(Press-News.org) Researchers at Emory University School of Medicine have identified a set of genes that act in muscles to modulate aging and resistance to stress in fruit flies.
Scientists have previously found mutations that extend fruit fly lifespan, but this group of genes is distinct because it acts specifically in muscles. The findings could help doctors better understand and treat muscle degeneration in human aging.
The results were published online this week by the journal Developmental Cell.
The senior author is Subhabrata Sanyal, PhD, assistant professor of cell biology at Emory University School of Medicine. The first author of the paper is postdoc Alysia Vrailas-Mortimer. Collaborators from Howard University and the University of Athens contributed to the paper.
Vrailas-Mortimer, Sanyal and colleagues started investigating a pair of genes called "p38 MAP kinase" in fruit flies with the expectation that they could play a role in learning and memory. Along the way, they discovered that mutations in these genes speed up the process of aging and make the flies more sensitive to oxidative stress.
"It was really just dumb luck, because we found a mutant that had almost completely lost gene activity, but had enough activity to be born," Sanyal says.
If both genes are defective in the same fly, the flies die very early. They begin to develop motor problems, becoming unable to fly and climb, a few days after birth. The mutant flies are also more sensitive to heat, being deprived of food and water, and exposure to oxidative stress. The researchers could correct the effects of the mutations by restoring the genes' activity in muscles, but not nerve cells.
"The experiment that made us nervous was when we asked whether having more p38 could increase lifespan," Sanyal says. "You can make flies sick and shorten their lives in a hundred different ways easily, but finding one gene that makes a big change in lifespan is more significant."
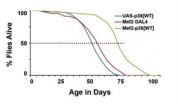
Fruit flies normally live about fifty days in Sanyal's laboratory, depending on temperature and conditions. Some strains of fly that overproduce p38 MAP kinase live on average about 75 days, 50 percent longer than regular flies (green line in graph below). For this effect, it is sufficient that p38 is overproduced in muscles only.
Vrailas-Mortimer showed that a protein that protects cells against oxidative stress that is found in mitochondria, superoxide dismutase (MnSOD), is responsible for at least some of p38 MAP kinase's effects on aging. A third gene called MEF2 is also involved, in between p38 MAP kinase and MnSOD. Mitochondria are cells' miniature power plants and are more abundant in muscle.
Giving flies more MnSOD can restore a more normal lifespan to the p38 mutants. Other types of antioxidant enzymes don't rescue lifespan in flies with p38 mutations, the researchers found.
P38, MEF2 and MnSOD's action in muscles distinguishes them from a well-studied genetic circuit regulating aging in the worm C. elegans as well as flies and mice, which appears to work through insulin-like hormone responses in the brain and other tissues. Caloric restriction (consistently eating less), an established way of lengthening lifespan, acts through this insulin-like signaling pathway.
"It may be that oxidative stress is especially important in flies' muscles because flies' energy use is so high," Sanyal says. "The role oxidative stress plays in aging is well-known, so its involvement here was not a surprise. I think what's new here is finding a genetic pathway regulating aging that is specific to muscles and separate from insulin signaling."
Sanyal says he and his team plan to examine what kinds of dietary antioxidants can extend lifespan in flies without p38. They also plan to probe how caloric restriction interacts with p38 deficiency.
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health and Emory's University Research Committee.
Reference:
A. Vrailas-Mortimer et al. A muscle-specific p38 MAPK/Mef2/MnSOD pathway regulates stress, motor function and lifespan in Drosophila. Dev Cell 21, 783-795 (2011).
Muscling toward a longer life: Genetic aging pathway identified in flies
2011-10-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
"Impact of US Domestic Tonnage Regulations on Design, Maintenance and Manning" Topic of Free WorkBoat.com Webinar on October 26
2011-10-19
Designing a vessel to meet a tonnage parameter has proven to be the bane of designers, builders and owners since the earliest days of the maritime industry. Today, regulations initially established over 140 years ago in a surveyor's office in London can dramatically affect the construction of virtually every commercial vessel at work in the United States.
"Every boat needs to have a tonnage certificate for whatever its type of function and any modification to a vessel can result in ramifications to the tonnage certificate," said David Krapf, editor in chief ...
Amorphous diamond, a new super-hard form of carbon created under ultrahigh pressure
2011-10-19
An amorphous diamond – one that lacks the crystalline structure of diamond, but is every bit as hard – has been created by a Stanford-led team of researchers.
But what good is an amorphous diamond?
