(Press-News.org) Chemical reactions happen all of the time: some things burn or rust, others react to light exposure--even batteries use chemical reactions to supply electricity. One of the big challenges chemists continually face is finding new ways to control these reactions or create conditions that promote desirable reactions and limit undesirable ones.
Recently, researchers at New York University demonstrated an ability to make new materials with empty space on the inside, which could potentially control desired and unwanted chemical reactions.
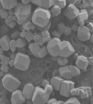
Mike Ward, of NYU's Department of Chemistry and a team of researchers, essentially created a "molecular flask," self-assembling cages capable of housing other compounds inside of them. These "flasks" may eventually allow researchers to isolate certain chemical reactions within or outside the cage.
The research is published in the July 22, 2011 issue of the journal Science.
"We wanted to create frameworks to serve as the 'hotel' for 'guest' molecules, which can deliver the function independent of framework design," said Ward. "This makes it possible to separate chemicals based on size or perform reactions inside well-defined cages, which could potentially give you more control over chemical reactivity and reaction products. Moreover, these frameworks may prove ideal for encapsulating a wide range of guest molecules, producing materials with new optical or magnetic properties."
The molecular "hotels" described by Ward and his collaborators take the shape of a truncated octahedron, one of 13 shapes described as an Archimedean solid, discovered by the Greek mathematician Archimedes. Archimedean solids are characterized by a specific number of sides that meet at corners which are all identical. The regularity of these shapes often means they are of particular interest to chemists and materials researchers looking to create complex materials that assemble themselves.
The extraordinary aspect of this work, supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF), is the self-assembly of the molecular tiles into a polyhedron, a well-defined, three-dimensional, geometric solid. The individual polyhedra assemble themselves using the attractive interactions associated with hydrogen bonds. They then further organize into a crystal lattice that resembles a porous structure called zeolite, an absorbent material with many industrial uses.
The new material differs from zeolite because it is constructed from organic building blocks rather than inorganic ones, which make it more versatile and easier to engineer. In general, inorganic compounds are considered mineral in origin, while organic compounds are considered biological in origin.
This discovery paves the way towards development of a new class of solids with properties that may prove useful for a range of industrial and consumer products.
"By using geometric design principles and very simple chemical precursors, the Ward group has been able to construct relatively sturdy materials which contain many identically sized and shaped cavities," explained Michael Scott, program director in the Division of Materials Research at NSF. "The hollow space inside these materials offers many exciting opportunities for chemists to do things such as isolate unstable molecules, catalyze unknown reactions and separate important chemical compounds."
Future research projects will try to create other types of Archimedean solids or use the truncated octahedron to house different types of functional molecules.
INFORMATION:
Chemists create molecular flasks
Researchers design a self-assembling material that can house other molecules
2011-07-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Diamonds pinpoint start of colliding continents
2011-07-22
Washington, D.C.—Jewelers abhor diamond impurities, but they are a bonanza for scientists. Safely encased in the super-hard diamond, impurities are unaltered, ancient minerals that can tell the story of Earth's distant past. Researchers analyzed data from the literature of over 4,000 of these mineral inclusions to find that continents started the cycle of breaking apart, drifting, and colliding about 3 billion years ago. The research, published in the July 22, 2011, issue of Science, pinpoints when this so-called Wilson cycle began.
Lead author Steven Shirey at the ...
Chemists create molecular polyhedron -- and potential to enhance industrial and consumer products
2011-07-22
Chemists have created a molecular polyhedron, a ground-breaking assembly that has the potential to impact a range of industrial and consumer products, including magnetic and optical materials.
The work, reported in the latest issue of the journal Science, was conducted by researchers at New York University's Department of Chemistry and its Molecular Design Institute and the University of Milan's Department of Materials Science.
Researchers have sought to coerce molecules to form regular polyhedra—three-dimensional objects in which each side, or face, is a polygon—but ...
Link between competing phases in cuprates leads to new theory
2011-07-22
UPTON, NY - A team of scientists studying the parent compound of a cuprate (copper-oxide) superconductor has discovered a link between two different states, or phases, of that matter - and written a mathematical theory to describe the relationship. This work, appearing in the July 22, 2011, issue of Science, will help scientists predict the material's behavior under varying conditions, and may help explain how it's transformed into a superconductor able to carry current with no energy loss.
"The ultimate goal is to use what we learn to design copper-oxide materials with ...
