(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Liverpool have resolved the debate over the mechanisms involved in the shut-down process during cell division in the body.
Research findings, published in the journal PNAS, may contribute to future studies on how scientists could manipulate this shut-down process to ensure that viruses and other pathogens do not enter the cells of the body and cause harm.
Previous research has shown that when cells divide, they cannot perform any other task apart from this one. They cannot, for example, take in food and fluids at the same time as managing the important process of dividing into 'daughter cells' to replicate the body's genetic information. Cells, instead, shut-down the intake of food and fluid during cell division and for many years it was thought that they did this by preventing a vehicle - called a receptor - from transporting nutrients through the cell membrane.
In recent years scientists have shown evidence to suggest that this theory may be wrong. Scientists have argued that the cell does not shut down the mechanisms that allow food and fluid to enter the cell as previously thought, but rather the receptors that transport this fuel are absent altogether during cell division, allowing the cell to focus on the one task of dividing.
Studies at Liverpool, however, have now shown that the original theory, first documented in 1965, is accurate. The receptors are present and able to transport food and fluid during cell division, but the mechanism that allows them through the membrane of the cell shuts-down until cell division is complete.
Dr Stephen Royle, from the University's Institute of Translational Medicine, explains: "We know that cells in the body do not have the ability to multi-task during cell division. It can only focus on the job of dividing and not on other important tasks such as uptake of nutrients. If we think of the cell membrane like a dock at a port and the receptors as a boat delivering cargo, we have shown that the boat, or receptor, is present but the dock, or membrane, does not allow it to unload or go any further.
"Viruses and pathogens use the same route into cells as nutrients, so the next stage of this work is to identify the trigger for this shut-down process, so that we understand whether this on/off switch can be manipulated to prevent harmful infections passing through the cell membrane. This is a long way in the future, but this work puts us closer to understanding how the cells in the body work."
###The work was funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC).
Study resolves debate on human cell shut-down process
2012-04-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Multitasking – not so bad for you after all?
2012-04-13
Our obsession with multiple forms of media is not necessarily all bad news, according to a new study by Kelvin Lui and Alan Wong from The Chinese University of Hong Kong. Their work shows that those who frequently use different types of media at the same time appear to be better at integrating information from multiple senses - vision and hearing in this instance - when asked to perform a specific task. This may be due to their experience of spreading their attention to different sources of information while media multitasking. Their study is published online in Springer's ...
New advances in the understanding of cancer progression
2012-04-13
Researchers at the Hospital de Mar Research Institute (IMIM) have discovered that the protein LOXL2 has a function within the cell nucleus thus far unknown. They have also described a new chemical reaction of this protein on histone H3 that would be involved in gene silencing, one of which would be involved in the progression of breast, larynx, lung and skin tumours.
Led by Dr Sandra Peiró and published in Molecular Cell journal, the study is a significant advance in describing the evolution of tumours and opens the door to researching new treatments that block their ...
Genetic adaptation of fat metabolism key to development of human brain
2012-04-13
About 300 000 years ago humans adapted genetically to be able to produce larger amounts of Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids. This adaptation may have been crucial to the development of the unique brain capacity in modern humans. In today's life situation, this genetic adaptation contributes instead to a higher risk of developing disorders like cardiovascular disease.
The human nervous system and brain contain large amounts of polyunsaturated fatty acids, and these are essential for the development and function of the brain. These Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids occur ...
Stem cells 'by default'
2012-04-13
Casanova's notion is that stem cells emerge not because of the presence of factors that confer capacity to the stem cell but because of factors that repress the cellular signals for differentiation and specialization. Casanova believes that somehow all non-differentiated cells intrinsically carry the qualities of the stem cell by default and that there are factors at work that remove these capacities. Said another way: a stem cell is a stem cell because it has evaded differentiation. According to Casanova, if the idea of "a stem cell by default" is considered, research ...
Gulf Coast residents say BP Oil Spill changed their environmental views, UNH research finds
2012-04-13
DURHAM, N.H. -- University of New Hampshire researchers have found that residents of Louisiana and Florida most acutely and directly affected by the BP Deepwater Horizon disaster -- the largest marine oil spill in U.S. history -- said they have changed their views on other environmental issues as a result of the spill.
"If disasters teach any lessons, then experience with the Gulf oil spill might be expected to alter opinions about the need for environmental protection. About one-fourth of our respondents said that as a result of the spill, their views on other environmental ...
Biomarker family found for chemo resistant breast cancers
2012-04-13
Biomarkers which could help to predict resistance to chemotherapy in breast cancer patients have been identified by researchers from the University of Hull, UK.
The researchers found a family of proteins to be twice as prevalent in clinical samples obtained from breast cancer patients who were resistant to chemotherapy than those who were successfully treated.
Chemotherapy resistance is a major problem for some types of breast cancer and many patients undergo treatment that does not work, delaying other more suitable treatments and subjecting the patient to adverse ...
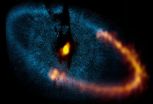
ALMA reveals workings of nearby planetary system
2012-04-13
The discovery was made possible by exceptionally sharp ALMA images of a disc, or ring, of dust orbiting Fomalhaut, which lies about 25 light-years from Earth. It helps resolve a controversy among earlier observers of the system. The ALMA images show that both the inner and outer edges of the thin, dusty disc have very sharp edges. That fact, combined with computer simulations, led the scientists to conclude that the dust particles in the disc are kept within the disc by the gravitational effect of two planets — one closer to the star than the disc and one more distant [1].
Their ...
BMC study shows diverting passengers to elevators could help reduce falls at Logan Airport
2012-04-13
(Boston) – A first of its kind study conducted by researchers at Boston Medical Center (BMC)'s Injury Prevention Center (IPC) found that one fall requiring first responder emergency medical services response occurs, on average, approximately every 56 hours at Boston Logan International Airport, with 37 percent of those incidents involving transport to a hospital. The study, which was done at the request of the Massachusetts Port Authority and Massport Fire/Rescue, concludes that diverting at-risk passengers from escalators to elevators could significantly reduce the number ...
Study finds significant skull differences between closely linked groups
2012-04-13
In order to accurately identify skulls as male or female, forensic anthropologists need to have a good understanding of how the characteristics of male and female skulls differ between populations. A new study from North Carolina State University shows that these differences can be significant, even between populations that are geographically close to one another.
The researchers looked at the skulls of 27 women and 28 men who died in Lisbon, Portugal, between 1880 and 1975. They also evaluated the skulls of 40 women and 39 men who died between 1895 and 1903 in the rural ...
Nowspeed Releases SEO Strategy White Paper
2012-04-13
Nowspeed, a top Internet marketing agency, has released a new search engine optimization (SEO) white paper entitled, How to Build a Winning SEO Strategy, written by President & Founder of Nowspeed, David Reske. The white paper explains how and why it is important for companies to incorporate a search engine optimization strategy to ensure a steady flow of new lead generation prospects.
Businesses will learn the efficiencies of SEO through 8 tips and best practices that will jumpstart your efforts to create a SEO friendly strategy that works. The goals of any SEO ...