"Sometimes amorphous forms of a material can have advantages over crystalline forms," said Yu Lin, a Stanford graduate student involved in the research.
The biggest drawback with using diamond for purposes other than jewelry is that even though it is the hardest material known, its crystalline structure contains planes of weakness. Those planes are what allow diamond ...
Canadian Pharmacy Customers Save Big on Wellbutrin XL
2011-10-19
Canada Drug Pharmacy offers Wellbutrin XL at a cheaper price, much cheaper when compared to purchasing the same drug from traditional retail stores. As more and more people turn to the internet to shop online, they are also searching for ways to save money. One of the benefits of buying Canadian drugs from CanadaDrugPharmacy.com is that the price of prescription medications is cheaper than traditional brick and mortar pharmacies. Purchasing online is also convenient since the consumers don't have to leave their house to buy their medicine. Customers can now log-in to Canada ...
Chinese-Americans don't overborrow, MU study finds
2011-10-19
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Bad mortgage loans and rampant consumer debt were two of the primary causes for the recent economic recession in the U.S. Despite a national trend of debt problems, a University of Missouri researcher has found one American population that holds almost no consumer debt outside of typical home mortgages. Rui Yao, an assistant professor of personal financial planning in the College of Human Environmental Sciences at the University of Missouri, found that while 72 percent of Chinese-American households hold a mortgage, only five percent of those households ...
Impurity atoms introduce waves of disorder in exotic electronic material
2011-10-19
UPTON, NY - It's a basic technique learned early, maybe even before kindergarten: Pulling things apart - from toy cars to complicated electronic materials - can reveal a lot about how they work. "That's one way physicists study the things that they love; they do it by destroying them," said Séamus Davis, a physicist at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and the J.G. White Distinguished Professor of Physical Sciences at Cornell University.
Davis and colleagues recently turned this destructive approach - and a sophisticated tool for "seeing" ...
Trudeau Institute reports new approach to treating Listeria infections
2011-10-19
Saranac Lake, N.Y.—Research underway at the Trudeau Institute could lead to new treatments for people sickened by Listeria and other sepsis-causing bacteria. Dr. Stephen Smiley's laboratory has published a study in the scientific journal Infection and Immunity that supports a new approach to treating these infections.
Listeria can cause serious illness, especially among the elderly, the very young and those with compromised immune systems. The bacteria can also cause significant complications in pregnant women, including miscarriage.
The CDC is reporting that one miscarriage ...
Diamonds, silver and the quest for single photons
2011-10-19
Building on earlier work showing how nanowires carved in impurity-laden diamond crystal can efficiently emit individual photons, researchers have developed a scalable manufacturing process to craft arrays of miniature, silver-plated-diamond posts that enable even greater photon control.
The development supports efforts to create robust, room-temperature quantum computers by setting the stage for diamond-based microchips. Additionally, the technology could support new tools capable of measuring magnetic fields at the nanometer scale.
Appearing early online in Nature ...
Katy Water Heaters Launches A New Website
2011-10-19
Katy Water Heaters, a full-service residential and commercial water heater repair and installation Katy plumbing company founded by master plumber Steve Williams announces the launch of our new website. Potential and existing customers can go to http://katywaterheaters.com/ to locate the plumber Katy services they need and request service via our online form or by calling us at (832) 886-4282.
Whether you own a tankless, solar, or conventional water heater, Katy Water Heaters has over 20 years of experience installing, repairing and replacing any type of water heater ...
Salk breathes new life into fight against primary killer of premature infants
2011-10-19
A discovery by scientists at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies might explain why some premature infants fail to respond to existing treatments for a deadly respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) and offers clues for new ways to treat the breathing disorder.
The scientists identified a new form of RDS in newborn mice and traced the problem to a cellular receptor for thyroid hormone, a key player in many developmental processes in the body. They found that two drugs used for treating overactive thyroid glands saved mice with a deadly genetic alteration that mimicked ...
AAP expands guidelines for infant sleep safety and SIDS risk reduction
2011-10-19
BOSTON - Since the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommended all babies should be placed on their backs to sleep in 1992, deaths from Sudden Infant Death Syndrome have declined dramatically. But sleep-related deaths from other causes, including suffocation, entrapment and asphyxia, have increased.
In an updated policy statement and technical report, the AAP is expanding its guidelines on safe sleep for babies, with additional information for parents on creating a safe environment for their babies to sleep.
"We have tried to make it easier for parents and providers ...