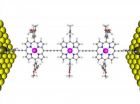
(Press-News.org) Porphyrins are organic molecules that appear in the central region of
macromolecules such as chlorophyll and hemoglobin, and have a metal atom
at their center that determines their specific function. The importance of these molecules
in the field of molecular electronics lies in their "ease of transfer
electrons from one region to another" explains the responsible of the work at the Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology Research Center (a joint research center of the CSIC, the University of Oviedo and the Government of the Principality of Asturias) Víctor Manuel García.
To determine the electronic transport mechanism in porphyrins, the
team has evaluated the change in their electrical conductivity as a function of
distance and temperature, in chains of one, two and three units of porphyrin
anchored at their ends to gold surfaces, which act as electrodes.
According to the laws governing hopping transport, the conductivity of the porphyrins increases with temperature but decreases slowly with distance. Under this
mechanism, electrons pass from one electrode to another by jumping from one region
of the molecule to another, thus being their movement more
similar to that of a particle than to a wave. The temperature increases their ability to jump and, therefore, the conductance, while the length decreases it.
On the contrary, the tunneling effect is based on the fact that electrons have a certain probability of disappearing from one electrode and reappearing in the other. This probability depends on the type of molecule between the electrodes.
Under this mechanism, the temperature can also increase the electrical conductance, "since it increases the amount of available electrons to be transported", explains García. However, the length effect changes the conductance exponentially. A increase of the length of the molecular wire drastically decreases the probability of electrons to appear at the other side.
The weak dependence of the porphyrins' conductivity as a function of distance as well as the temperature dependence "led to believe that the main transport mechanism was
hopping. However, experiments and theoretical calculations carried out by the
research team have shown that electron transport in these systems is actually led by the tunneling effect", says the researcher.
Computer Components
"The progressive miniaturization of integrated circuits make the electronic elements
increasingly approach the atomic limit", says Garcia. Therefore,
the research aims to find molecules that can perform the functions of
electronic components since they can be produced in a simple and cost-effective way.
The electron transport mechanism shown in this study may promote
the use of porphyrins in devices for quantum computers. These computers are
based on quantum mechanics, so the transport of electrons by tunneling
may be appropriate for them. When electrons disappear and reappear at one electrode or another "they retain their wave nature, and therefore also their
quantum properties", concludes Garcia.
INFORMATION:
The study counted on the participation of researchers from the UK universities
of Liverpool, Lancaster, Oxford and Cardiff, and the universities
of Zaragoza and Oviedo, belonging the researcher to the latter one.
The quantum tunneling effect leads electron transport in porphyrins
A research center of the CSIC participates in a study that refutes the hypothesis that their movement is based on jumps from one region to another. The porphyrins may be used in quantum computing since they keep the wave nature of electrons
2011-09-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Federal Study Determines Causes of Trucking Accidents
2011-09-02
Commercial tractor-trailers are involved in an increasing number of serious, and often fatal, accidents. To learn why, the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) and the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) conducted the Large Truck Crash Causation Study (LTCCS). This study provided vital information, including the reasons behind serious crashes involving large trucks.
Researchers reviewed 120,000 crashes that occurred between April 2001 and December 2003 and selected a nationally representative sample of 963 accidents. These accidents, ...
Decrease in smoking reduces death rates within months
2011-09-02
A study by the University of Liverpool has found that a decrease in smoking rapidly reduces mortality rates in individuals and entire populations within six months.
Research by Professor Simon Capewell and Dr Martin O'Flaherty at the Institute of Psychology, Health and Well-being, examined evidence from clinical trials and natural experiments. They found that a reduction in smoking has a positive impact on mortality rates in both individuals and populations within six months. Likewise, dietary improvements get very positive results within one to three years.
Professor ...
Sight fails when defective eye cells cripple renewal
2011-09-02
In a rare eye disease, the retina degenerates because light-receiving cells fail to regenerate, research led by a student at Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine shows.
The researchers include Dr. Samuel G. Jacobson's group at the University of Pennsylvania and Dr. Andreas Engel's group at University of Basel, Switzerland. They found that when the natural renewal process fails, metabolites are locked in, build up and turn toxic, killing cells over time in Enhanced S-Cone Syndrome.
