(Press-News.org) BOSTON – Contrary to popular perception, a large proportion of obese Americans can and do lose weight, say researchers at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center. What's more, they say, the old tried and true methods of eating less fat and exercising are some of the most effective paths to weight loss success.
The research results appear in the April 10 online issue of the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
"This is great news because studies have shown that even a 5 percent reduction in weight can lead to improved health," says lead author Jacinda M. Nicklas, MD, MPH, MA, a clinical research fellow at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School. "With more than a third of Americans now obese and fifty to seventy percent of them trying to lose weight, this is important because the health risks associated with carrying that extra weight are substantial."
Nicklas and colleagues analyzed data from more than 4,000 obese individuals culled from the 2001-2006 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to assess the health and nutritional status of adults in the United States.
Individuals included in the study were over 20 years of age with a body mass index of 30 or more 12 months prior to the interview.
Of those surveyed, 2,523 individuals reported trying to lose weight. Forty percent of these said they experienced weight loss of 5 percent or greater, and another 20 percent lost 10 percent or more.
"Those who exercised more and ate less fat were significantly more likely to lose weight," say the authors. "Additionally we found a correlation between joining weight loss programs and greater reported weight loss, which may speak to the importance of structure in a weight loss regimen" says Nicklas. And while those who used prescription weight loss medications also reported weight loss success, this represented only a small number of study participants.
In contrast, the authors found that, "self-reported use of popular diets, liquid diets, nonprescription weight loss pills and diet foods/products were not associated with weight loss."
"It's very encouraging to find that the most of the weight loss methods associated with success are accessible and inexpensive," says senior author Christina Wee, MD, MPH who conducts research on obesity and health disparities as the Co-Director of Research in BIDMC's Division of General Medicine and Primary Care. "There are lots of fad diets out there as well as expensive over-the-counter medications that have not necessarily been proven to be effective, and it is important that Americans discuss product claims with their doctor before trying such products."
This study did not look at the long-term impact of these interventions on an individual's ability to keep the weight off. The authors suggest that future research is needed to identify and address barriers to maintaining weight loss.
###
Other authors include Karen W. Huskey, MPH and Roger B. Davis, ScD both of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center is a patient care, teaching and research affiliate of Harvard Medical School, and currently ranks third in National Institutes of Health funding among independent hospitals nationwide. BIDMC is clinically affiliated with the Joslin Diabetes Center and is a research partner of Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center. BIDMC is the official hospital of the Boston Red Sox. For more information, visit www.bidmc.org.
More exercise, eating less fat and weight loss programs are in, popular diets are out
Strategies identified for successful weight loss among Americans who are obese
2012-04-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers identify successful strategies for weight loss in the obese
2012-04-10
San Diego, CA, April 10, 2012 – A third of Americans are now obese, and up to 70% of them are trying to lose weight. In a new study published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, researchers from Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston have found in a nationally representative sample that obese dieters who said they ate less fat, exercised more, and used prescription weight loss medications were more likely to lose weight. Diet foods and products, nonprescription diet pills, and popular diets were less successful, according ...
Frequent dental X-rays linked to most common brain tumor
2012-04-10
People who received frequent dental x-rays in the past have an increased risk of developing the most commonly diagnosed primary brain tumor in the United States. That is the finding of a study published early online in Cancer, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society. Although dental x-rays are necessary in many cases, these findings suggest that moderate use of this form of imaging may be of benefit to some patients.
Ionizing radiation is the primary environmental risk factor for developing meningioma, which is the most frequently diagnosed primary brain ...
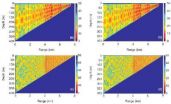
An efficient method for solving sound propagation in range-dependent ocean waveguides was found
2012-04-10
The coupled normal mode method is a powerful approach for solving range-dependent propagation problems in underwater acoustics. An important area of study is to improve stability and efficiency so as to be able to deal with complex scenarios in a realistic environment. Professor LUO Wenyu and his group from the State Key Laboratory of Acoustics, Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, set out to tackle this problem. After several years of innovative research, they have developed an accurate, efficient, and numerically stable coupled normal mode method to solve ...
Healthcare's Elite to Meet and Compete for Inaugural National Championship
2012-04-10
The Pharmaceutical Education and Research Institute (PERI) and PeerParty are pleased to announce the inaugural CME National Championship for the healthcare community. The Championship introduces a new approach to continuing education for healthcare practitioners - a fun, collaborative approach that rewards participants for learning and building their professional networks. This innovative approach employs a number of new techniques to challenge and reward participants, with the goal of positively affecting knowledge-sharing, learning and most importantly, improving patient ...
