(Press-News.org)
VIDEO:
GOES-13 satellite imagery in 15 minute intervals from July 16 at 7:31 a.m. EDT until July 18 at 7:31 a.m. EDT shows Bret developing from a low pressure area in...
Click here for more information.
The GOES-13 satellite that monitors weather over the eastern U.S. recorded a movie of the birth and strengthening of the Atlantic Ocean season's second tropical storm. Tropical Storm Bret was born in the northwestern Bahamas and continues to strengthen.
The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite called GOES-13 provides continuous visible and infrared imagery of the eastern U.S. and Atlantic Ocean basin from its position in space. GOES satellites are operated by NOAA, and the NASA GOES Project located at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. creates images and compiled them into the video of the storm as it developed on July 17 and developed in the early morning hours of July 18th into a tropical storm.
The animation includes sped up infrared and visible frames of data from the GOES-13 satellite and is squeezed down to 27 seconds. The movie shows satellite imagery that was captured in 15 minute intervals from July 16 at 1131 UTC (7:31 a.m. EDT) until July 18 at 1131 UTC (7:31 a.m. EDT).
Tropical Depression 2 formed at 5 p.m. EDT on Sunday, July 17. At that time it had maximum sustained winds near 35 mph and was just 100 miles northwest of Great Abaco Island, near 27.5 N and 78.2 W. The Abaco Islands are located in the northern Bahamas and are made up of the main islands of Great Abaco and Little Abaco with many smaller islands called "cays."
On July 18 at 8 a.m. EDT, Tropical Depression 2 strengthened into Tropical Storm Bret. Maximum sustained winds were up to 50 mph. At that time, Bret was just 65 miles north-northwest of Great Abaco Island (and about 200 miles off the eastern Florida coast) near 27.4N 77.5W, trudging along at 3 mph to the northeast. Minimum central pressure is 1001 millibars.
The National Hurricane Center has issued a tropical storm warning for Grand Bahama Island and the Abaco Islands in the northwest Bahamas. As a result, the northwestern Bahamas are 'under the gun' for the greatest impacts from Bret. Rainfall could reach between 2 and 4 inches, while winds can reach tropical storm-force today. Those winds should diminish tonight as Bret pulls away. Beach goers will have stay away from the ocean as locally high surf conditions are expected along northern and western facing beaches today.
INFORMATION:
GOES-13 movie catches Tropical Storm Bret form and intensify
2011-07-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Steps needed to ensure that home medical devices are easy-to-use and caregivers are well-trained
2011-07-19
WASHINGTON – A new report from the National Research Council recommends steps the Food and Drug Administration and other agencies and professional associations can take to ensure that the medical devices and health information technology used in home health care are easy and safe for laypeople to use and that caregivers, whether formal or informal, are well-trained.
For many reasons -- including the rising cost of health care, the aging of the U.S. population, and patients' desire to remain in their homes -- health care is increasingly moving from formal medical facilities ...
Researchers identify how a gene linked to both Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes works
2011-07-19
Researchers at Mount Sinai School of Medicine have identified how a gene for a protein that can cause Type 2 diabetes, also possibly kills nerve cells in the brain, thereby contributing to Alzheimer's disease.
The gene, called SorCS1, controls the generation of amyloid-beta (Abeta) in the brain. Abeta plays a key role in the development of Alzheimer's disease. The researchers previously linked SorCS1 to Alzheimer's disease and identified where the molecules lived in the cell, but not how they control Abeta. The new data were presented today at the Alzheimer's Association's ...
MIT: The tallest tree in the land
2011-07-19
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- The next time you're outdoors, see if you can spot the tallest tree. If you're in the desert Southwest, this may be an easy task — trees there are few and far between, and tend to hunch low to the ground to conserve resources. In the temperate Northeast, dense forests make the exercise a bit more difficult. And in the rainy Northwest, the towering stands of sequoias often reach higher than the eye can estimate.
