.
Even if you thought there might be problems, an actual diagnosis of cerebral palsy is still devastating. It's a diagnosis that thousands of parents hear every year, as almost ...
Study explores best motivating factors for pursuing a shared goal such as giving
2011-07-14
People who see the "glass as half empty" may be more willing to contribute to a common goal if they already identify with it, according to researchers from The University of Texas at Austin, University of Chicago and Sungkyunkwan University.
According to the studies, individuals who already care a lot (highly identify) with a cause are more likely to financially support the cause if a solicitation is framed by how much is still needed (for example, "we still need $50,000 to reach our goal"). However, if individuals care very little prior to a solicitation (low identify), ...
Research provides insight into new drug resistance in hospital microbes
2011-07-14
Boston (July 13, 2011) – Hospitals struggle to prevent the infections that complicate treatment for cancer, joint replacement, heart surgery and other conditions. Hospital-acquired infections are often resistant to multiple antibiotics, leading to approximately 100,000 deaths and more than $30 billion in additional health care costs yearly. New drugs are being developed to combat these infections, but resistance invariably emerges to these last-line drugs.
Daptomycin, a new antibiotic approved by the FDA in 2003, is used to treat infections caused by multi-drug resistant ...
Student Loans May Be Reclassified As Dischargeable in Bankruptcy
2011-07-14
With the nation's economy struggling, and unemployment still at historic levels, it is no surprise that many former students are struggling with repaying their loans. Last year, the United States Student Association estimated that borrowers held $730 billion in student loan debt, with 60 percent ($440 billion) in deferment or default. With student loan debt outpacing revolving credit card debt, bankruptcy is becoming a consideration for more struggling with crippling student loan debt, even though current law does not allow discharge of such debt, except under limited circumstances.
There ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
[Press-News.org] Narrowest bridges of gold are also the strongest, study findsTechnology used to probe tiny samples is licensed to Western New York firm