(Press-News.org) Scientists at University College Dublin have discovered a new way of measuring the potential success rate of an embryo before it is transferred back into the womb during in vitro fertilisation (IVF).
According to the findings published online in the journal Fertility and Sterility, the fluid within a woman's ovaries that surrounds the egg or oocyte holds metabolic information that can improve predictions on which embryo is more likely to lead to pregnancy.
"We analysed samples of the follicular fluid surrounding the immature ovum or egg before it was retrieved for IVF," says Dr Lorraine Brennan, UCD Conway Institute, University College Dublin, Ireland.
"We identified clear metabolic differences between the follicular fluids from women who successfully achieved pregnancy as a result of IVF to the fluids from the women who did not."
"Before the test can be regularised for use during IVF, our results need to be validated across a larger cohort of women undergoing treatment, and we are hopeful that the results obtained from larger samples will support our initial findings," says Dr Brennan.
Today, approximately 32% of IVF cycles result in pregnancy, so the standard procedure involves the transfer of multiple embryos back into the womb to increase the potential success rate.
But when more than one embryo is transferred back, there is an increased chance of multiple births like twins and triplets.
There are increased health risks associated with multiple pregnancies for both mother and infants including an increased risk of miscarriages and preterm labour, leading to premature infants with admission to neonatal intensive care.
"In more recent years there has been an increase in the number of single embryo transfer (SET) as an effective way of reducing potential multiple births, but the widespread acceptance of SET is limited because there is no fully accurate method of embryo assessment and selection for transfer during IVF cycles."
"At the Merrion Fertility Clinic we are committed to maintaining a high pregnancy rate while minimising multiple pregnancies. This study forms part of our ongoing research into improving means of selecting the best single embryo to transfer in an IVF cycle", said Dr Mary Wingfield, Medical Director of Merrion Fertility Clinic, Dublin, Ireland.
The research involved almost 60 IVF patients. It was conducted by a team of scientists from University College Dublin, Ireland, and the Merrion Fertility Clinic, Dublin (a not-for-profit clinic linked with The National Maternity Hospital in Holles Street, Dublin, Ireland).
INFORMATION: Funding was received from the Irish Research Council for Science, Engineering & Technology (IRCSET).
END
By means of cloud computing, enterprises can access scalable computing power and storage capacity. A people cloud, by contrast, supplies a scalable number of workers via the internet. It is used when non-automated tasks are executed, such as allocating images, searching information, or writing texts. The challenge is to maintain the quality of the work results on a constant high level. Now, this is achieved by a quality management system developed by KIT.
Also in times of constantly increasing computing power, people are indispensable for executing certain tasks. Such ...
Children involved in bullying – as both a victim and a bully – are three times more likely to have suicidal thoughts by the time they reach 11 years old, according to research from the University of Warwick.
In a paper published in the latest issue of the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, the researchers found children who are both victims and bullies ('bully-victims'), are at highly increased risk of considering suicide, or have planned and engaged in suicidal or self-harming behaviour by 11-12 years of age. These increased odds were ...
Three of the world's subspecies of tigers are now extinct. A new study found that the Sumatran tiger subspecies is nearing extinction as a result of human activities, particularly the conversion of natural forests into forestry and agricultural plantations, leading to habitat loss.
The study, conducted by Virginia Tech and World Wildlife Fund (WWF), is the first of its kind to systematically investigate the use of different land cover types — not just forests but also plantation areas — for tiger habitat.
Published in the Public Library of Science's online journal PLoS ...
SALT LAKE CITY — A team of global scientists, led by researchers at Intermountain Medical Center in Salt Lake City, has developed a safer and more accurate way to administer warfarin, one of the most commonly prescribed but also potentially dangerous medications in the United States.
As part of a worldwide study, the research team developed and tested a new formula that combines individual genetic data with a mathematical model to help physicians more accurately predict patient response to the popular blood-thinning drug.
Researchers found that the formula was safer ...
For more than four decades, a drug called diethylstilbestrol (DES) was prescribed to millions of expecting mothers in an effort to prevent miscarriages. Prescriptions for the drug were written until 1971, when researchers discovered a link between prenatal exposure to DES and the development of reproductive tract cancers. Notably, researchers discovered health issues of developing breast cancer not only in the expecting mothers themselves, but also in their daughters decades later after being exposed to DES in utero. These victims have come to be known as the DES daughters.
As ...
New York, February 29, 2012 – A revealing study published in Epilepsy & Behavior provides evidence that the perception of epilepsy is not faring well in social media. Kate McNeil and colleagues from Dalhousie University in Canada analyzed data collected from Twitter to provide a snapshot of how epilepsy is portrayed within the twitter community.
Twitter, a social networking platform launched in 2006, allows its users to communicate through posting of "tweets" limited to 140 characters. Twitter has gained worldwide popularity since its inception, with approximately 110 ...
Wild bees are important pollinators and numerous studies dealing with pollination of wild plants and crops underline their vital role in ecosystems functioning. While honey bees can be easily transported to various location when needed, wild bees' presence is dependent on the availability of high quality semi-natural habitats. Some crops, such as apples and cherries, and many wild flowers are more effectively pollinated by wild bees and other insects rather than managed honey bees.
Although heavy metal pollution is recognized to be a problem affecting large parts of the ...
Researchers from the Mayo Clinic confirm that ultrasound-based transient elastography (TE) provides excellent diagnostic accuracy for detecting cirrhosis due to recurrent infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection following liver transplantation. Findings from the study published in the March issue of Liver Transplantation, a journal of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, suggest that detection of significant fibrosis is more accurate when comparing patients with chronic HCV of the native liver.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), ...
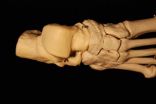
Law enforcement officials who are tasked with identifying a body based on partial skeletal remains have a new tool at their disposal. A new paper from North Carolina State University researchers details how to determine the biological sex of skeletal remains based solely on measurements of the seven tarsal bones in the feet.
"Tarsals are fairly dense bones, and can be more durable than other bones – such as the pelvis – that are used to determine biological sex," says Dr. Troy Case, an associate professor of anthropology at NC State and co-author of a paper describing ...
As the baby boomer generation grows older, decisions related to selling the family home and moving, in order to provide aging family members with additional care, will become increasingly important for many American families. For some, this decision will focus on two alternative housing options in particular: assisted living facilities and nursing homes. There are advantages and disadvantages to both types of housing, though both are governed by sets of laws that protect residents and ensure their proper care.
Nursing homes have gained a bad reputation over the past ...