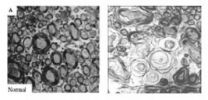
(Press-News.org) Washington, DC -- Babies born with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) often develop kidney failure because they have very large kidneys filled with tiny cysts. Even with excellent medical care, about 30% die shortly after birth. New research now provides clues into how gene defects may cause this condition, which occurs in 1 out of 20,000 newborns. The findings appear in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society Nephrology (JASN), a publication of the American Society of Nephrology.
Mutations in a gene named PKHD1 cause ARPKD, but it's not clear how. Jason Bakeberg and Christopher Ward, ChB, PhD (Mayo Clinic) led a team that bred mice to have a small tag inserted into this gene. This tag allowed the researchers to follow the activities of the protein made by the gene, called fibrocystin.
"We found that small vesicles, termed exosome-like vesicles (ELVs), present in urine and other bodily fluids have abundant fibrocystin on their surface. This has allowed us to follow ELVs as they interact with primary cilia, or small hair-like structures that project into the urine from cells within the kidney's tubules," said Dr. Ward. "We believe that ELVs are involved in transporting a range of signals through urine and that ELV interactions with cilia are central to this signaling."
The findings may help investigators to understand how PKHD1 gene mutations cause ARPKD and to develop tests for the disease. "For example we are working on urine-based tests for polycystic kidney disease based on the use of ELVs," said Dr. Ward.
###
Study co-authors include John Woollard, Marie Hogan, MD, PhD, Han-Fang Tuan, Ming Li, Jan van Deursen, PhD, Yanhong Wu, PhD, Bing Huang, PhD, Vicente Torres, MD, PhD, Peter Harris, PhD (Mayo Clinic); and Rachaneekorn Tammachote, PhD( Chulalongkorn University, in Thailand).
Disclosures: The authors reported no financial disclosures.
The article, entitled "Epitope-tagged Pkhd1 Tracks the Processing, Secretion, and Localization of Fibrocystin," will appear online at http://jasn.asnjournals.org/ on Monday, October 24, 2011, doi:10.1681/ASN.2010111173.
The content of this article does not reflect the views or opinions of The American Society of Nephrology (ASN). Responsibility for the information and views expressed therein lies entirely with the author(s). ASN does not offer medical advice. All content in ASN publications is for informational purposes only, and is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, drug interactions, or adverse effects. This content should not be used during a medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. Please consult your doctor or other qualified health care provider if you have any questions about a medical condition, or before taking any drug, changing your diet or commencing or discontinuing any course of treatment. Do not ignore or delay obtaining professional medical advice because of information accessed through ASN. Call 911 or your doctor for all medical emergencies.
Founded in 1966, and with more than 12,000 members, the American Society of Nephrology (ASN) leads the fight against kidney disease by educating health professionals, sharing new knowledge, advancing research, and advocating the highest quality care for patients.
Clues revealed to cause of deadly kidney disease in newborns
The gene that's implicated in the disease is important for signaling in the kidneys
2011-10-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Genetic difference in staph infects some heart devices, not others
2011-10-25
DURHAM, N.C. -- Infectious films of Staph bacteria around an implanted cardiac device, such as a pacemaker, often force a second surgery to replace the device at a cost of up to $100,000. But not all implanted cardiac devices become infected.
Now researchers from Duke University Medical Center and Ohio State University (OSU) have discovered how and why certain strains of Staphylococcus aureus (SA) bacteria, the leading cause of these device infections, have infected thousands of implanted cardiac devices. About 4 percent of the 1 million annually implanted devices become ...
Perinatal antidepressant stunts brain development in rats
2011-10-25
Rats exposed to an antidepressant just before and after birth showed substantial brain abnormalities and behaviors, in a study funded by the National Institutes of Health.
After receiving citalopram, a serotonin-selective reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), during this critical period, long-distance connections between the two hemispheres of the brain showed stunted growth and degeneration. The animals also became excessively fearful when faced with new situations and failed to play normally with peers – behaviors reminiscent of novelty avoidance and social impairments seen in ...
City of Kingston: Sustainability in Ontario
2011-10-25
In a report in Energy Digital, the City of Kingston explains that through a cooperation among City, community and business Kingston is on its way to becoming the most energy efficient municipality in Canada.
