(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR, Mich.---The results of a study on candidates' use of Twitter in the 2010 midterm elections suggest that Republicans and Tea Party members used the social medium more effectively than their Democratic rivals.
The University of Michigan study, among the first to examine the Tea Party's social media strategies, also showed that analyzing Twitter activity can lead to good predictions of election winners.
Various social media tools have become a key part of campaign strategies in recent years. In 2010, nearly a quarter of online adults used social networks including Twitter to engage with the election.
In this study, researchers from the U-M School of Information and the College of Engineering looked at more than 460,000 tweets---three years' worth from 687 candidates running for national House, Senate and gubernatorial seats.
"The conservative candidates---Republicans and Tea Party members---definitely used Twitter more visibly and showed a more coherent set of messages and topics," said Eytan Adar, assistant professor in the School of Information and the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. "They also followed each other much more closely. I think it's fair to say they were much more cohesive in a lot of ways and at the end of the day that makes for a stronger campaign."
Conservatives, who made major gains in the 2010 midterm elections, tweeted about similar topics and conveyed a coherent message with a particular attention to economic issues, the researchers found. The top terms in Republicans' posts were "spending," "bills," "budget," "WSJ" (Wall Street Journal), "Bush" and "deficit." Over the study period, Republicans tweeted an average of 723 times.
With an average of 551 tweets (text entries) during the study period, Democrats posted less frequently. Their tweets covered a wider range of topics. Top terms were "education," "jobs," "oil_spill," "clean_energy," "Afghanistan," and "reform."
The study zeroed in on the posts of self-identified Tea Party members. Despite its grassroots nature, the Tea Party appeared to be running an organized campaign. Not only did members tweet more often, averaging 901 tweets during the study period, they exhibited behaviors suggesting a stronger community than their counterparts.
Tea Party members retweeted one another more often, rebroadcasting a colleague's message an average of 82.6 times, compared with 52.3 retweets for Republicans and 40 for Democrats. They used hashtags (keywords used to categorize tweets) an average of 753 times, compared with Republicans' 404 times and Democrats' 196. The researchers suggest this may be because the Tea Party members joined forces on Twitter to attack key Democrats. Among the party's most popular terms were "Nancy Pelosi," "Barney Frank," and "Clinton."
The researchers found that overuse of Twitter might not correlate with better election performance, though.
"In fact over usage might even repel the targeted audience to some extent," said Avishay Livne, a doctoral student in the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science.
The study examined how Twitter behaviors could help predict election winners. By looking at the content of candidates' tweets, the number of followers they had, and whether the candidate was an incumbent, they were able to predict election outcomes with 88 percent accuracy.
"We found that candidates who are close to the middle of the network, and the middle of what is being discussed by everyone are more likely to be elected," said Lada Adamic, associate professor in the School of Information and the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science.
Adamic says the work also sheds light on how a candidate's positions correspond to his or her likelihood of being elected.
"This has been attempted in the past by looking at, for example, a candidate's past voting record or their responses to standardized surveys," Adamic said. "However, this data was frequently incomplete. It is interesting to see how candidate's activity on Twitter is connected with election outcomes."
INFORMATION:
Livne presented the findings July 19 at the International Conference on Weblogs and Social Media in Barcelona. Matthew P. Simmons, a graduate student in the School of Information, is also a co-author. The study was funded in part by a grant from the National Science Foundation.
For more information:
Full text of paper: "The Party is Over Here: Structure and Content in the 2010 Election" http://www.cond.org/partyat.pdf.
Eytan Adar: http://www.si.umich.edu/people/eytan-adar
Lada Adamic: http://www-personal.umich.edu/~ladamic
END
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The development of a new cell-culture system that mimics how specific nerve cell fibers in the brain become coated with protective myelin opens up new avenues of research about multiple sclerosis. Initial findings suggest that myelin regulates a key protein involved in sending long-distance signals.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease characterized by damage to the myelin sheath surrounding nerve fibers. The cause remains unknown, and it is a chronic illness affecting the central nervous system that has no cure.
