(Press-News.org) STANFORD, Calif. — Using tiny solar-panel-like cells surgically placed underneath the retina, scientists at the Stanford University School of Medicine have devised a system that may someday restore sight to people who have lost vision because of certain types of degenerative eye diseases.
This device — a new type of retinal prosthesis — involves a specially designed pair of goggles, which are equipped with a miniature camera and a pocket PC that is designed to process the visual data stream. The resulting images would be displayed on a liquid crystal microdisplay embedded in the goggles, similar to what's used in video goggles for gaming. Unlike the regular video goggles, though, the images would be beamed from the LCD using laser pulses of near-infrared light to a photovoltaic silicon chip — one-third as thin as a strand of hair — implanted beneath the retina.
Electric currents from the photodiodes on the chip would then trigger signals in the retina, which then flow to the brain, enabling a patient to regain vision.
A study, to be published online May 13 in Nature Photonics, discusses how scientists tested the photovoltaic stimulation using the prosthetic device's diode arrays in rat retinas in vitro and how they elicited electric responses, which are widely accepted indicators of visual activity, from retinal cells . The scientists are now testing the system in live rats, taking both physiological and behavioral measurements, and are hoping to find a sponsor to support tests in humans.
"It works like the solar panels on your roof, converting light into electric current," said Daniel Palanker, PhD, associate professor of ophthalmology and one of the paper's senior authors. "But instead of the current flowing to your refrigerator, it flows into your retina." Palanker is also a member of the Hansen Experimental Physics Laboratory at Stanford and of the interdisciplinary Stanford research program, Bio-X. The study's other senior author is Alexander Sher, PhD, of the Santa Cruz Institute of Particle Physics at UC Santa Cruz; its co-first authors are Keith Mathieson, PhD, a visiting scholar in Palanker's lab, and James Loudin, PhD, a postdoctoral scholar. Palanker and Loudin jointly conceived and designed the prosthesis system and the photovoltaic arrays.
There are several other retinal prostheses being developed, and at least two of them are in clinical trials. A device made by the Los Angeles-based company Second Sight was approved in April for use in Europe, and another prosthesis-maker, a German company called Retina Implant AG, announced earlier this month results from its clinical testing in Europe.
Unlike these other devices — which require coils, cables or antennas inside the eye to deliver power and information to the retinal implant — the Stanford device uses near-infrared light to transmit images, thereby avoiding any need for wires and cables, and making the device thin and easily implantable.
"The current implants are very bulky, and the surgery to place the intraocular wiring for receiving, processing and power is difficult," Palanker said. The device developed by his team, he noted, has virtually all of the hardware incorporated externally into the goggles. "The surgeon needs only to create a small pocket beneath the retina and then slip the photovoltaic cells inside it." What's more, one can tile these photovoltaic cells in larger numbers inside the eye to provide a wider field of view than the other systems can offer, he added.
Stanford University holds patents on two technologies used in the system, and Palanker and colleagues would receive royalties from the licensing of these patents.
The proposed prosthesis is intended to help people suffering from retinal degenerative diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration and retinitis pigmentosa. The former is the foremost cause of vision loss in North America, and the latter causes an estimated 1.5 million people worldwide to lose sight, according to the nonprofit group Foundation Fighting Blindness. In these diseases, the retina's photoreceptor cells slowly degenerate, ultimately leading to blindness. But the inner retinal neurons that normally transmit signals from the photoreceptors to the brain are largely unscathed. Retinal prostheses are based on the idea that there are other ways to stimulate those neurons.
The Stanford device uses near-infrared light, which has longer wavelength than normal visible light. It's necessary to use such an approach because people blinded by retinal degenerative diseases still have photoreceptor cells, which continue to be sensitive to visible light. "To make this work, we have to deliver a lot more light than normal vision would require," said Palanker. "And if we used visible light, it would be painfully bright." Near-infrared light isn't visible to the naked eye, though it is "visible" to the diodes that are implanted as part of this prosthetic system, he said.