The City of Kingston is heavily focused on creating a more sustainable community. Through promotion of LEED construction, collaboration with community partners and the encouragement of renewable energy use, Kingston is already on its way to becoming the most sustainable municipality in Canada for generations to come.
The City of Kingston's green initiatives are ...
First Plastic Surgeon in Scottsdale / Phoenix Arizona to Offer CoolSculpting to Reduce Fat Bulges
2011-10-25
The SHAW Center for Aesthetic Enhancement (www.theshawcenter.com) is the first plastic surgery practice to add CoolSculpting by Zeltiq to it's list of fat reduction, body contouring procedures in the Scottsdale / Phoenix Metro area. With over twenty-five years of body contouring experience, Dr. Lawrence W. Shaw, a Scottsdale plastic surgeon, feels there is definitely a place for this non-invasive fat reduction procedure in his busy plastic surgery practice.
"I've been looking for many years, without success, to find an effective, scientifically proven, non-surgical ...
Stanford researchers build transparent, super-stretchy skin-like sensor
2011-10-25
VIDEO:
Using carbon nanotubes bent to act as springs, Stanford researchers have developed a stretchable, transparent skin-like sensor. The sensor can be stretched to more than twice its original length and...
Click here for more information.
Imagine having skin so supple you could stretch it out to more than twice its normal length in any direction - repeatedly - yet it would always snap back completely wrinkle-free when you let go of it. You would certainly never need ...
Relaxation dynamics of 2D nanoparticle systems
2011-10-25
Soft matters maintain their structures via weak interactions, such as Van der Waals, capillary, hydrogen bonds etc. The entropy plays a key role in the ordering of this kind of materials. They behave as a solid until a sufficiently large stress is applied, and then behave as a viscoelastic liquid. Due to the unique structures and rheological properties, soft matter such as concentrated suspensions, emulsions, pastes and gels often exhibit unusual slow relaxation and aging effect. Studying the relaxation dynamics may gain more insight into the microstructure of the material ...
How does the initial free volume distribution affect shear band formation in metallic glass?
2011-10-25
Introducing heterogeneities into the structure is an effective way to enhance the plasticity of metallic glasses (MGs). The original randomly distributed free volume in MGs, a natural heterogeneity, has been found to promote plasticity. However, the exact correlation between the free volume distribution and mechanical response is still unclear. Professor Dai Lanhong and his group from the State Key Laboratory of Nonlinear Mechanics, Institute of Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, set out to tackle this problem. They investigated the shear banding in MGs with different ...
Network Marketing Leaders and Top Earners Aaron & Sophia Rashkin Named CarbonCopy PRO Elite Marketing Partners of the Year
2011-10-25
When Aaron & Sophia Rashkin began their first online business with CarbonCopy PRO Elite back in August of 2008, they had no idea that their persistence and tenacity would become their biggest allies en route to internet marketing success.
The couple had a background in traditional multi-level marketing, but after building an organization of over 10,000 distributors and still hardly being able to pay for their two kids, two cars and two mortgages, they took their desire to become financially free to the internet.
Recently named "Marketing Partners of the ...
Poisonous oceans delayed animal evolution
2011-10-25
"We have investigated the cycling of molybdenum (Mo) in ancient oceans by studying the elemental and isotopic composition of Mo in sedimentary rocks from Grand Canyon that formed in the oceans 750 million years ago", explains Tais W. Dahl, who did this research in collaboration with researchers from Arizona State University, Harvard University and the Nordic Center of Earth Evolution in Denmark (NordCEE).
Molybdenum tracks the presence of poisonous sulfide in ancient oceans
The study uses a new method to determine the extent of anoxia and presence of sulfide in the ...
Life beyond cancer: Starting a family following treatment
2011-10-25
CHICAGO - Five years ago, Sheri Scott was beginning a new chapter in her life. The recently engaged 31-year-old was eagerly browsing bridal magazines and busy planning for her big day. Unfortunately, just weeks following her engagement, Scott was diagnosed with breast cancer. Suddenly, she was juggling medical appointments and planning a double mastectomy instead of a wedding. Soon after her diagnosis, Scott was approached by her doctor at Northwestern Memorial Hospital about preserving her fertility. He explained that cancer treatment could compromise her fertility and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Clues revealed to cause of deadly kidney disease in newbornsThe gene that's implicated in the disease is important for signaling in the kidneys