(Press-News.org) The second Human Rights and Science symposium of the German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina was held in Strasbourg. At the event scientists and scholars, representatives of human rights organisations, and delegates from European academies of sciences and humanities came together to discuss human rights violations in academic work. The ethics of biosciences were the main focus of the public symposium.
Researchers regularly face human rights issues in their work. In some countries – including those in Europe – they repeatedly come against state repression if they publicly express their opinions or criticise social injustices. They must also often ask themselves if their work violates human rights – for example from the perspective of medical ethics. From 8 to 9 September the Human Rights Committee (HRC) of the Leopoldina held its second symposium on this topic. It invited scientists and scholars, representatives of human rights organisations, and delegates from European academies of sciences and humanities to come together at the Palais d'Europe in Strasbourg and discuss the worldwide violation of human rights in academic work and of researchers and students.
Prof. Hans-Peter Zenner, member of the Leopoldina Presidium and chair of the Human Rights Committee, underlines the necessity to enhance the coordination of the human rights activities of all the players in this field, particularly with the European Federation of National Academies of Sciences and Humanities (ALLEA). In addition to reports from European academies of sciences and humanities, participants also heard about the Council of Europe's activities in the field of bioethics, and about the work of the European Court of Human Rights. A valuable contribution was the report and the discussion of the National Academy of Sciences of Belarus.
###The German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina has founded its Human Rights Committee in 2001. In July 2003 the HRC became a member of the International Human Rights Network of Academies and Scholarly Societies (IHRN). In doing so, it joined around 70 other member academies and scholarly societies from all over the world. The Network and its member academies work on behalf of persecuted scientists and scholars around the world. They visit prisons and write notes to the relevant authorities, urging them to respect human rights. Disimprisonment and improvement of the conditions of custody have been achieved this way. They also hold symposia and compile publications to raise awareness of human rights issues in sciences and humanities, and to support the work of other human rights organisations. The general public and even academic institutions themselves are largely unfamiliar with the activities of the Network and know little about the many human rights violations suffered by academics today. This is why the Leopoldina regularly organises events to provide information on human rights standards and institutions, and to explore topics that are particularly relevant to Europe.
Leopoldina Symposium focuses on human rights violations in sciences and humanities
2011-09-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Out of the darkness
2011-09-13
San Diego, September 12, 2011 - The Journal of Emergency Medical Services (JEMS) today announces the publication of a special 150-page four-volume digital issue featuring first-person accounts of responders who were thrust into the world spotlight the morning of September 11, 2001, when terrorists invaded their response districts – and their lives – and changed the way they, and most responders throughout the world, think, train, respond and live their lives.
A.J. Heightman, Editor-in-Chief of JEMS, and Teresa McCallion, Editor of the EMS Insider newsletter – both published ...
A study analyzes how to improve the European patent
2011-09-13
This press release is available in Spanish.
"From the point of view of efficiency, establishing one sole format for a European patent in which English is the language used for the procedure seems obvious, even though the diffusion of the innovation is translated into other EU languages," the researchers asserted. This would simplify the current system, they explained, in which the inventor can decide whether to present a European patent in English or to request the patent in the government office of his/her country and in its official language. In addition, it would ...
New species of ancient predatory fish discovered
2011-09-13
PHILADELPHIA (September 12, 2011) – The Academy of Natural Sciences today announced
the discovery of a new species of large predatory fish that prowled ancient North American
waterways during the Devonian Period, before backboned animals existed on land.
Drs. Edward "Ted" Daeschler and Jason Downs of the Academy and colleagues from
the University of Chicago and Harvard University describe the new denizen of the Devonian
they named Laccognathus embryi in the current issue of the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology.
The 375-million-year-old beast was discovered by the ...
Honduran earthquake of 2009 destroyed half of coral reefs of Belizean Barrier Reef lagoon
2011-09-13
Earth's coral reefs have not been faring well in recent decades, facing multiple threats from pollution, disease, elevated water temperatures, and overfishing. Often referred to as the "rainforests of the Sea," coral reefs support a wide variety of marine life, help protect shorelines, and contribute significantly to tourism and the fishing industry. A new study looks at a rare but catastrophic impact on reefs: the damage caused by natural disasters such as an earthquakes.
In May of 2009, a powerful, magnitude-7.3 earthquake shook the western Caribbean, causing lagoonal ...
Recent Changes to New York Cellphone Laws Mean Increased Driver Violation Points
2011-09-13
Since 2001, New York has restricted cellphone use while driving. Drivers could receive traffic citations, with up to a $185 fine, for using handheld cellphones while driving. Law enforcement officials, however, have found that the possibility of a ticket is not enough of a deterrent as drivers continue to talk on handheld cellphones and text while driving -- and, even worse, continue to cause accidents. In 2008, more than 45,000 motor vehicle accidents in New York -- about 18 percent of the state's accidents that year -- involved driver distraction or inattention.
In ...
Even low-dose aspirin may increase risk of GI bleeding
2011-09-13
The risk of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding needs to be considered when determining the potential preventive benefits associated with low-dose aspirin for cardiovascular disease and cancer. According to a new study in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the use of low-dose aspirin increases the risk for GI bleeding, with the risk being increased further with accompanying use of cardiovascular disease-preventing therapies, such as clopidogrel and anticoagulants. In patients who took proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), bleeding risk decreased. Clinical Gastroenterology and ...
New clues to molecular understanding of autism
2011-09-13
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- The first transgenic mouse model of a rare and severe type of autism called Timothy Syndrome is improving the scientific understanding of autism spectrum disorder in general and may help researchers design more targeted interventions and treatments.
The research is described in a paper published last week by scientists at the University at Buffalo and Stanford University in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The transgenic mouse developed at UB exhibits the repetitive physical behaviors, altered social behaviors and impaired communication ...
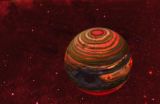
Astronomers find extreme weather on an alien world
2011-09-13
TORONTO, ON – A University of Toronto-led team of astronomers has observed extreme brightness changes on a nearby brown dwarf that may indicate a storm grander than any seen yet on a planet. Because old brown dwarfs and giant planets have similar atmospheres, this finding could shed new light on weather phenomena of extra-solar planets.
As part of a large survey of nearby brown dwarfs – objects that occupy the mass gap between dwarf stars and giant planets – the scientists used an infrared camera on the 2.5m telescope at Las Campanas Observatory in Chile to capture repeated ...
Medical Malpractice Attorney Fayrell Furr Jr. Recognized by Myrtle Beach Herald
2011-09-13
Fayrell Furr Jr., of Furr & Henshaw, Attorneys at Law, has been named the best medical malpractice attorney in the Myrtle Beach area for 2011 by the Myrtle Beach Herald. Mr. Furr has also been named to the list of South Carolina Super Lawyers for 2008, 2009 and 2010. He is board-certified as a civil trial attorney by the National Board of Trial Advocacy.
Furr & Henshaw has offices in Myrtle Beach and Columbia. The firm represents injured people statewide, as well as out-of-state visitors who were hurt in South Carolina, and has a well-established record of helping ...
Health fears over CO2 storage are unfounded, study shows
2011-09-13
Capturing CO2 from power stations and storing it deep underground carries no significant threat to human health, despite recently voiced fears that it might, a study has shown.
Researchers found that the risk of death from poisoning as a result of exposure to CO2 leaks from underground rocks is about one in 100 million – far less than the chances of winning the lottery jackpot.
Scientists from the University of Edinburgh studied historical data on deaths from CO2 poisoning in Italy and Sicily, where the gas seeps naturally from the ground because of volcanic activity. ...