(Press-News.org) Taiwan experienced a landfall and a soaking from Typhoon Fanapi, and NASA and JAXA's TRMM satellite noted a large area of very heavy rain in the system before it made landfall this weekend. NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites also captured impressive visible images of Fanapi just before the Taiwan landfall, and as it was making landfall in eastern China very early today.
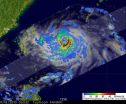
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite known as TRMM captured an image of Typhoon Fanapi's rainfall on Sept. 18 at 0653 UTC (2:53 a.m. EDT) after the typhoon had intensified to 105 knots (~121 mph). TRMM rainfall data showed heavy rain, falling at a rate greater than 2 inches per hour, circling the Fanapi's eye, except in the north of the circulation. Most rainfall outside of the center was falling moderately.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument flies on both NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites and provides high resolution images of tropical cyclones, fires, ice and various other areas on Earth. This past weekend, both satellites were flying over the Pacific Northwest Ocean where Typhoon Fanapi was making landfall twice, in Taiwan and China.
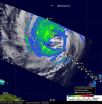
On Sept. 18 at 220 UTC NASA's Terra satellite captured Typhoon Fanapi approaching Taiwan. Two days later, today, Sept. 20, the MODIS instrument on NASA's Aqua satellite captured Typhoon Fanapi making landfall in China at 05:15 UTC (1:15 a.m. EDT).
Just before Fanapi made landfall, NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared look at the cold cloud tops of the storm. The infrared image of Typhoon Fanapi from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument aboard Aqua showed that the strongest convection, strongest thunderstorms and heaviest rainfall on Sept. 20 at 05:11 UTC (1:11 a.m. EDT) were still over the South China Sea and had not yet moved inland. Since that time, the heavy rainfall has moved inland.
After Typhoon Fanapi made landfall earlier today it weakened quickly. By 0900 UTC (5 a.m. EDT) Fanapi had already weakened to a tropical storm with maximum sustained winds near 56 mph. Fanapi made landfall more than 100 miles north of Hong Kong and continues to move inland in a westerly direction. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center placed the storm's center about 125 miles northeast of Hong Kong near 23.8 North latitude and 115.2 East longitude. Fanapi is expected to dissipate sometime on Tuesday, Sept. 21.
INFORMATION:
NASA captures very heavy rain in Typhoon Fanapi and 2 landfalls
2010-09-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Introducing 'Champagne', new disease-resistant fig
2010-09-21
BATON ROUGE, LA—The ancient fig tree, first imported to the United States during the 16th century, thrives in areas of California and the South Atlantic and Gulf Coast areas of the U.S. One of the most popular trees grown in Southern backyards, fig is favored for its versatile fruit and low-maintenance production.
Charles E. Johnson, Ed O'Rourke, and James E. Boudreaux, from the Louisiana State University Agricultural Center in Baton Rouge, introduced a new fig they named "Champagne" in a recent issue of HortScience. According to the report, the new fig performed well ...
NASA's MODIS and AIRS instruments watch Igor changing shape, warming over 3 days
2010-09-21
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS, is an instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites and provides incredible views of tropical cyclones like Hurricane Igor, from its vantage point in space. Imagery from the MODIS instruments on these two satellites captured from Sept. 18 to 20 showed that powerful Hurricane Igor in the Atlantic Ocean is morphing from a rounded storm to more of a comma-shaped storm.
The MODIS instrument on NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of Igor at 11:30 am on Sept. 18, while MODIS in the Aqua satellite ...
Food for thought, er, well...
2010-09-21
Ever wonder why it's such an effort to forget about work while on vacation or to silence that annoying song that's playing over and over in your head?
Mathematicians at Case Western Reserve University may have part of the answer.
They've found that just as thinking burns energy, stopping a thought burns energy - like stopping a truck on a downhill slope.
"Maybe this explains why it is so tiring to relax and think about nothing," said Daniela Calvetti, professor of mathematics, and one of the authors of a new brain study. Their work is published in an advanced online ...
Low-calorie cheesecake? Why we have trouble estimating calories
2010-09-21
When it comes to estimating calorie counts, Americans aren't really on the ball. According to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research, this may be because of the order in which we encounter the food.
"The sequence in which items are considered often influences our evaluations of these items," writes author Alexander Chernev (Northwestern University). "The focus on sequential estimation is important because many meals are ordered and consumed sequentially rather than at once. Moreover, to control their daily calorie intake, people often estimate not only the amount ...
Santa Fe homeowners weigh in on landscape preferences
2010-09-21
LAS CRUCES, NM—While municipalities may mandate communitywide water conservation measures, individuals—particularly homeowners—can make significant contributions to water conservation in urban environments. Hoping to provide urban planners with more information about how residents' landscape preferences affect municipal water supplies, a team from New Mexico State University surveyed homeowners in Santa Fe about their attitudes toward high desert plants. Rolston St. Hilaire, Dawn M. VanLeeuwen, and Patrick Torres reported on their study of residents' preferences for urban ...
Scientists uncover process enabling toxoplasmosis parasite to survive homelessness
2010-09-21
INDIANAPOLIS — The parasite responsible for toxoplasmosis requires a stress response system that helps it survive the move to infect new cells, Indiana University School of Medicine scientists have reported, a discovery that could lead to new treatments to control the disease.
Parasites such as Toxoplasma gondii invade host cells, replicate and then must exit to find new host cells to invade. Traveling outside their host cell exposes the parasites to environmental stresses that limit how long they can remain viable while searching for new host cells.
The researchers ...
Learning how consumers value products
2010-09-21
Suggesting to consumers that they will use a product frequently can actually reduce their interest in purchasing the product, according to a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research.
"When consumers estimate the value of a durable product, they consider not only the absolute number of times they think they will use the product, but also the number of time they will use the product relative to other consumers," write authors Rebecca W. Hamilton, Rebecca K. Ratner (both University of Maryland, College Park), and Debora Viana Thompson (Georgetown University).
The ...
Could learning self-control be enjoyable?
2010-09-21
When it comes to self-control, consumers in the United States are in trouble. But a new study in the Journal of Consumer Research says there's hope; we just need a little help to see self-regulation as fun.
"Self-control failures depend on whether people see activities involving self-control (e.g., eating in moderate quantities) as an obligation to work or an opportunity to have fun," write authors Juliano Laran (University of Miami) and Chris Janiszewski (University of Florida, Gainesville).
According to the authors, approximately one in five U.S. citizens over the ...
Windborne dust on high peaks dampens Colorado River runoff
2010-09-21
On spring winds, something wicked this way comes--at least for the mountains of the Colorado River Basin and their ecosystems, and for people who depend on snowmelt from these mountains as a regional source of water.
"More than 80 percent of sunlight falling on fresh snow is reflected back to space," says scientist Tom Painter of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., and the University of California at Los Angeles. "But sprinkle some dark particles on the snow and that number drops dramatically."
The darker dust absorbs sunlight, reducing the amount of ...
Buyer backlash: Why do slogans about saving money increase spending?
2010-09-21
A new study in the Journal of Consumer Research reveals a strange facet of consumer behavior: people behave differently when they encounter companies' brands than they do when they encounter their slogans.
"Exposure to the retailer brand name Walmart, typically associated with saving money, reduces subsequent spending, whereas exposure to the Walmart slogan, (Save money. Live better.) increases spending," write authors Juliano Laran (University of Miami), Amy N. Dalton (Hong Kong University of Science and Technology), and Eduardo B. Andrade (University of California, ...