(Press-News.org) People whose blood pressure drops rapidly when they move from lying down to standing, known as orthostatic hypotension, may have a higher risk of developing heart failure, according to research published in Hypertension, an American Heart Association journal.
The link between orthostatic hypotension and heart failure was stronger in people 45-55 years old compared to those 56-64, researchers said. High blood pressure, which was present in over half of people who developed heart failure, may be partially responsible for the association.
Over an average 17.5 years of follow-up, researchers looked at the association between orthostatic hypotension and developing heart failure. They measured patients' blood pressure while lying down and shortly after standing up.
They defined orthostatic hypotension as a decrease of 20 points or more in the systolic (top number) or a decrease of 10 or more points in the diastolic (bottom number) blood pressure measurements.
The researchers, who based the definition of heart failure on either hospital admission or death certificate diagnoses, found:
About 11 percent of patients who developed heart failure had orthostatic hypotension at the start of the study, compared with only 4 percent of those who did not develop heart failure.
People with orthostatic hypotension had 1.54 times the risk of developing heart failure than those without orthostatic hypotension; however, after excluding those with high blood pressure, the risk fell to 1.34 times.
"Orthostatic hypotension appears to be related to the development of heart failure along with other conditions known to cause heart failure," said Christine DeLong Jones, M.D., study lead author and preventive medicine resident at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
"Hypertension, diabetes and coronary heart disease are already known to contribute to a person's risk of developing heart failure. Orthostatic blood pressure measurement may supplement what is already known about the risk for heart failure and requires no additional equipment, just a standard blood pressure cuff."
Researchers found that even when adjusting for existing diseases, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and coronary heart disease, participants with orthostatic hypotension at the start of the study were still more likely to develop heart failure than those without it.
The study is the first of its kind to include both Caucasian and African-Americans. Prior studies in Europe included mostly Caucasians.
"The association of orthostatic hypotension with heart failure did not vary greatly when we compared white and African-American participants," Jones said.
Study participants were part of the Atherosclerosis Risk In Communities (ARIC) Study, an ongoing longitudinal study of men and women in communities throughout the United States.
Heart failure, which affects about 5.7 million people in the United States and caused over 281,000 deaths in 2008, cost the healthcare system about $34.4 billion in 2010, according to the American Heart Association.
The disease occurs when the heart pumps inefficiently, which results in inadequate delivery of blood to the body's cells and organs. Discovering factors that may predict heart failure is important to preventing the disease, Jones said.
INFORMATION:
The National Heart, Blood, and Lung Institute funded the study.
Co-authors are: Christine DeLong Jones, M.D., M.S.; Laura Loehr, M.D., Ph.D.; Nora Franceschini, M.D., M.P.H.; Wayne D. Rosamond, Ph.D.; Patricia P. Chang, M.D., M.H.S; Eyal Shahar, M.D.; David J. Couper, Ph.D.; and Kathryn M. Rose, Ph.D. Author disclosures and sources of funding are on the manuscript.
Statements and conclusions of study authors published in American Heart Association scientific journals are solely those of the study authors and do not necessarily reflect the association's policy or position. The association makes no representation or guarantee as to their accuracy or reliability. The association receives funding primarily from individuals; foundations and corporations (including pharmaceutical, device manufacturers and other companies) also make donations and fund specific association programs and events. The association has strict policies to prevent these relationships from influencing the science content. Revenues from pharmaceutical and device corporations are available at http://www. heart.org/corporatefunding.
NR12 – 1050 (Hyper/Jones)
Additional Resources:
Learn more about heart failure, http://www.heart.org/heartfailure.
How to talk to your doctor about heart failure.
Learn more about Target: Heart Failure and Get With The Guidelines, http://www.heart.org/quality.
Watch an animation of heart failure compared to the healthy heart.
Sudden blood pressure drop with position change linked to higher risk of heart failure
2012-03-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
JCI early table of contents for March 19, 2012
2012-03-20
EDITOR'S PICK
A clearer understanding of glaucoma | Back to top
Glaucoma is one of the leading causes of vision loss and blindness worldwide. In glaucoma patients, the optic nerve, which relays information from the eye to the brain, is damaged, though the molecular cause of nerve damage is unclear. Dr. Simon John, from Tufts University in Boston, and colleagues specifically wanted to understand the earliest events that lead to optic nerve damage in glaucoma. Using a mouse model of the disease, the researchers showed that inflammatory immune cells called monocytes cross ...
