(Press-News.org) The problem is the sheer number: In the family tree of modern-day corn, there are two main groups with 10,000 pure-breed lines each. Each of these lines could potentially be used for producing a new variety by means of cross-breeding. In mathematical terms, that equates to 100 billion possibilities. In terms of corn, however, a parent's performance is no indicator of what potential lies hidden in their offspring. Even the feeblest of parents can produce mighty offspring when cross-bred.
But time is of essence: Currently it takes approximately 10 years for breeders to develop a new variety. Issues such as climate change, food shortages and the increasing demand for more energy, however, are making it essential to find solutions even faster.
Prof. Dr. Albrecht Melchinger, PhD student Christian Riedelsheimer and their research partners are experimenting with a new technique to solve both problems. The best parent plants are selected in two steps, beginning when they are not even planted yet or when they are just small plantlets. This saves time and guarantees the highest rate of success right from the very start.
Trick Nr. 1: Use mathematics and experience when selecting
Riedelsheimer takes a tiny sample from a kernel of corn. Not enough to harm the kernel, but enough to get a full picture of its DNA structure. This analysis is conducted jointly by the University of Hohenheim and the IPK Gatersleben.
The rest is mathematics and experience. "We know today that there is no single gene which determines whether a stalk of corn will grow up strong or produce lots of kernels on the cob. Instead there are numerous sequences in its DNA which all contribute to the plant's development. We can now examine up to 56,000 of these sequences using the latest techniques in genome analysis", Riedelsheimer explains.
The analysis does not involve modifying the DNA, but rather creating a unique profile of each parent, a so-called "genome profile" or "genetic fingerprint".
To analyse the fingerprint, scientists have spent the past three years and more planting, cross-breeding, analysing chromosomes and recording yields. The observations in the field have been used to develop a mathematical-statistical model which can be used to predict a parent's genetic potency.
Trick Nr. 2: Early selection
The composition of the leaves is a second indicator of which plants make for especially good parents. More specifically, it is about the amounts of starch, sugar, amino acids, chlorophyll and other substances. As with the genetic information, this data allows for a statistical prognosis of a plant's breeding capabilities.
Tests can be conducted to find out the levels shortly after the seeds have been sown, when the plantlets are roughly three weeks old and 20 cm tall. Compared with analysing the plant's genetic structure, taking samples in the field is rather an athletic activity. "The plant's metabolism varies constantly throughout the course of a day and that makes it necessary to collect the leaves quickly and shock freeze the samples immediately", says Riedelsheimer. "All in all we collected 6,000 samples- in just 69 minutes!"
For the technically-challenging task of analysing the substances, plant breeders work in collaboration with experts from the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Plant Physiology in Golm. The rest involves cutting-edge statistics. "Similar to the DNA profile, it is not the individual substances which are important for making predictions, but rather how these substances stand in relation to one another", Riedelsheimer explains.
New technology saves time, money and expensive acreage
"This new technique allows us to select the most promising parents with high accuracy and to focus all of our resources on these", says Prof. Dr. Melchinger.
This method also saves cultivatable land, which, in turn, saves money. "In order to test all possible crosses, we would have to plant corn on half of the earth's surface", a utopian, if not an expensive undertaking. "A single field plot costs us 50 euros. We test on two plots per genotype at ten different locations, making a total of 1,000 euros", Prof. Dr. Melchinger explains. An analysis of the genome using a chip and a robot costs approximately 150 euros.
Impressive as well is the amount of time saved. DNA analysis of the kernels can be conducted during the winter months. Meanwhile, the plantlets to be analysed for their substance composition grow in the greenhouse. As a result, the best parent plants can be chosen and cultivated that same year.
Paradigm shift opens door to new research approaches
Nonetheless, it will take another few years until the new breed is ready. Breeders worldwide also know another trick, especially when it comes to corn. One that has been around for decades.
Prof. Dr. Melchinger describes a paradoxical phenomenon: "With corn, the offspring tend to be especially large when the parents stem from generations of in-breeding." Experts speak of "heterosis", hobby gardeners of "hybrids".
The most promising parent plants are sorted out and self-pollinated over many generations. Only then does cross-pollination take place in preparation for the sowing of the new hybrid variety.
Heterosis as a biological phenomenon has yet to be fully researched in detail, according to Prof. Dr. Melchinger. "We were able to determine in earlier research projects that the reasons for the phenomenon lie in the extremely complex interaction of many different genes."
For researchers, this has led to a paradigm shift. "We've moved away from the search for individual super genes." Instead we focus on the interplay among the diverse elements in the genetic code. "This new perspective on plants will help the hybrid breeding programme immensely", Prof. Dr. Melchinger believes. "There is so much genetic diversity in corn. One must simply know how to combine it in the right way."
INFORMATION:
Bibliography
Christian Riedelsheimer, Angelika Czedik-Eysenberg, Christoph Grieder, Jan Lisec, Frank Technow, Ronan Sulpice, Thomas Altmann, Mark Stitt, Lothar Willmitzer & Albrecht E Melchinger, Genomic and metabolic prediction of complex heterotic traits in hybrid maize, Nature Genetics's, Advance Online Publication (AOP) on 15 January at 1800 London time / 1300 US Eastern time, http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ng.1033
Background: GABI research project
The current research activities are based on the results of earlier studies conducted on Arabidopsis. The newly-publicised procedure was discovered as part of the research project GABI-ENERGY. The acronym GABI stands for "Genomanalyse im biologischen System Pflanze", a funding program of the Federal Ministry of Education and Research for projects towards innovation in the field of genetic research with plants (www.gabi.de). The Ministry has allocated €2.7 mil. towards the project.
Good parents are predictable -- at least when it comes to corn
For a bigger harvest and faster results: The University of Hohenheim, the MPI for Molecular Plant Physiology and the Leibniz Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research in Gatersleben start a new chapter in plant breeding
2012-01-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers use sugar to halt esophageal cancer in its tracks
2012-01-16
Scientists working at the Medical Research Council have identified changes in the patterns of sugar molecules that line pre-cancerous cells in the esophagus, a condition called Barrett's dysplasia, making it much easier to detect and remove these cells before they develop into esophageal cancer. These findings, reported in the journal Nature Medicine, have important implications for patients and may help to monitor their condition and prevent the development of cancer.
Oesophageal cancer is the fifth biggest cause of cancer death in the United Kingdom and the eighth leading ...
Scientists shed new light on link between 'killer cells' and diabetes
2012-01-16
Killer T-cells in the human body which help protect us from disease can inadvertently destroy cells that produce insulin, new research has uncovered.
The study provides the first evidence of this mechanism in action and could offer new understanding of the cause of Type 1 diabetes.
Professor Andy Sewell, an expert in human T-cells from Cardiff University's School of Medicine worked alongside diabetes experts from King's College London to better understand the role of T-cells in the development of Type 1 diabetes.
The team isolated a T-cell from a patient with Type ...
Ultra short telomeres linked to osteoarthritis
2012-01-16
Telomeres, the very ends of chromosomes, become shorter as we age. When a cell divides it first duplicates its DNA and, because the DNA replication machinery fails to get all the way to the end, with each successive cell division a little bit more is missed. New research published in BioMed Central's open access journal Arthritis Research & Therapy shows that cells from osteoarthritic knees have abnormally shortened telomeres and that the percentage of cells with ultra short telomeres increases the closer to the damaged region within the joint.
While the shortening of ...
CSHL team introduces automated imaging to greatly speed whole-brain mapping efforts
2012-01-16
Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y. – A new technology developed by neuroscientists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) transforms the way highly detailed anatomical images can be made of whole brains. Until now, means of obtaining such images – used in cutting-edge projects to map the mammalian brain -- have been painstakingly slow and available only to a handful of highly specialized research teams.
By automating and standardizing the process in which brain samples are divided into sections and then imaged sequentially at precise spatial orientations in two-photon microscopes, ...
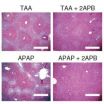
Rutgers, Massachusetts General investigators find novel way to prevent drug-induced liver injury
2012-01-16
NEW BRUNSWICK, N.J. – Rutgers University and Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigators have developed a novel strategy to protect the liver from drug-induced injury and improve associated drug safety.
In a report receiving advance online publication in the journal Nature Biotechnology, the team reports that inhibiting a type of cell-to-cell communication can protect against damage caused by liver-toxic drugs such as acetaminophen.
"Our findings suggest that this therapy could be a clinically viable strategy for treating patients with drug-induced liver injury," ...
Online Auto Insurance: Mercury Ruled Not Liable in California Court Case
2012-01-16
A recent California court decision highlights the need for state residents who buy a car from a private party to make sure that they are covered under a policy before driving it away, according to Online Auto Insurance (OAI).
New car buyers in the Golden State must purchase California auto insurance for any car they plan to drive, but consumers may be uncertain when the coverage provided by the seller's policy ceases. And that issue played a large role in a recent California court decision.
The state's 6th Court of Appeals found that Daniel Thiel--who purchased ...