Mechanical properties and microstructure of cranial and beak bones of the woodpecker and the lark
2012-04-10
The bio-mechanisms of the woodpecker's resistance to head impact injury are an interesting scientific question. Professor FAN Yubo and his group from the Key Laboratory for Biomechanics and Mechanobiology of the Ministry of Education, School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, and the School of Materials Science and Engineering, Wuhan University of Technology, set out to study this problem. After 3 years of innovative research, they are making progress in uncovering the explanation for the avoidance of head impact injury by woodpeckers. Their ...
Geographic information systems demonstrate links between health and location
2012-04-10
San Diego, CA, April 10, 2012 – The neighborhoods in which children and adolescents live and spend their time play a role in whether or not they eat a healthy diet, get enough exercise or become obese, concludes a collection of studies in a special theme issue of the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
Each of the six studies uses the latest concepts and methods in geographic information systems (GIS)-based research to determine how the geographic location affects physical health. A study titled "Spatial Classification of Youth Physical Activity Patterns" shows, ...
Mushatt's No.9 Psoriasis Skin Care Donates 2% of Sales Revenue to Support The National Psoriasis Foundation Research Program
2012-04-10
Psoriasis is a non-contagious, genetic disease of the immune system and manifests itself in the skin and/or joints of the body. It affects about 2% of the population or 7,500,000 people in the United States alone. Research is the top priority of The National Psoriasis Foundation, whose efforts are aimed at searching for better treatments and a cure for psoriasis.
"The National Psoriasis Foundation appreciates the dedication of our corporate partners who so willingly support our mission goal of research for a cure," says Eric Kimble, a Board of Trustee of the ...
How many calories does it take to reach childhood obesity prevention goals?
2012-04-10
In order for the nation to achieve goals set by the federal government for reducing obesity rates by 2020, children in the United States would need to eliminate an average of 64 excess calories per day, researchers calculated in a study published today in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine. This reduction could be achieved by decreasing calorie intake, increasing physical activity, or both. Without this reduction, the authors predict that the average U.S. youth would be nearly four pounds heavier than a child or teen of the same age was in 2007-2008, and more than ...
Dental X-rays linked to common brain tumor
2012-04-10
Boston, MA – Meningioma, the most common primary brain tumor in the United States, accounts for about 33 percent of all primary brain tumors. The most consistently identified environmental risk factor for meningioma is exposure to ionizing radiation. In the largest study of its kind, researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH), Yale University School of Medicine, Duke University, UCSF and Baylor College of Medicine have found a correlation between past frequent dental x-rays, which are the most common source of exposure to ionizing radiation in the U.S, and an ...
UBC president helps identify key steps to respond to growing Asia Pacific research strengths
2012-04-10
The most dramatic new developments in science are taking place among nations in the Asia-Pacific and the phenomenon is changing the dynamic of science around the globe, according to three science and academic leaders from the U.S., Canada and Singapore.
In an article published in the current issue of the journal Science, University of British Columbia President Stephen J. Toope, National University of Singapore President Chorh Chuan Tan and the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) Board Chair Nina V. Fedoroff cite a Royal Society report that shows ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How Japanese medical trainees view artificial intelligence in medicine
MambaAlign fusion framework for detecting defects missed by inspection systems
Children born with upper limb difference show the incredible adaptability of the young brain
How bacteria can reclaim lost energy, nutrients, and clean water from wastewater
Fast-paced lives demand faster vision: ecology shapes how “quickly” animals see time
Global warming and heat stress risk close in on the Tour de France
New technology reveals hidden DNA scaffolding built before life ‘switches on’
New study reveals early healthy eating shapes lifelong brain health
Trashing cancer’s ‘undruggable’ proteins
Industrial research labs were invented in Europe but made the U.S. a tech superpower
Enzymes work as Maxwell's demon by using memory stored as motion
Methane’s missing emissions: The underestimated impact of small sources
Beating cancer by eating cancer
How sleep disruption impairs social memory: Oxytocin circuits reveal mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities
Natural compound from pomegranate leaves disrupts disease-causing amyloid
A depression treatment that once took eight weeks may work just as well in one
New study calls for personalized, tiered approach to postpartum care
The hidden breath of cities: Why we need to look closer at public fountains
Rewetting peatlands could unlock more effective carbon removal using biochar
Microplastics discovered in prostate tumors
ACES marks 150 years of the Morrow Plots, our nation's oldest research field
Physicists open door to future, hyper-efficient ‘orbitronic’ devices
$80 million supports research into exceptional longevity
Why the planet doesn’t dry out together: scientists solve a global climate puzzle
Global greening: The Earth’s green wave is shifting
You don't need to be very altruistic to stop an epidemic
Signs on Stone Age objects: Precursor to written language dates back 40,000 years
MIT study reveals climatic fingerprints of wildfires and volcanic eruptions
A shift from the sandlot to the travel team for youth sports
Hair-width LEDs could replace lasers
[Press-News.org] More exercise, eating less fat and weight loss programs are in, popular diets are outStrategies identified for successful weight loss among Americans who are obese