Advance toward an imaging agent for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease
2012-01-13
(Press-News.org) Scientists are reporting development and initial laboratory tests of an imaging agent that shows promise for detecting the tell-tale signs of Alzheimer's disease (AD) in the brain — signs that now can't confirm a diagnosis until after patients have died. Their report appears in the journal ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters.
Masahiro Ono and colleagues explain that no proven laboratory test or medical scan now exists for AD, which is claiming an increasingly heavy toll with the graying of the world's population. Patients now get a diagnosis of AD based on their medical history and symptoms, and symptoms like memory loss often are identical to those of normal aging. Currently, the only definitive way to diagnose AD involves an autopsy with examination of brain samples for the presence of the clumps and tangles of abnormal protein that occur in the disease.
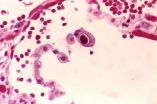
The scientists describe the synthesis and lab testing of a new imaging agent (called FPPDB), which bound tightly to ß-amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles — signs of AD — in human brain samples. In normal laboratory mice, which served as stand-ins for humans, FPPDB stayed in the body long enough for a PET scan (a sophisticated medical imaging technique). With further development, the imaging agent may allow early AD diagnosis in humans, the scientists indicate.
INFORMATION:
The authors acknowledge funding from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 163,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society contact newsroom@acs.org.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-01-13
Promoting immunizations as a part of routine office-based medical practice is needed to improve adult vaccination rates, a highly effective way to curb the spread of diseases across communities, prevent needless illness and deaths, and lower health care costs, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Increasingly, vaccinations are being offered outside of physician offices at pharmacies, workplaces and retail medical clinics. Even so, office-based medical practice continues to be central to the delivery of recommended vaccinations to adults.
"Regardless of where vaccines ...
2012-01-13
Similar to the way pavement, softened by a hot sun, will slow down a car, graphene—a one-atom-thick sheet of carbon with wondrous properties—slows down an object sliding across its surface. But stack the sheets and graphene gets more slippery, say theorists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), who developed new software to quantify the material's friction.
"I don't think anyone expects graphene to behave like a surface of a three-dimensional material, but our simulation for the first time explains the differences at an atomic scale," says NIST ...
2012-01-13
A new clinical Standard Reference Material (SRM) from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) will help health care professionals more accurately diagnose and treat cytomegalovirus (CMV), a common pathogen that is particularly dangerous for infants and persons with weakened immune systems.
CMV is found in 50 to 80 percent of the population. It is a member of the herpes family of viruses that includes two herpes simplex viruses (the causes of cold sores and genital herpes), the varicella-zoster virus (the cause of chicken pox and shingles) and the Epstein-Barr ...
2012-01-13
With a random-looking spatter of paint specks, a pair of cameras and a whole lot of computer processing, engineer Mark Iadicola of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has been helping the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA), in cooperation with the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO), to assure the safety of hundreds of truss bridges across the United States. Iadicola has been testing the use of a thoroughly modern version of an old technique—photographic measurement or "photogrammetry"—to watch the failure ...
2012-01-13
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), in collaboration with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), has developed two new Standard Reference Materials (SRMs) for measurements of human exposure to environmental toxins. Used as a sort of chemical ruler to check the accuracy of tests and analytic procedures, the new reference materials replace and improve older versions, adding measures for emerging environmental contaminants such as perchlorate, a chemical that the Environmental Protection Agency has targeted for regulation as a contaminant ...
2012-01-13
The chemical industry, which touches 96 percent of all manufactured goods, is seeing some positive signs for 2012, although the overall outlook is not very rosy. Growing demand for chemicals used in agriculture, electronics, cars and airplanes will boost an industry that generates $674 billion in sales in the U.S. alone, but expiring patents and global economic woes will take a toll. These forecasts and others are in the cover story in the current issue of Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, the world's largest scientific ...
2012-01-13
Imagine the following scenarios: a co-worker is spoken to condescendingly, excluded from a meeting, or ignored by a supervisor. How does it make you feel? Do you feel differently depending on whether your co-worker is a man or a woman? According to a new study, workers who witness incivility towards colleagues feel negative emotions – especially when the incivility is aimed at workers of the same sex. The work, by Kathi Miner from Texas A&M University and Angela Eischeid from Buena Vista University, Iowa, is the first to look at the relationship between employees' observations ...
2012-01-13
Astronomers using the partially completed ALMA observatory have found compelling evidence for how star-forming galaxies evolve into 'red and dead' elliptical galaxies, catching a large group of galaxies right in the middle of this change.
For years, astronomers have been developing a picture of galaxy evolution in which mergers between spiral galaxies could explain why nearby large elliptical galaxies have so few young stars. The theoretical picture is chaotic and violent: The merging galaxies knock gas and dust into clumps of rapid star formation, called starbursts, ...
2012-01-13
A better understanding of the universe will be the outgrowth of the discovery of the Higgs boson, according to a team of University of Oklahoma researchers. The team predicts the discovery will lead to supersymmetry or SUSY—an extension of the standard model of particle physics. SUSY predicts new matter states or super partners for each matter particle already accounted for in the standard model. SUSY theory provides an important new step to a better understanding of the universe we live in.
Howard Baer, Homer L. Dodge Professor of High Energy Physics in the OU Department ...
2012-01-13
Tropical Storm Heidi is forecast to make landfall today along the Pilbara coast of Western Australia as warnings pepper the coast. NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead early in the day and captured a visible image showing Heidi's center still north of the Pilbara coast, while her outer bands continue to bring rainfall and gusty winds to coastal residents.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Heidi on January 11, 2012 at 02:30 UTC (Jan. 10 at 10:30 a.m. EST) and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer captured a visible image of the storm. The image showed that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Advance toward an imaging agent for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease