(Press-News.org) (Santa Barbara, Calif.) –– Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) on the nanoscale and the ever-elusive quantum computer are among the advancements edging closer toward the realm of possibility, and a new study co-authored by a UC Santa Barbara researcher may give both an extra nudge. The findings appear today in Science Express, an online version of the journal Science.
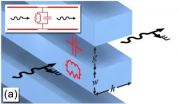
Ania Bleszynski Jayich, an assistant professor of physics who joined the UCSB faculty in 2010, spent a year at Harvard working on an experiment that coupled nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond to nanomechanical resonators. That project is the basis for the new paper, "Coherent sensing of a mechanical resonator with a single spin qubit."
A nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center is a specific defect in diamond that exhibits a quantum magnetic behavior known as spin. When a single spin in diamond is coupled with a magnetic mechanical resonator –– a device used to generate or select specific frequencies –– it points toward the potential for a new nanoscale sensing technique with implications for biology and technology, Jayich explained.
Among those possible future applications of such a technique is magnetic resonance imaging on a scale small enough to image the structure of proteins –– an as-yet unaccomplished feat that Jayich called "one of the holy grails of structural biology."
"The same physics that will allow the NV center to detect the magnetic field of the resonator, hopefully, will allow MRI on the nanoscale," Jayich said. "It could make MRI more accurate, and able to see more. It's like having a camera with eight megapixels versus one with two megapixels and taking a picture of someone's face. You can't see features that are smaller than the size of a pixel. So do they have three freckles, or do they all look like one big freckle?
"That's the idea," Jayich continued. "To resolve individual freckles, so to speak, to see what a protein is made up of. What we found in this paper suggests that it is possible, although a significant amount of work still needs to be done."
Though further into the future based on the approach used for this paper, Jayich said, there is also the potential for such a coupling to be advanced and exploited as a possible route toward the development of a hybrid quantum system, or quantum computer.
INFORMATION:
Jayich collaborated on the project with researchers Shimon Kolkowitz, Quirin Unterreithmeier, Steven Bennett, and Mikhail Lukin, all from Harvard; Peter Rabl, from the Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information of the Austrian Academy of Science; and J.G.E. Harris, from Yale. The work was supported in part by the National Science Foundation, the Center for Ultracold Atoms, and the Packard Foundation.
UC Santa Barbara researcher's new study may lead to MRIs on a nanoscale
2012-02-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New York Civil Rights Violation Lawyer from The Perecman Firm Comments on NYPD Killing of Unarmed Teen
2012-02-24
The funeral service of 18-year-old Ramarley Graham was held at a Bronx church on Saturday, reported WNYC (2/18/2012). The Bronx teen was gunned down by police inside his home in early February.
New York civil rights violation lawyer David Perecman agrees with a number of mourners that the killing appeared to be unjustified.
According to the New York Daily News (2/18/2012), Graham was killed by an officer from the NYPD's narcotics unit who believed he spotted a gun in Graham's waistband and followed him to his family's apartment. Graham was shot in the bathroom after ...
Mechanism behind capacitor's high-speed energy storage discovered
2012-02-24
Researchers at North Carolina State University have discovered the means by which a polymer known as PVDF enables capacitors to store and release large amounts of energy quickly. Their findings could lead to much more powerful and efficient electric cars.
Capacitors are like batteries in that they store and release energy. However, capacitors use separated electrical charges, rather than chemical reactions, to store energy. The charged particles enable energy to be stored and released very quickly. Imagine an electric vehicle that can accelerate from zero to 60 miles ...
New York Auto Accident Lawyer from The Perecman Firm Comments on Wrongful Death After Boy Killed When Driver Failed to Yield Right-of-Way
2012-02-24
A 6-year-old boy died in a two-car accident in upstate New York on Saturday night, reported The Wall Street Journal (2/19/2012).
Tyler McIntyre was killed when a 2008 Mercury failed to yield the right of way to another vehicle at an intersection in the town of Milton, said the YNN Hudson Valley (2/19/2012).
The boy died several hours after the upstate New York auto accident. The other people involved in the auto accident were treated for non-life threatening injuries and there was no indication alcohol was involved, according to the WSJ.
"Having an experienced ...
Penn researchers build first physical 'metatronic' circuit
2012-02-24
PHILADELPHIA -- The technological world of the 21st century owes a tremendous amount to advances in electrical engineering, specifically, the ability to finely control the flow of electrical charges using increasingly small and complicated circuits. And while those electrical advances continue to race ahead, researchers at the University of Pennsylvania are pushing circuitry forward in a different way, by replacing electricity with light.
"Looking at the success of electronics over the last century, I have always wondered why we should be limited to electric current in ...
SEAT Reveals the New Five Door Mii City Car
2012-02-24
SEAT is revealing an expansion to the Mii city car line-up with the first glimpse of an even more versatile five-door version.
The additional rear doors turn the super-compact SEAT into a unique combination of exceptional driving fun, sporty design and outstanding functionality.
Of course the new five-door Mii remains true to core SEAT principles - meaning it's both a pleasure to drive, and a pleasure to own.
In either three- or five-door form the Mii scores top marks for fuel consumption and emissions thanks to its lightweight design and efficient drivetrains. ...
Genome sequencing finds unknown cause of epilepsy
2012-02-24
Only 10 years ago, deciphering the genetic information from one individual in a matter of weeks to find a certain disease-causing genetic mutation would have been written off as science fiction.
It was the time of the Human Genome Project, and it had taken armies of sequencing robots working around the clock for almost a decade to unravel the complete sequence of the human genetic code – referred to as the genome – by churning out the DNA alphabet letter by letter.
Now a team headed by Michael Hammer from the University of Arizona applied Next Generation Genome Sequencing ...
HotRussianBrides.com and RussianLoveMatch.com to Stream Live Beauty Pageant from Odessa, Ukraine on February 25
2012-02-24
Russian dating websites HotRussianBrides.com and RussianLoveMatch.com announced that both will live stream "Precious Pearl", a beauty pageant taking place in Odessa, Ukraine on February 25, 2012 at approximately 12:30pm Eastern Time.
Complete with choreographed dance numbers, a talent segment, and a fashion segment, the pageant will feature single Ukrainian women from around the country, all vying to be crowned Miss Precious Pearl. The event is coordinated by a local dating agency affiliate based in Odessa with branches all over Ukraine. This is the second ...
Naked mole-rats bear lifesaving clues
2012-02-24
Could blind, buck-toothed, finger-sized naked mole-rats harbor in their brain cells a survival secret that might lead to better heart attack or stroke treatments?
University of Illinois at Chicago biologist Thomas Park and colleagues at UIC and the University of Texas Heath Science Center at San Antonio think the subterranean lifestyle of the pasty-looking rodents may indeed hold clues to keeping brain cells alive and functioning when oxygen is scarce. The key may lie in how brain cells regulate their intake of calcium.
"Normally, calcium in brain cells does wonderful ...
A rainbow for the palm of your hand
2012-02-24
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- University at Buffalo engineers have developed a one-step, low-cost method to fabricate a polymer with extraordinary properties: When viewed from a single perspective, the polymer is rainbow-colored, reflecting many different wavelengths of light.
Used as a filter for light, this material could form the basis of handheld multispectral imaging devices that identify the "true color" of objects examined. An image of the material is available here: http://www.buffalo.edu/news/13214.
"Such portable technology could have applications in a wide range of fields, ...
Track and Field News: Felix Sanchez Sets Indoor World Record in Two Consecutive Races
2012-02-24
Felix Sanchez (also known as El Super Sanchez) is one of the most decorated 400m Hurdlers in history. To his name, he already has an Olympic Gold Medal, 2 Outdoor World Championships, 2 Pan American Championships and numerous other accolades. This past week, the 34 year old Sanchez made history again by breaking the Indoor World Record in two consecutive races by nearly half a second in each race.
The previous World Record of 49.73 seconds was set in 2010 by Sanchez as well. On February 4th, Sanchez competed in Mondeville, France, finishing his race in 49.25 seconds, ...