Knowing how tall trees can grow in any given region can give ecologists a wealth of information, from the potential density of a forest and ...
Face value
2011-07-19
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- The looks of political candidates are a key factor influencing voters, a phenomenon identified by a number of scholars in recent years. Now, a new study by MIT political scientists adds to this body of research by detailing which types of citizens are most influenced by candidate appearances, and why: The tendency is most prevalent among low-information voters who watch a lot of television.
Using data from the 2006 U.S. Senate and governors' races, the study shows that for every 10-point increase in the advantage a candidate has when rated by voters ...
John Theurer Cancer Center researchers shared 14 leading edge studies at recent ASCO meeting
2011-07-19
HACKENSACK, N.J. (July 18, 2011) — Researchers from the John Theurer Cancer Center at Hackensack University Medical Center presented results from 14 cancer-related studies during the recently concluded American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, which took place June 3 – 7, 2011 in Chicago. The studies examined new cancer treatments, ways to predict the best treatment outcomes, and patient quality of life issues.
"ASCO is a great venue for sharing best practices and learning about new treatment approaches – we are proud to help contribute by presenting ...
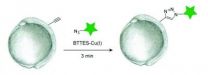
Click chemistry with copper -- a biocompatible version
2011-07-19
Biomolecular imaging can reveal a great deal of information about the inner workings of cells and one of the most attractive targets for imaging are glycans – sugars that are ubiquitous to living organisms and abundant on cell surfaces. Imaging a glycan requires that it be tagged or labeled. One of the best techniques for doing this is a technique called click chemistry. The original version of click chemistry could only be used on cells in vitro, not in living organisms, because the technique involved catalysis with copper, which is toxic at high micromolar concentrations. ...
Cancer stem cells recruit normal stem cells to fuel ovarian cancer, U-M study finds
2011-07-19
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — Researchers at the University of Michigan Comprehensive Cancer Center have found that a type of normal stem cell fuels ovarian cancer by encouraging cancer stem cells to grow.
Cancer stem cells are the small number of cells in a tumor that drive its growth and spread. Traditional cancer treatments do not kill these cells, which is why cancer treatments often fail.
In a study published online in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, researchers looked in ovarian tissue at the mesenchymal stem cells, which are normal cells found throughout the body. ...
New therapy provides hope for millions of people suffering from bowel incontinence
2011-07-19
CHICAGO- A new procedure is now available for the treatment of chronic bowel incontinence, a disorder impacting the lives of more than 18 million Americans. The treatment, called InterStim® Therapy is a minimally invasive procedure which uses electrical impulses to stimulate the sacral nerve and improve muscle function. It is one of the only effective long-term treatments for bowel incontinence available to patients and Northwestern Memorial Hospital is one of the first medical centers in the country to offer the procedure.
"Bowel control problems can have a significant, ...
Research identifies genes vital to preventing childhood leukemia
2011-07-19
Researchers at The University of Western Ontario have identified genes that may be important for preventing childhood leukemia. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a cancer of the blood that occurs primarily in young children. It's frequently associated with mutations or chromosomal abnormalities that arise during embryonic or fetal development. Working with mice, researchers led by Rodney DeKoter identified two key genes that appear essential in the prevention of B cell ALL, the most common form of ALL in children. The study is published online in Blood, the Journal ...
Grand Cayman blue iguana: Back from the brink of extinction
2011-07-19
While thousands of species are threatened with extinction around the globe, efforts to save the Grand Cayman blue iguana represent a rarity in conservation: a chance for complete recovery, according to health experts from the Wildlife Conservation Society's Bronx Zoo and other members of the Blue Iguana Recovery Program.
Coordinated by the National Trust for the Cayman Islands, the Blue Iguana Recovery Program—a consortium of local and international partners—has successfully released more than 500 captive-bred reptiles since the initiative's inception in 2002, when the ...