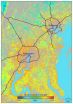
(Press-News.org) If you've been thinking our world is more green than frozen these days, you're right. A recent study has found that spring is indeed arriving earlier – and autumn later – in the suburbs of Baltimore and Washington, D.C. The reason? The urban landscape traps heat in the summer and holds it throughout the winter, triggering leaves to turn green earlier in the spring and to stay green later into autumn. The result is a new, extended growing season.
Scientists used high-resolution satellite data collected over the past 25 years to look at the number days that trees have green leaves in the forests of the Mid-Atlantic. The study found that urban heat islands affected the growing season in areas within 20 miles of the city. As a result, gardeners may have more time to grow their vegetables and plant new varieties.
The longer growing season also has a profound impact on forests. Forests are, in effect, the world's air filters. Green leaves on trees turn carbon dioxide – a greenhouse gas that traps heat in our atmosphere – into oxygen. Carbon dioxide also helps trees grow since they use energy from the sun to convert the gas into plant matter. A longer growing season could change quickly forests grow and increase the amount of carbon dioxide taken out of the atmosphere.
"Everything changes when the leaves turn green," said the study's lead author Dr. Andrew Elmore of the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science. "Trees start pumping water into the atmosphere. They take carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere. They make sugars and build plant tissue. It's as if the entire landscape goes from exhaling to inhaling."
The study also pinpointed other factors that influence the timing of spring and autumn in areas outside the influence of urban heat islands, including the elevation of the landscape, proximity to tidal water, and cold air drainage in small valleys.
Not all forests are the same, however, and predicting which forests will grow faster during a longer growing season requires detailed satellite measurements. This study is the first to apply high-resolution satellite data to the problem. "We are trying to understand how forests function so we can understand how they might respond to global warming," said Dr. Elmore. "With more detailed data, we can do better job of predicting what might happen to a forest impacted by urbanization, for instance."
INFORMATION:
The study, "Landscape controls on the timing of spring, autumn, and growing season length in mid-Atlantic forests," was published in the February issue of Global Change Biology by Andrew Elmore and Steven Guinn of the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science, Burke Minsley of the U.S. Geological Survey, and Andrew Richardson of Harvard University.
PHOTOGRAPHY AVAILABLE UPON REQUEST.
UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND CENTER FOR ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE
The University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science unleashes the power of science to transform the way society understands and manages the environment. By conducting cutting-edge research into today's most pressing environmental problems, we are developing new ideas to help guide our state, nation, and world toward a more environmentally sustainable future through five research centers—the Appalachian Laboratory in Frostburg, the Chesapeake Biological Laboratory in Solomons, the Horn Point Laboratory in Cambridge, the Institute of Marine and Environmental Technology in Baltimore, and the Maryland Sea Grant College in College Park. www.umces.edu
Mid-Atlantic suburbs can expect an early spring thanks to the heat of the big city
2012-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
LA BioMed investigator, Dr. Rowan Chlebowski, co-authors study on menopausal hormone therapy
2012-03-12
LOS ANGELES (March 9, 2012) – Rowan T. Chlebowski, M.D., Ph.D., an LA BioMed investigator whose research activities have focused on breast cancer therapy and prevention, and chronic diseases impacting women's health, is co-author of a study that indicates that women who use the estrogen-only form of menopausal hormone therapy appear less likely to develop breast cancer in the longer term, according to new research which was recently published The Lancet Oncology.
A follow-up study of over 7,500 women from the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) trial who took estrogen for ...
Health monitoring? There's an app for that
2012-03-12
Researchers in New Zealand have developed a prototype Bluetooth-enabled medical monitoring device that can be connected wirelessly to your smart phone and keep track of various physiological parameters, such as body temperature, heart rate, blood pressure and movements. The prototype could be extended to include sensors for other factors such as blood glucose as well as markers for specific diseases. The connectivity would allow patients to send data directly to their healthcare provider and receive timely advice and medication suggestions.
Writing in the International ...
