(Press-News.org) Gastric cancer is a major cause of cancer deaths in the world. The outcome of large gastric tumors and those with lymph node involvement remains poor after surgical resection. The optimal adjuvant therapy after surgical resection remains to be determined. The most common strategies in the adjuvant treatment of gastric cancers include fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy with or without radiation. The introduction of capecitabine has largely replaced continuous-infusion 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) owing to its ease of administration. However, its efficacy is not proven in randomized phase III trials involving gastric cancers.
A research article published on August 7, 2010 in the World Journal of Gastroenterology addresses this question. In this retrospective review study, the authors examined the role of capecitabine with radiation and compared its efficacy to the 5-FU with radiation regimen and fluoropyrimidinebased chemotherapy alone.
This study showed that capecitabine with concurrent radiation was as effective as 5-FU with radiation or fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy alone without radiation when given as adjuvant treatment for locally advanced gastric cancer.
The result from this hypothesis-generating study provides the basis for a further prospective study in evaluating the role of radiation with concurrent capecitabine as adjuvant therapy in resected gastric cancers.
INFORMATION:
Reference: Tham CK, Choo SP, Poon DYH, Toh HC, Ong SYK, Tan SH, Wang MLC, Foo KF. Capecitabine with radiation is an effective adjuvant therapy in gastric cancers. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(29): 3709-3715
http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i29/3709.htm
Correspondence to: Dr. Chee Kian Tham, Department of Medical Oncology, National Cancer Centre Singapore, 11 Hospital Drive, Singapore 169610, Singapore. tham.c.k@nccs.com.sg
Telephone: +65-64368000 Fax: +65-62272759
About World Journal of Gastroenterology
World Journal of Gastroenterology (WJG), a leading international journal in gastroenterology and hepatology, has established a reputation for publishing first class research on esophageal cancer, gastric cancer, liver cancer, viral hepatitis, colorectal cancer, and H. pylori infection and provides a forum for both clinicians and scientists. WJG has been indexed and abstracted in Current Contents/Clinical Medicine, Science Citation Index Expanded (also known as SciSearch) and Journal Citation Reports/Science Edition, Index Medicus, MEDLINE and PubMed, Chemical Abstracts, EMBASE/Excerpta Medica, Abstracts Journals, Nature Clinical Practice Gastroenterology and Hepatology, CAB Abstracts and Global Health. ISI JCR 2009 IF: 2.092. WJG is a weekly journal published by WJG Press. The publication dates are the 7th, 14th, 21st, and 28th day of every month. WJG is supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 30224801 and No. 30424812, and was founded with the name of China National Journal of New Gastroenterology on October 1, 1995, and renamed WJG on January 25, 1998.
END
Delayed hepatic arterial hemorrhage after pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD) is not a common but a fatal complication, occurring in 7% of all patients. Its ideal management remains unclear and controversial.
A research article published on August 7, 2010 in the World Journal of Gastroenterology addresses this question. The authors reported the clinical outcome of 9 patients with life-threatening hemorrhage from a ruptured hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm after PD after treatment with a new interventional technique, namely placement of stent-grafts. This technique provides a good ...
Severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) requires an adequate nutritional support. Enteral nutrition (EN) should be preferred to total parenteral nutrition in patients with SAP, as it is associated with reduced mortality and complications. However, in clinical practice EN is employed far less frequently than it should. The main obstacle to EN diffusion is that it is considered complicated, as to ensure full pancreatic rest, nutrition tubes should be placed in the jejunum, requiring often troublesome procedures. In the past few years, it has been proposed that EN through nasogastric ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The incidence of hockey-related injuries among children aged 9 to 14 leading to emergency department visits more than doubled between 1990 and 2006, according to a new nationwide study.
There were 2,935 hockey injuries treated in emergency departments in that age group in 1990, increasing to 7,713 in 2006 – an increase of 163 percent.
The injury incidence among teens aged 15 to 18 didn't increase as much as that of younger children, but still grew 85 percent during the same time period.
The startling increase in injuries calls for more attention to ...
New research from University of Minnesota hearing scientists shows that fewer than 20 percent of teenagers in the United States have a hearing loss as a result of exposure to loud sounds, thus offering a different analysis of data reported in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) in August.
The U of M's research, forthcoming in the Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, points out that the small hearing losses that audiologist are trying to identify with conventional hearing tests are subject to measurement error and that as many as 10 percent ...
Too much television, video games and Internet can increase body fat in teens. A five-year study from the University of Montreal and the Sainte-Justine Hospital Research Center, published in the American Journal of Epidemiology, has found teenagers have four different patterns of screen use: increasers, decreasers, consistently high and consistently low users.
Even teens from the consistently low group exceeded two hours per day of screen time on average, yet organizations such as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Canadian Paediatric Society recommend limiting ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Elderly people might not benefit from some of the tuberculosis vaccines currently in development, recent research suggests.
Some vaccines under study are designed to activate a specific molecule that is an early participant in the immune response against TB in young people. But a recent Ohio State University study suggests that in older people, this molecule remains relatively inactive, even in the face of TB infection.
The animal research suggests that the presence of this molecule, called a toll-like receptor, is not required in an old mouse to generate ...
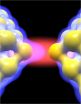
HOUSTON – (Sept. 20, 2010) – Everybody who's ever used a TV, radio or cell phone knows what an antenna does: It captures the aerial signals that make those devices practical. A lab at Rice University has built an antenna that captures light in the same way, at a small scale that has big potential.
Condensed matter physicist Doug Natelson and graduate student Dan Ward have found a way to make an optical antenna from two gold tips separated by a nanoscale gap that gathers light from a laser. The tips "grab the light and concentrate it down into a tiny space," Natelson said, ...
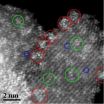
HOUSTON – (Sept. 20, 2010) – A nanoparticle-based catalyst developed at Rice University may give that tiger in your tank a little more roar.
A new paper in the Journal of the American Chemical Society details a process by Rice Professor Michael Wong and his colleagues that should help oil refineries make the process of manufacturing gasoline more efficient and better for the environment.
In addition, Wong said, it could produce higher-octane gasoline and save money for an industry in which a penny here and a penny there add millions to the bottom line.
Wong's team ...
MANHASSET, NY – The fine particles of pollution that hang in the air can increase the risk for sudden cardiac arrest, according to a new study conducted by a team from Long Island Jewish (LIJ) Medical Center and The Feinstein Institute for Medical Research.
Robert A. Silverman, MD, and his colleagues have been interested in the effects of ambient fine particulate matter on a number of medical conditions, including cardiovascular disease and asthma. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) keeps tabs on air pollution through dozens of strategically placed pollution ...
WASHINGTON – Holocaust survivors show remarkable resilience in their day-to-day lives, but they still manifest the pain of their traumatic past in the form of various psychiatric symptoms, according to an analysis of 44 years of global psychological research.
Jewish Holocaust survivors living in Israel also have higher psychological well-being than those who live in other countries, which suggests living in that country could serve as a protective factor, according to researchers in Israel and the Netherlands. Their findings are reported in Psychological Bulletin, which ...