(Press-News.org) Proposals to remove the carbon dioxide caused by burning fossil fuel from the atmosphere include letting commercially managed forests grow longer between harvests or not cutting them at all.
An article published in the journal Forests says, however, that Pacific Northwest trees grown and harvested sustainably, such as every 45 years, can both remove existing carbon dioxide from the air and help keep the gas from entering the atmosphere in the first place. That's provided wood is used primarily for such things as building materials instead of cement and steel – which require more fossil fuels in their manufacture – and secondarily that wood wastes are used for biofuels to displace the use of fossil fuels.
"When it comes to keeping carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere, it makes more sense to use trees to recycle as much carbon as we can and offset the burning of fossil fuel than it does to store carbon in standing forests and continuing burning fossil fuels," said Bruce Lippke, University of Washington professor emeritus of forest resources.
Lippke is one of eight co-authors of the article in Forests. It is the first to comprehensively calculate using woody biomass for bioenergy in addition to using wood for long-lived products. The article focuses on the extra carbon savings that can be squeezed from harvesting trees if wood not suitable for long-term building materials is used for bioenergy. Such wood can come from the branches and other debris left after harvesting, materials thinned from stands or from plantations of fast-growing trees like willow.
For the article, the co-authors looked at selected bioenergy scenarios using wood from the U.S. Pacific Northwest, Southeast and Northeast.
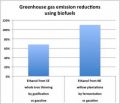
They considered two ways of producing ethanol from woody biomass – gasification and fermentation – and used what's called life cycle analysis to tally all the environmental effects of gathering, processing and using the resulting fuels. Ethanol from woody biomass emits less greenhouse gas than an equivalent amount of gasoline, between 70 percent and a little over 100 percent less.
How much of a reduction depends on the process. Achieving slightly more than a 100 percent reduction in greenhouse gas emissions is possible, for example, using a fermentation process that both produces ethanol and generates enough electricity to offset the fossil fuel used in the fermentation process.
In contrast, producing and using corn ethanol to displace gasoline reduces greenhouse gas emissions 22 percent on average, according to the Environmental Protection Agency's fact sheet "Greenhouse Gas Impacts of Expanded Renewable and Alternative Fuels Use."
While biofuels from woody biomass are carbon friendly, Lippke cautions that the U.S. should not use tax breaks or other incentives that inadvertently divert wood to bioenergy that is better used for long-lived building materials and furniture.
"Substituting wood for non-wood building materials can displace far more carbon emissions than using the wood for biofuel," the article says. "This fact creates a hierarchy of wood uses that can provide the greatest carbon mitigation for each source of supply."
Lippke said using wood for products and bioenergy can be considered carbon neutral because the carbon dioxide trees absorb while growing eventually goes back to the atmosphere when, for instance, wood rots after building demolition or cars burn ethanol made from woody debris. With sustainably managed forests, that carbon dioxide is then absorbed by the growing trees awaiting the next harvest.
The co-authors aren't advocating that all forests be harvested, just the ones designated to help counter carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Older forests, for instance, provide ecological values even though they absorb less carbon dioxide as they age.
In the article the authors also urge policymakers and citizens to consider not just carbon mitigation but also to find ways to weigh the importance of energy independence from fossil fuels when considering how to use woody biomass for bioenergy.
"Simply burning woody biomass to generate heat or electricity makes sense for carbon mitigation," he says, "But there's no energy independence gained," Lippke said. So carbon efficiency is only one part of the equation. Transportation fuels depend heavily on imported oil and therefore biofuels that replace them make additional contributions to the domestic economy, including energy independence and rural economic development, the authors said.
INFORMATION:
Other co-authors are Richard Gustafson and Elaine Oneil with the UW, Richard Venditti with North Carolina State University, Timothy Volk with the State University of New York, Leonard Johnson with the University of Idaho, Maureen Puettmann of WoodLife Environmental Consultants and Phillip Steele with Mississippi State University.
The publication integrates findings across many previous reports generated by a consortium of 17 research institutions that have been involved in life cycle analysis of wood products for more than 15 years through the Consortium for Research on Renewable Industrial Materials, based at the UW. The recent biofuel life cycle research was funded with a grant from the U.S. Forest Service's Forest Products Laboratory.
For more information:
Lippke, 206-322-8205, office 206-543-8684, cell 206-931-7297, blippke@uw.edu
Oneil, UW faculty and executive director CORRIM, office 206-543-8684, eoneil@uw.edu
Gustafson, UW faculty, advanced biofuels such as ethanol from cellulose, 206-543-2790, pulp@uw.edu
Puettmann, CORRIM's consultant for reviewing life cycle data, 541-231-2627, maureen.puettmann@q.com
Suggested websites
Abstract and link to pdf of article
http://www.mdpi.com/1999-4907/2/4/861/
Bruce Lippke
http://www.cfr.washington.edu/SFRPublic/People/FacultyProfile.aspx?PID=11
EPA fact sheet "Greenhouse Gas Impacts of Expanded Renewable and Alternative Fuels Use"
http://tinyurl.com/EPAFactSheetAltFuels
Consortium for Research on Renewable Industrial Materials
http://www.corrim.org/
Carbon mitigation strategy uses wood for buildings first, bioenergy second
2011-11-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Choice Hotels Recognises its Best UK Hotels
2011-11-23
Choice Hotels International, Inc. (NYSE: CHH), the global hotel group behind the Comfort, Quality, and Clarion brands and one of the largest and most successful lodging franchisors in the world, has announced the winners of its various "Hotels of the Year" awards.