Palanker explained what he's done by comparing the eye to camera, in which the retina is the film or the digital chip, and each photoreceptor is a pixel. "In our model we replace those photoreceptors with photosensitive diodes," he said. "Every pixel is like a little solar cell; you send light, then you get current and that current stimulates neurons in the inner nuclear layer of the retina." That, in turn, should have a cascade effect, activating the ganglion cells on the outer layer of the retina, which send the visual information to the brain that allows us to see.
For this study, Palanker and his team fabricated a chip about the size of a pencil point that contains hundreds of these light-sensitive diodes. To test how these chips responded, the researchers used retinas from both normal rats and blind rats that serve as models of retinal degenerative disease. The scientists placed an array of photodiodes beneath the retinas and placed a multi-electrode array above the layer of ganglion cells to gauge their activity. The scientists then sent pulses of light, both visible and near-infrared, to produce electric current in the photodiodes and measured the response in the outer layer of the retinas.
In the normal rats, the ganglions were stimulated, as expected, by the normal visible light, but they also presented a similar response to the near-infrared light: That's confirmation that the diodes were triggering neural activity.
In the degenerative rat retinas, the normal light elicited little response, but the near-infrared light prompted strong spikes in activity roughly similar to what occurred in the normal rat retinas. "They didn't respond to normal light, but they did to infrared," said Palanker. "This way the sight is restored with our system." He noted that the degenerated rat retinas required greater amounts of near-infrared light to achieve the same level of activity as the normal rat retinas.
While there was concern that exposure to such doses of near-infrared light could cause the tissue to heat up, the study found that the irradiation was still one-hundredth of the established ocular safety limit.
Since completing the study, Palanker and his colleagues have implanted the photodiodes in rats' eyes and been observing and measuring their effect for the last six months. He said preliminary data indicates that the visual signals are reaching the brain in normal and in blind rats, though the study is still under way.
While this and other devices could help people to regain some sight, the current technologies do not allow people to see color, and the resulting vision is far from normal, Palanker said.
###Other members of Palanker's lab involved in the research are graduate students Georges Goetz, David Boinagrov and Lele Wang; senior research associate Philip Huie; research associates Ludwig Galambos and Susanne Pangratz-Fuehrer, PhD; and postdoctoral scholars Yossi Mandel, MD, PhD, and Daniel Lavinsky, MD, PhD. In addition, Theodore Kamins, PhD, a consulting professor in electrical engineering, and James Harris, PhD, professor of electrical engineering, are co-authors.
Funding was provided by the National Institutes of Health, the Air Force Office of Scientific Research and Stanford's Bio-X program. Information about Stanford's Department of Ophthalmology, which also supported the research, is available at http://ophthalmology.stanford.edu/.
The Stanford University School of Medicine consistently ranks among the nation's top medical schools, integrating research, medical education, patient care and community service. For more news about the school, please visit http://mednews.stanford.edu. The medical school is part of Stanford Medicine, which includes Stanford Hospital & Clinics and Lucile Packard Children's Hospital. For information about all three, please visit http://stanfordmedicine.org/about/news.html.
New type of retinal prosthesis could better restore sight to blind, Stanford study says
2012-05-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Berkeley Lab scientists generate electricity from viruses
2012-05-14
Imagine charging your phone as you walk, thanks to a paper-thin generator embedded in the sole of your shoe. This futuristic scenario is now a little closer to reality. Scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have developed a way to generate power using harmless viruses that convert mechanical energy into electricity.
The scientists tested their approach by creating a generator that produces enough current to operate a small liquid-crystal display. It works by tapping a finger on a postage stamp-sized electrode ...
Wasted milk is a real drain on our resources, study shows
2012-05-14
Milk poured down Britain's kitchen sinks each year creates a carbon footprint equivalent to thousands of car exhaust emissions, research shows.
Scientists say the 360,000 tonnes of milk wasted in the UK each year creates greenhouse gas emissions equivalent to 100,000 tonnes of CO2. The study by the University of Edinburgh says this is the same as is emitted by about 20,000 cars annually.
The research identifies ways that consumers could also help curb greenhouse gas emissions – by reducing the amount of food they buy, serve and waste. They also suggest the food industry ...