A description of their work is online and will be published in print in ...
Hubble movies reveal solar-system-sized traffic jams
2011-09-02
When it comes to big-budget action movies, Rice University astronomer Patrick Hartigan prefers Hubble to Hollywood.
Using Hubble Space Telescope images collected over 14 years, Hartigan has created time-lapse movies that offer astronomers their first glimpse of the dynamic behavior of stellar jets, huge torrents of gas and particles that spew from the poles of newborn stars.
An analysis of the movies that was published in The Astrophysical Journal is forcing astronomers to rethink some of the processes that occur during the latter stages of star birth. And in an effort ...
Distracted Driving Still a Problem Despite Cell Phone Ban
2011-09-02
With more than 22 million drivers on its roads, California became the largest state to enact formal distracted driving laws in 2008. Sections 23123 and 23124 of the California Vehicle Code prohibited use of cell phones without a hands-free device, which enables drivers to dial phone numbers or complete calls without taking their hands from the steering wheel. The law also prohibited all drivers under age 18 from using cell phones behind the wheel. Proponents of the new law suggested that hands-free devices provided the safety and convenience drivers needed to make calls ...
Living with parents in adult life can prolong family conflict
2011-09-02
"We have worked with young people, in this case, in the family environment, to see what happens during the 'full nest syndrome', i.e., when children reach 18 years of age and they continue living at home," explained Beatriz Rodríguez, researcher from the University of La Laguna and co-author of the study.
Researchers classified adolescents into three stages: early teens (12 and 13 years), mid-teens (14 and 15), and late teens (16-18). Those 18-25 were called 'emerging adults'.
In Spain, given the country's social, economic and cultural characteristics, children leave ...
Using less water to grow more potatoes
2011-09-02
This press release is available in Spanish.
Research conducted in part at the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) has confirmed that in some production systems, planting potatoes in flat beds can increase irrigation water use efficiency.
Agricultural Research Service (ARS) agricultural engineer Bradley King, who works at the ARS Northwest Irrigation and Soils Research Laboratory in Kimberly, Idaho, was one of the scientists who led these studies. ARS is USDA's chief intramural scientific research agency, and this research supports the USDA commitment to enhancing ...
Increased resistance training does not benefit cardiac rehabilitation patients
2011-09-02
Philadelphia, PA, September 1, 2011 – For patients undergoing rehabilitation following cardiac events, aerobic exercise training (AT) is widely recommended. Resistance training (RT) has also been shown to be beneficial because it enhances muscular strength and endurance, functional capacity and independence, and quality of life, while reducing disability. In a study scheduled for publication in the October issue of the Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, researchers compared two RT regimens of different intensity in combination with AT. They determined that ...
Truck Mounted Boom Collapses Into a Brooklyn Building, New York Construction Accident Lawyer Comments
2011-09-02
A truck-mounted boom tipped and hit a Brooklyn brownstone, but as New York construction accident lawyer David Perecman is happy to note, the construction workers all escaped injury.
According to the New York Daily News, the non-injury construction accident in New York occurred while a construction crew was adding a third-story extension on the Cobble Hill building. The weight of the sheetrock and plywood was apparently too much and the boom collapsed, leaving the truck on a 45-degree angle.
No one was injured in the New York construction accident.
The construction ...
Mapping a model: International research on plant species appears in journal Nature
2011-09-02
MANHATTAN, KAN. -- Two Kansas State University researchers have been collaborating on an international project involving genomes of a model plant species that can offer insights into other plants.
Christopher Toomajian, assistant professor of plant pathology, and Katie Hildebrand, doctoral student in plant pathology, Stafford, are researching genetic variation in Arabidopsis thaliana, a small flowering plant that has a short life cycle, making it one of the best model species for scientific study.
For some of their latest research, they have worked with researchers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
[Press-News.org] The quantum tunneling effect leads electron transport in porphyrinsA research center of the CSIC participates in a study that refutes the hypothesis that their movement is based on jumps from one region to another. The porphyrins may be used in quantum computing since they keep the wave nature of electrons