It has awarded Comfort Hotel Great Yarmouth the title of "UK Comfort Hotel of the Year", Quality Hotel Edinburgh Airport the "UK Quality Hotel of the Year" award and Clarion Hotel Carrickfergus the "UK Clarion Hotel of the Year" accolade.
The hotels were judged to ...
The Radisson Blu Hotel, Kuwait Hosts The Concert of Hope
2011-11-23
The Radisson Blu Hotel, Kuwait recently hosted the third Concert of Hope. This beautiful musical black tie event under the patronage of H.E. The British Ambassador Mr. Frank Baker O.B.E. was in association with The Kuwait Chamber Philharmonia.
Held in the Al Hashemi Ballroom at the hotel, the evening of musical delight featured opera singing sensation from 'Arabs Got Talent', Abdulrahman Al Mahmeed as well as a variety of other musical talent.
The recent winner of 'Arabs Got Talent', Abdulrahman Al Mahmeed is known to hold his audiences spellbound as he sings a varied ...
Special delivery: Nematode-infected insect cadavers
2011-11-23
This press release is available in Spanish.
A custom-made machine for packaging mealworms infected with beneficial nematodes could improve the delivery, timing and use of the wormlike organisms as biological control agents.
The machine is the result of a cooperative research and development agreement involving US Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists and Southeastern Insectaries, Inc., of Perry, Ga.
The Heterorhabditis and Steinernema nematodes being used can infect and kill a wide array of insect crop pests, including Japanese beetles, vine weevils, root borers ...
New class of drugs for the reversible inhibition of proteasomes
2011-11-23
This press release is available in German.
As the "recycling plant" of the cell, the proteasome regulates vitally important functions. When it is inhibited, the cell chokes on its own waste. Cancer cells, in particular, are very sensitive because they need the proteasome for their uncontrolled growth. Biochemists at the Technische Universitaet Muenchen (TUM) have now identified the lead structure of a new class of drugs that attacks the proteasome in an unusual way. New medication could be developed on the basis of this previously unknown binding mechanism. The scientists ...
The National Trust Reveals Consumers Need a Leg Up with Farming Knowledge
2011-11-23
The National Trust has revealed the results from a new survey* which show that the vast majority (93 per cent) of people in Great Britain don't know the best time of year to enjoy eating British lamb.
Only seven per cent of respondents correctly identified autumn as the time for tucking into one of Britain's favourites, with half (49 per cent) choosing spring as the best time to serve lamb - the time of year when most lambs are born.
The research marks six months of the National Trust's mass on-line MyFarm experiment at its 1,200 acre organic farm at Wimpole in Cambridgeshire. ...
Monroe North Carolina Hotel Announces a Special 20% Savings Deal for Guests
2011-11-23
Super 8 Monroe North Carolina Hotel announces a special savings package for their hotel guest to enjoy. Guests who book their stay of 3 or more nights, from now through November 22, 2011 will receive a 20% discount off Best Available Rates (excluding taxes and incidentals). Stays must be completed by November 30, 2011. This offer cannot be combined with any other special rates and is subject to availability.
As an additional bonus, now Wyndham Rewards members can earn DOUBLE miles or points with the stays you book until November 18th. All stays must be completed by ...
Great Lakes fish feed on invading shrimp
2011-11-23
The latest invader of the Great Lakes—Hemimysis anomala, or more commonly the bloody red shrimp after its bright red spots—may become a new food source for fish, allaying concerns about how it will impact native fish populations.
"Forecasting how an invader will affect the growth and production of a specific native fish species is very relevant to conservation groups and government agencies hoping to conserve those fish," says Biology graduate student Mike Yuille.
Mr. Yuille is the lead author of a study that suggests for the first time that several native fish species ...
Smithsonian scientists use fossil feathers reveal lineage of extinct, flightless ibis
2011-11-23
A remarkable first occurred recently at the Smithsonian's National Museum of Natural History when ornithologists Carla Dove and Storrs Olson used 700- to 1,100-year-old feathers from a long extinct species of Hawaiian ibis to help determine the bird's place in the ibis family tree. The feathers are the only known plumage of any of the prehistorically extinct birds that once inhabited the Hawaiian Islands.
Discovered with a nearly complete skeleton, the feathers retained enough microscopic structure to allow the scientists to confirm the classification of the bird, known ...
Anorexia nervosa study finds inner conflicts over the 'real' self that have treatment implications
2011-11-23
"It feels like there's two of you inside – like there's another half of you, which is my anorexia, and then there's the real K, the real me, the logic part of me, and it's a constant battle between the two." - 36 year old study participant with anorexia nervosa.
(Garrison, NY) People with anorexia nervosa struggle with questions about their real, or "authentic," self – whether their illness is separate from or integral to them – and this conflict has implications for compulsory treatment, concludes a study in the Hastings Center Report. The researchers also conclude that ...
405 Acres of Iowa Hunting Land for Sale by Spook Nation Farms
2011-11-23
Spook Spann, of Spook Nation TV, is selling 405 acres of hunting land in Grant, Iowa. Located in the heart of Iowa's prime buck land with a one acre working vineyard, this Iowa hunting property contains a great number of existing amenities and is sure to impress the most avid deer hunter.
"I have personally harvested several great bucks off of this land, and I know that this will make an awesome farm for someone who is serious about hunting true world class bucks," asserts Spook Spann, professional hunter and manager of Spook Nation Farms. "When it comes ...