(Press-News.org) Although cold and gaseous rather than a desert world, the newfound planet Kepler-16b is still the closest astronomers have come to discovering Luke Skywalker's home world of Tatooine. Like Tatooine, Kepler-16b enjoys a double sunset as it circles a pair of stars approximately 200 light-years from Earth. It's not thought to harbor life, but its discovery demonstrates the diversity of planets in our galaxy.
"Kepler-16b is the first confirmed, unambiguous example of a circumbinary planet - a planet orbiting not one, but two stars," said Josh Carter of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA). "Once again, we're finding that our solar system is only one example of the variety of planetary systems Nature can create."
Carter is second author on the study announcing the discovery, which appears in the Sept. 15th issue of the journal Science. He is presenting the finding today at the Extreme Solar Systems II conference in Jackson Hole, Wyoming.
Kepler-16b weighs about a third as much as Jupiter and has a radius three-fourths that of Jupiter, making it similar to Saturn in both size and mass. It orbits its two parent stars every 229 days at a distance of 65 million miles - similar to Venus' 225-day orbit.
Both stars are smaller and cooler than our Sun. As a result, Kepler-16b is quite cold, with a surface temperature of around -100 to - 150° Fahrenheit.
NASA's Kepler mission detected the planet through what is known as a planetary transit - an event where a star dims when a planet crosses in front of it. The planet's discovery was complicated by the fact that the two stars in the system eclipse each other, causing the total brightness to dim periodically.
Astronomers noticed that the system's brightness sometimes dipped even when the stars were not eclipsing one another, hinting at a third body. The additional dimming events reappeared at irregular time intervals, indicating that the stars were in different positions in their orbit each time the third body passed. This showed that this third body was circling, not just one, but both stars.
Although Kepler data provided the relative sizes and masses of the stars and planet, astronomers needed more information to get absolute numbers. The crucial missing information came from the Tillinghast Reflector Echelle Spectrograph (TRES) on the 60-inch telescope at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory's Whipple Observatory in Arizona.
TRES monitored the changing velocity of the primary star as it moved around in its orbit. This yielded an orbital solution that set the scale of the Kepler-16 system. The team found that the two stars orbit each other every 41 days at an average distance of 21 million miles.
"Much of what we know about the sizes of stars comes from such eclipsing binary systems, and most of what we know about the size of planets comes from transits," said lead author and Kepler scientist Laurance Doyle of the SETI Institute. "Kepler-16 combines the best of both worlds, with stellar eclipses and planetary transits in one system."
INFORMATION:
For more information about the Kepler mission, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/kepler.
From Star Wars to science fact: Tatooine-like planet discovered
2011-09-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Yellow patches around eyelids predict risk of heart problems
2011-09-16
Raised yellow patches of skin (xanthelasmata) around the upper or lower eyelids are markers of an individual's increased risk of having a heart attack or suffering from heart disease, finds research published on bmj.com today.
The study, led by Professor Anne Tybjærg-Hansen at the University of Copenhagen, also concludes that white or grey rings around the cornea (arcus corneae) are not linked to an increased risk.
Previous research has established that both xanthelasmata and arcus corneae are deposits of cholesterol. However, around half of the individuals who have ...
Seaside fortress was a final stronghold of early Islamic power
2011-09-16
Archaeologists have long known that Yavneh-Yam, an archaeological site between the Israeli cities of Tel Aviv and Ashdod on the Mediterranean coast, was a functioning harbor from the second millennium B.C. until the Middle Ages. Now Tel Aviv University researchers have uncovered evidence to suggest that the site was one of the final strongholds of Early Islamic power in the region.
According to Prof. Moshe Fischer of TAU's Department of Archaeology and Near Eastern Cultures and head of the Yavneh-Yam dig, the recent discovery of a bath house from the Early Islamic period ...
Prasugrel: Indications of an additional benefit for some patients, but also of greater harm
2011-09-16
In order to better prevent blood clots, the drugs clopidogrel or prasugrel can be prescribed to patients with acute ischaemia of the heart muscle, in addition to acetylsalicylic acid (ASA). The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) has now investigated whether, in patients whose vessels were dilated by a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), the combination of prasugrel plus ASA has a higher patient-relevant benefit than ASA alone, or than combination therapy with clopidogrel plus ASA. The findings of the assessment provide indications that ...