LA Copy and Print Center is Offering a Discount for CSUN Students and Faculty
2012-01-16
With winter session classes already in full gear, CSUN students and faculty are just within reach of the 2012 spring semester. While things have been financially tight for the CSU system, everyone is still looking towards this new year with excitement and hope for what it has to bring. This is why the leading printing company in Los Angeles is now offering a 10% discount on all services to CSUN students and faculty to take just a little bit of the burden off of the already struggling California university system.
While tuition may seem bad these days, the real problems ...
Recent Gun Crimes Could Trigger New Pennsylvania Self-Defense Law
2012-01-16
Recent Gun Crimes Could Trigger New Pennsylvania Self-Defense Law
News outlets from Pittsburgh to Philadelphia recently reported on Pennsylvania homicide cases involving firearms that implicate Pennsylvania's new "stand-your-ground" law. Recent changes by lawmakers strengthened so-called Castle Doctrine principles in the state criminal code.
House Bill 40 passed with wide majorities in both houses of the Pennsylvania General Assembly last summer, and took effect in late August after it was signed by Governor Tom Corbett. The new law redefines general principles ...
Quantitative imaging application to gut and ear cells are reported in 2 Nature papers
2012-01-16
BOSTON, MA -- From tracking activities within bacteria to creating images of molecules that make up human hair, several experiments have already demonstrated the unique abilities of the revolutionary imaging technique called multi-isotope imaging mass spectometry, or MIMS, developed by researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH). MIMS can produce high-resolution, quantitative three-dimensional images of stable isotope tags within subcellular compartments in tissue sections or cells.
With its use of stable isotopes as tracers, MIMS has opened the door for biomedical ...
Fewer children require hospitalization following drowning-related incidents
2012-01-16
Fewer children required hospitalization following a drowning incident over the last two decades, according to a new study from the Johns Hopkins Center for Injury Research and Policy. According to the study, pediatric hospitalizations from drowning-related incidents declined 51 percent from 1993 to 2008. The rates declined significantly for all ages and for both genders, although drowning-related hospitalizations remained higher for boys at every age. Hospitalization rates also decreased significantly across the U.S., with the greatest decline in the South. Despite the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Fecal transplants from older mice significantly improve ovarian function and fertility in younger mice
Delight for diastereomer production: A novel strategy for organic chemistry
Permafrost is key to carbon storage. That makes northern wildfires even more dangerous
Hairdressers could be a secret weapon in tackling climate change, new research finds
Genetic risk for mental illness is far less disorder-specific than clinicians have assumed, massive Swedish study reveals
A therapeutic target that would curb the spread of coronaviruses has been identified
Modern twist on wildfire management methods found also to have a bonus feature that protects water supplies
AI enables defect-aware prediction of metal 3D-printed part quality
Miniscule fossil discovery reveals fresh clues into the evolution of the earliest-known relative of all primates
World Water Day 2026: Applied Microbiology International to hold Gender Equality and Water webinar
The unprecedented transformation in energy: The Third Energy Revolution toward carbon neutrality
Building on the far side: AI analysis suggests sturdier foundation for future lunar bases
Far-field superresolution imaging via k-space superoscillation
10 Years, 70% shift: Wastewater upgrades quietly transform river microbiomes
Why does chronic back pain make everyday sounds feel harsher? Brain imaging study points to a treatable cause
Video messaging effectiveness depends on quality of streaming experience, research shows
Introducing the “bloom” cycle, or why plants are not stupid
The Lancet Oncology: Breast cancer remains the most common cancer among women worldwide, with annual cases expected to reach over 3.5 million by 2050
Improve education and transitional support for autistic people to prevent death by suicide, say experts
GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic could cut risk of major heart complications after heart attack, study finds
Study finds Earth may have twice as many vertebrate species as previously thought
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings and research at AAOS 2026
New journal highlights how artificial intelligence can help solve global environmental crises
Study identifies three diverging global AI pathways shaping the future of technology and governance
Machine learning advances non targeted detection of environmental pollutants
ACP advises all adults 75 or older get a protein subunit RSV vaccine
New study finds earliest evidence of big land predators hunting plant-eaters
Newer groundwater associated with higher risk of Parkinson’s disease
New study identifies growth hormone receptor as possible target to improve lung cancer treatment
Routine helps children adjust to school, but harsh parenting may undo benefits
[Press-News.org] Good parents are predictable -- at least when it comes to cornFor a bigger harvest and faster results: The University of Hohenheim, the MPI for Molecular Plant Physiology and the Leibniz Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research in Gatersleben start a new chapter in plant breeding