MS has long been considered ...
Rockville, Md. — Several reports indicate that prolonged viewing of mobile devices and other stereo 3D devices leads to visual discomfort, fatigue and even headaches. According to a new Journal of Vision study, the root cause may be the demand on our eyes to focus on the screen and simultaneously adjust to the distance of the content.
Scientifically referred to as vergence-accommodation, this conflict and its effect on viewers of stereo 3D displays are detailed in a recent Journal of Vision article, The Zone of Comfort: Predicting Visual Discomfort with Stereo Displays. ...
Stem cell researchers at UCLA have generated the first genome-wide mapping of a DNA modification called 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) in embryonic stem cells, and discovered that it is predominantly found in genes that are turned on, or active.
The finding by researchers with the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA may prove to be important in controlling diseases like cancer, where the regulation of certain genes plays a role in disease development.
"Any way you can control genes will be hugely important for human ...
Red may mean STOP or I LOVE YOU! A red splash on a toxic butterfly's wing screams DON'T EAT ME! In nature, one toxic butterfly species may mimic the wing pattern of another toxic species in the area. By using the same signal, they send a stronger message: DON'T EAT US!
Now several research teams that include Smithsonian scientists in Panama, have discovered that Heliconius butterflies mimic each other's red wing patterns through changes in the same gene.
Not only does this gene lead to the same red wing patterns in neighboring species, it also leads to a large variety ...
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (July 21, 2011) – A normal but concerning consequence of pregnancy is the fact that pregnant women are more susceptible to infection. University of Minnesota Medical School researchers have identified the underlying mechanisms for this physiologic immune suppression that may lead to new therapies to help ward off infections during pregnancy.
In pregnancy, immune system suppressing cells (called regulatory T cells) increase in number to protect the baby from attack by the mother's immune system. Because these cells are busy protecting the developing ...
A genetic study focusing on the Central American river turtle (Dermatemys mawii) recently turned up surprising results for a team of Smithsonian scientists involved in the conservation of this critically endangered species. Small tissue samples collected from 238 wild turtles at 15 different locations across their range in Southern Mexico, Belize and Guatemala revealed a "surprising lack" of genetic structure, the scientists write in a recent paper in the journal Conservation Genetics.
The turtles, which are entirely aquatic, represent populations from three different ...
Recent research conducted at Harvard Medical School and the Harvard School of Public Health may have strong implications for informing the controversial debate currently surrounding national health care reform.
In a study published in the July edition of the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, the Harvard research team, led by first author Aakanksha Pande, a doctoral student in the Department of Population Medicine at HMS and Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute, found that Massachusetts health reform has effectively increased access to health care and reduced disparities. ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — Children with public insurance are 22 percent less likely to receive comprehensive primary care than those with private insurance, according to new research from the University of Michigan Medical School.
Public insurance programs cover one-third of U.S. children, many of whom belong to the most vulnerable groups, including minorities, the underprivileged and those in poor health. This includes children covered by Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP).
The study, available online ahead of print in Academic Pediatrics, determined ...
The eye of a tropical cyclone is an indication of a strong storm, and Typhoon Ma-on's eye was apparent in visible and infrared imagery captured by NASA's Aqua satellite. Ma-on just achieved Category Four status on the Saffir-Simpson scale that measures hurricane intensity.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite took an image of Typhoon Ma-on that clearly shows the storm's eye, although it has some high clouds in it. The image was taken at 04:15 UTC (12:15 a.m. EDT) on July 15 as Typhoon Ma-on continues ...
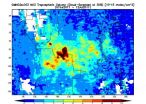
Fires raging in central Africa are generating a high amount of pollution that is showing up in data from NASA's Aura Satellite, with the ominous shape of a dark red butterfly in the skies over southern part of the Democratic Republic of the Congo and northern Angola.
An image of the pollution from agricultural fires in central Africa was created from data of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) levels over the period from July 7 to 12, 2011. It was created from Ozone Measuring Instrument (OMI) data using the NASA Giovanni system by Dr. James Acker at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center ...