Even privately insured have hard time getting psychiatric care in Massachusetts: Harvard study
2011-07-22
A new study by Harvard Medical School researchers published today [July 21] in the Annals of Emergency Medicine finds that access to outpatient psychiatric care in the greater Boston area is severely limited, even for people with reputedly excellent private health insurance. Given that the federal health law is modeled after the Massachusetts health reform, the findings have national implications, the researchers say.
Study personnel posed as patients insured by Blue Cross Blue Shield of Massachusetts PPO, the largest insurer in Massachusetts. They called every Blue Cross-contracted ...
Dolphins' 'remarkable' recovery from injury offers important insights for human healing
2011-07-22
Washington, DC – A Georgetown University Medical Center (GUMC) scientist who has previously discovered antimicrobial compounds in the skin of frogs and in the dogfish shark has now turned his attention to the remarkable wound healing abilities of dolphins.
A dolphin's ability to heal quickly from a shark bite with apparent indifference to pain, resistance to infection, hemorrhage protection, and near-restoration of normal body contour might provide insights for the care of human injuries, says Michael Zasloff, M.D., Ph.D.
For a "Letter" published today in the Journal ...
Liver, belly fat may identify high risks of heart disease in obese people
2011-07-22
Obese people with high levels of abdominal fat and liver fat may face increased risks for heart disease and other serious health problems, according to research published in Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology: Journal of the American Heart Association.
Obesity is commonly associated with heart disease risk and problems called cardiometabolic abnormalities, including insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, cholesterol disorders, hypertension and gout.
Researchers in Sweden and Finland found that obese people at the highest risk have increased secretion of ...
Vascular changes linked to dementia
2011-07-22
The same artery-clogging process (atherosclerosis) that causes heart disease can also result in age-related vascular cognitive impairments (VCI), according to a new American Heart Association/American Stroke Association scientific statement published online in Stroke: Journal of the American Heart Association.
Cognitive impairment, also known as dementia, includes difficulty with thinking, reasoning and memory, and can be caused by vascular disease, Alzheimer's disease, a combination of both and other causes.
Atherosclerosis is a build- up of plaque in the arteries ...
Optimism associated with lower risk of having stroke
2011-07-22
A positive outlook on life might lower your risk of having a stroke, according to new research reported in Stroke: Journal of the American Heart Association.
In an observational study, a nationally representative group of 6,044 adults over age 50 rated their optimism levels on a 16-point scale. Each point increase in optimism corresponded to a 9 percent decrease in acute stroke risk over a two-year follow-up period.
"Our work suggests that people who expect the best things in life actively take steps to promote health," said Eric Kim, study lead author and a clinical ...
Adolescent boys among those most affected by Washington state parental military deployment
2011-07-22
In 2007, nearly two million children in the United States had at least one parent serving in the military. Military families and children, in particular, suffer from mental health problems related to long deployments.
A new study from researchers at the University of Washington (UW) concludes that parental military deployment is associated with impaired well-being among adolescents, especially adolescent boys. The study, "Adolescent well-being in Washington state military families," was published online in the American Journal of Public Health.
Lead author Sarah ...
4 unusual views of the Andromeda Galaxy
2011-07-22
These four observations made by Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys give a close up view of the Andromeda Galaxy, also known as Messier 31 (M 31). Observations of most galaxies do not show the individual stars — even the most powerful telescopes cannot normally resolve the cloudy white shapes into their hundreds of millions of constituent stars.
In the case of the Andromeda Galaxy, however, astronomers have a few tricks up their sleeves. Firstly, images from Hubble Space Telescope have unparalleled image quality as a result of the telescope's position above the atmosphere. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
Adults with concurrent hearing and vision loss report barriers and challenges in navigating complex, everyday environments
Breast cancer stage at diagnosis differs sharply across rural US regions
Concrete sensor manufacturer Wavelogix receives $500,000 grant from National Science Foundation
California communities’ recovery time between wildfire smoke events is shrinking
Augmented reality job coaching boosts performance by 79% for people with disabilities
Medical debt associated with deferring dental, medical, and mental health care
AAI appoints Anand Balasubramani as Chief Scientific Programs Officer
Prior authorization may hinder access to lifesaving heart failure medications
Scholars propose transparency, credit and accountability as key principles in scientific authorship guidelines
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
[Press-News.org] Chemists create molecular flasksResearchers design a self-assembling material that can house other molecules