Reducing post-traumatic stress after ICU
2012-05-14
Women are more likely to suffer post-traumatic stress than men after leaving an intensive care unit (ICU), finds a new study published in BioMed Central's open access journal Critical Care. However, psychological and physical 'follow-up' can reduce both this and post-ICU depression.
Patients in the ICU often suffer post-traumatic stress, anxiety, or depression due, not only to the illness or trauma that put them there, but to the very nature of the ICU and life-saving treatment. As a result, follow-up schemes have been put in to place to help alleviate these psychological ...
BGI reports the completed sequence of foxtail millet genome
2012-05-14
May 13, 2012, Shenzhen, China – BGI, the world's largest genomics organization, in cooperation with Zhangjiakou Academy of Agricultural Science, has completed the genome sequence and analysis of foxtail millet (Setaria italica), the second-most widely planted species of millet. This study provides an invaluable resource for the study and genetic improvement of foxtail millet and millet crops at a genome-wide level. Results of the latest study were published online today in Nature Biotechnology.
Foxtail millet is an important cereal crop providing food and feed in semi-arid ...
Researchers map path to quantum electronic devices
2012-05-14
DURHAM, N.C. – A team of Duke University engineers has created a master "ingredient list" describing the properties of more than 2,000 compounds that might be combined to create the next generation of quantum electronics devices.
The goal is topological insulators (TI), man-made crystals that are able to conduct electrical current on their surfaces, while acting as insulators throughout the interior of the crystal. Discovering TIs has become of great interest to scientists, but because of the lack of a rational blueprint for creating them, researchers have had to rely ...
Americans support national clean-energy standard
2012-05-14
The average U.S. citizen is willing to pay 13 percent more for electricity in support of a national clean-energy standard (NCES), according to Yale and Harvard researchers in Nature Climate Change.
Americans, on average, are willing to pay $162 per year in higher electricity bills to support a national standard requiring that 80 percent of the energy be "clean," or not derived from fossil fuels. Support was lower for a national standard among nonwhites, older individuals and Republicans.
In addition, the results suggest that the Obama Administration's proposal for ...
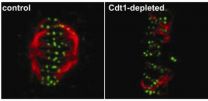
DNA replication protein also has a role in mitosis, cancer
2012-05-14
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – The foundation of biological inheritance is DNA replication – a tightly coordinated process in which DNA is simultaneously copied at hundreds of thousands of different sites across the genome. If that copying mechanism doesn't work as it should, the result could be cells with missing or extra genetic material, a hallmark of the genomic instability seen in most birth defects and cancers.
University of North Carolina School of Medicine scientists have discovered that a protein known as Cdt1, which is required for DNA replication, also plays an important ...
Time, place and how wood is used are factors in carbon emissions from deforestation
2012-05-14
A new study from the University of California, Davis, provides a deeper understanding of the complex global impacts of deforestation on greenhouse gas emissions.
The study, published May 13 in the advance online edition of the journal Nature Climate Change, reports that the volume of greenhouse gas released when a forest is cleared depends on how the trees will be used and in which part of the world the trees are grown.
When trees are felled to create solid wood products, such as lumber for housing, that wood retains much of its carbon for decades, the researchers ...
New study discovers powerful function of single protein that controls neurotransmission
2012-05-14
NEW YORK (May 13, 2012) -- Scientists at Weill Cornell Medical College have discovered that the single protein -- alpha 2 delta -- exerts a spigot-like function, controlling the volume of neurotransmitters and other chemicals that flow between the synapses of brain neurons. The study, published online in Nature, shows how brain cells talk to each other through these signals, relaying thoughts, feelings and action, and this powerful molecule plays a crucial role in regulating effective communication.
In the study, the investigators also suggest how the widely used pain ...
Blood pressure drugs don't protect against colorectal cancer
2012-05-14
A new study has found that, contrary to current thinking, taking beta blockers that treat high blood pressure does not decrease a person's risk of developing colorectal cancer. Published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, the study also revealed that even long-term use or subtypes of beta blockers showed no reduction of colorectal cancer risk.
In recent years, researchers have thought that beta blockers, which are prescribed to many older adults for high blood pressure and heart conditions, might be linked with a decreased ...