Mobile phone electromagnetic field affects local glucose metabolism in the human brain
2011-09-16
Recent PET-measurements in Turku, Finland, show that the GSM mobile phone electromagnetic field suppresses glucose metabolism in temporoparietal and anterior temporal areas of the hemisphere next to the antenna.
Thirteen young healthy males were exposed to the GSM signal for 33 minutes. The study, initiated by Centre for Cognitive Neuroscience (CCN) at University of Turku, was methodologically unique combining the expertice in brain imaging (National PET-Center and CCN), measurements and modeling of radiation (Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority in Finland, STUK) ...
Archivist in the sound library
2011-09-16
People are adept at recognizing sensations such as sounds or smells, even when many stimuli appear simultaneously. But how the association works between the current event and memory is still poorly understood. Scientists at the Bernstein Center and the Ludwig-Maximilians Universität (LMU) München have developed a mathematical model that accurately mimics this process with little computational effort and may explain experimental findings that have so far remained unclear. (PLoS ONE, September 14, 2011)
The so-called 'cocktail party-problem' has already kept scientists ...
How the Milky Way got its spiral
2011-09-16
PITTSBURGH—The signature spiral arms of the Milky Way galaxy were likely formed by an epic collision between the Milky Way and the Sagittarius Dwarf galaxy, according to a University of Pittsburgh researcher and his collaborators, published today in the prestigious British journal Nature.
Supercomputer simulations by Christopher W. Purcell, postdoctoral research associate in the Department of Physics and Astronomy in Pitt's School of Arts and Sciences, and colleagues report their findings in a paper titled "The Sagittarius Impact as an Architect of Spirality and Outer ...
Los Angeles Dentist Achieves Exceptional Level of Invisalign Case Experience
2011-09-16
Dr. Shervin Louie, best Los Angeles dentist, has earned the status of Invisalign premier provider. This certificate is only awarded to those dental professionals who have achieved an exceptional level of Invisalign case experience.
Invisalign Preferred Providers have achieved a level of clinical training and experience in treating patients with the Invisalign system. Dentists must maintain regular treatment submission and complete ongoing training classes in order to earn the designation as a Preferred Provider of Invisalign.
"I am honored to be name an Invisalign ...
Restoring forests and planting trees on farms can greatly improve food security
2011-09-16
NAIROBI, KENYA (12 SEPTEMBER 2011) – Restoring and preserving dryland forests and planting more trees to provide food, fodder and fertilizer on small farms are critical steps toward preventing the recurrence of the famine now threatening millions of people in the Horn of Africa, according to forestry experts from the CGIAR Consortium.
Across the Horn, drought-induced famine has claimed tens of thousands of lives and swelled refugee camps in Kenya, Ethiopia and elsewhere, with millions of starving people – many of them children. Bearing the brunt of the crisis is Somalia, ...
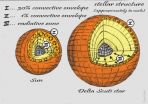
The turbulent lives of stars
2011-09-16
This press release is available in German.
The stars are boiling! The reason is the energy generated in the center of the star that wants to escape. If this does not happen quickly enough, the star starts to 'boil' in the outer layers causing vibrations that result in light variations, like in the Sun. Such oscillations have now been discovered by Victoria Antoci and collaborators using the NASA spacecraft Kepler, but in a much hotter star. The scientists publish this in the most recent issue of Nature.
Besides the discovery of earth-like planets, astronomy is concerned ...
Serotonin levels affect the brain's response to anger
2011-09-16
Fluctuations of serotonin levels in the brain, which often occur when someone hasn't eaten or is stressed, affects brain regions that enable people to regulate anger, new research from the University of Cambridge has shown.
Although reduced serotonin levels have previously been implicated in aggression, this is the first study which has shown how this chemical helps regulate behaviour in the brain as well as why some individuals may be more prone to aggression. The research findings were published today, 15 September, in the journal Biological Psychiatry.
For the study, ...