Trauma drives HIV epidemic in women
2012-03-20
Physical violence, sexual abuse and other forms of childhood and adult trauma are major factors fueling the epidemic of HIV/AIDS among American women. Scientists have known for years that traumatized women are at greater risk of becoming infected.
Now, two new studies from the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) and Harvard Medical School demonstrate that a high rate of trauma among women already infected with HIV also plays a role in the epidemic.
Described in back-to-back papers in the journal AIDS and Behavior, the new work demonstrates that women with ...
A clearer understanding of glaucoma
2012-03-20
Glaucoma is one of the leading causes of vision loss and blindness worldwide. In glaucoma patients, the optic nerve, which relays information from the eye to the brain, is damaged, though the molecular cause of nerve damage is unclear. Dr. Simon John, from Tufts University in Boston, and colleagues specifically wanted to understand the earliest events that lead to optic nerve damage in glaucoma. Using a mouse model of the disease, the researchers showed that inflammatory immune cells called monocytes cross blood vessels and invade the optic nerve. Remarkably, mice treated ...
Open surgical and minimally invasive hernia repair techniques compared
2012-03-20
CHICAGO – The minimally invasive hernia repair procedure known as total extraperitoneal inguinal hernioplasty (TEP) was associated with higher patient satisfaction, less chronic pain and less impairment of inguinal (groin) sensation compared to the open surgical Lichtenstein repair, according to a study published in the March issue of Archives of Surgery, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
Chronic pain and hypoesthesia (reduced sensitivity) are increasingly measured after inguinal hernia repair but few randomized clinical trials have compared TEP with Lichtenstein repair, ...
Clinical trial examines antioxidant effects for Alzheimer's disease on cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers
2012-03-20
CHICAGO – An antioxidant combination of vitamin E, vitamin C and α-lipoic acid (E/C/ALA) was not associated with changes in some cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers related to Alzheimer disease in a randomized controlled trial, according to a study published Online First by Archives of Neurology, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
Oxidative damage in the brain is associated with aging and is widespread in Alzheimer disease (AD) patients. Some observational studies have suggested that an antioxidant-rich diet may reduce the risk of AD, but antioxidant randomized clinical ...
Review of multilevel surgery in patients with obstructive sleep apnea
2012-03-20
CHICAGO – Patients with obstructive sleep apnea who undergo surgery for their condition should be closely monitored after their procedures are performed but may not need to be in an intensive care unit, according to a report published Online First by Archives of Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
Surgical procedures in patients with sleep apnea (a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing) have traditionally been considered dangerous and potentially life threatening if not monitored with caution because these patients are ...
Spotting ancient sites, from space
2012-03-20
A Harvard archaeologist has dramatically simplified the process of finding early human settlements by using computers to scour satellite images for the tell-tale clues of human habitation, and in the process uncovered thousands of new sites that might reveal clues to the earliest complex human societies.
As described in a paper published March 19 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Jason Ur, the John L. Loeb Associate Professor of the Social Sciences, worked with Bjoern Menze, a research affiliate in MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence ...
Sanford-Burnham scientists unravel cancer drug's secret to resistance
2012-03-20
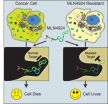
LA JOLLA, Calif., March 19, 2012 – Drug resistance is a serious problem for cancer patients—over time, a therapy that was once providing some benefit simply stops working. Scientists at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute (Sanford-Burnham) recently discovered how cancer cells develop resistance to a drug called MLN4924. This experimental therapy is currently being tested in a number of Phase I and Phase I/II clinical trials to determine its efficacy against several different types of cancer, including multiple myeloma, leukemia, and lymphoma.
Published online March ...
Solving the mystery of blood clotting
2012-03-20
How and when our blood clots is one of those incredibly complex and important processes in our body that we rarely think about. If your blood doesn't clot and you cut yourself, you could bleed to death, if your blood clots too much, you could be in line for a heart attack or stroke. Dr. Hans Vogel, a professor at the University of Calgary, has thought a lot about blot clotting and recently published research in the prestigious Journal of the American Chemical Society that helps to better understand the clotting process.
Vogel and his graduate student Hao Huang were able ...
Smell is a symphony
2012-03-20
Just like a road atlas faithfully maps real-word locations, our brain maps many aspects of our physical world: Sensory inputs from our fingers are mapped next to each other in the somatosensory cortex; the auditory system is organized by sound frequency; and the various tastes are signaled in different parts of the gustatory cortex.
The olfactory system was believed to map similarly, where groups of chemically related odorants - amines, ketones, or esters, for example - register with clusters of cells that are laid out next to each other.
When researchers at the Stowers ...