Environmentally friendly cleaning and washing
2012-03-12
Detergents are everywhere – in washing powders, dishwashing liquids, household cleaners, skin creams, shower gels, and shampoos. It is the detergent that loosens dirt and fat, makes hair-washing products foam up and allows creams to be absorbed quickly. Up until now, most detergents are manufactured from crude oil – a fossil fuel of which there is only a limited supply. In their search for alternatives, producers are turning increasingly to detergents made from sustainable resources, albeit that these surfactants are usually chemically produced. The problem is that the ...
TacSat-4 enables polar region SatCom experiment
2012-03-12
WASHINGTON -- The U.S. Coast Guard Cutter HEALY (WAGB 20) successfully experimented with NRL's TacSat-4 communications satellite, Jan. 24, by communicating from the Bering Sea off the western coast of Alaska to Coast Guard Island, Alameda, Calif.
Returning from an escort and icebreaking mission to Nome, Alaska, assisting the Russian tanker Renda delivery of emergency fuel to the town, USCGC HEALY — Coast Guard's only polar icebreaker — was approximately 260 nautical miles south of the Arctic Circle at the time of the test.
Deployed into a unique, highly elliptical ...
Mapping the Moho with GOCE
2012-03-12
The first global high-resolution map of the boundary between Earth's crust and mantle – the Moho – has been produced based on data from ESA's GOCE gravity satellite. Understanding the Moho will offer new clues into the dynamics of Earth's interior.
Earth's crust is the outermost solid shell of our planet. Even though it makes up less than 1% of the volume of the planet, the crust is exceptionally important not just because we live on it, but because is the place where all our geological resources like natural gas, oil and minerals come from.
The crust and upper mantle ...
Meteorites reveal another way to make life's components
2012-03-12
Creating some of life's building blocks in space may be a bit like making a sandwich – you can make them cold or hot, according to new NASA research. This evidence that there is more than one way to make crucial components of life increases the likelihood that life emerged elsewhere in the Universe, according to the research team, and gives support to the theory that a "kit" of ready-made parts created in space and delivered to Earth by impacts from meteorites and comets assisted the origin of life.
In the study, scientists with the Astrobiology Analytical Laboratory ...
Infection control certification associated with lower MRSA infection rates
2012-03-12
Washington, DC, March 9, 2012 -- Hospitals whose infection prevention and control programs are led by a director who is board certified in infection prevention and control have significantly lower rates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bloodstream infections (BSI) than those that are not led by a certified professional, according to a new study published in the March issue of the American Journal of Infection Control, the official publication of APIC - the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology.
A team of researchers ...
Orientation of desert ants: Every cue counts
2012-03-12
Desert ants have adapted to a life in a barren environment which only provides very few landmarks for orientation. Apart from visual cues and odors the ants use the polarized sunlight as a compass and count their steps in order to return safely to their home after searching for food. In experiments with ants of the genus Cataglyphis in their natural habitats in Tunisia and Turkey, behavioral scientists of the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology in Jena, Germany, have now discovered that ants can also use magnetic and vibrational landmarks in order to find their way ...
Researchers 'print' polymers that bend into 3-D shapes
2012-03-12
Christian Santangelo, Ryan Hayward and colleagues at the University of Massachusetts Amherst recently employed photographic techniques and polymer science to develop a new technique for printing two-dimensional sheets of polymers that can fold into three-dimensional shapes when water is added. The technique may lead to wide ranging practical applications from medicine to robotics
The journal Science publishes the research in its March 9 issue.
Researchers used a photomask and ultraviolet (UV) light to "print" a pattern onto a sheet of polymers, a technique called photolithography. ...
Genetic marker for painful food allergy points to improved diagnosis, treatment
2012-03-12
Researchers have identified a genetic signature for a severe, often painful food allergy – eosinophilic esophagitis – that could lead to improved diagnosis and treatment for children unable to eat a wide variety of foods.
The scientists, from Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, report in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology that they have pinpointed a dysregulated microRNA signature for eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), a disease that also may cause weight loss, vomiting, heartburn and swallowing difficulties.
Interestingly, the dysregulated microRNA ...