(Press-News.org)
VIDEO:
Sippy cups, bottles and pacifiers are popular items used by many parents for their kids. However, a new study shows that these items can be dangerous if a child is...
Click here for more information.
A new study by researchers in the Center for Biobehavioral Health and the Center for Injury Research and Policy at Nationwide Children's Hospital examined pediatric injuries associated with baby bottles, pacifiers and sippy cups. Researchers found that from 1991 to 2010, an estimated 45,398 children younger than three years of age were treated in U.S. emergency departments for injuries related to the use of these products. This equates to an average of 2,270 injuries per year, or one child treated in a hospital emergency department every four hours for these injuries.
The study, which is being released online May 14, 2012 and being published in the June 2012 print issue of Pediatrics, found that baby bottles accounted for 66 percent of injuries, followed by pacifiers at 20 percent and sippy cups at 14 percent. Body regions most commonly injured were the mouth (71 percent) and the head, face or neck (20 percent).
Most injuries were the result of falls while using the product (86 percent), which suggests that children were walking or running with the product in their mouth at the time of the injury.
"Two-thirds of injuries examined in our study were to one-year-old children who are just learning to walk and more prone to falls," said the study's co-author Sarah Keim PhD, MA, MS, principal investigator in the Center for Biobehavioral Health at Nationwide Children's Hospital. "Having children sit down while drinking from baby bottles or sippy cups can help reduce the occurrences of these injuries."
Both the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD) recommend that children be transitioned to regular, lidless cups at 12 months of age. The AAP also suggests that parents try to limit pacifier use after six months of age as use after that age may increase the risk of ear infections.
"These are products that almost everyone uses," noted study co-author, Lara McKenzie, PhD, principal investigator in the Center for Injury Research and Policy at Nationwide Children's Hospital. "Educating parents and caregivers about the importance of transitioning their children away from these products at the ages recommended by the AAP and AAPD could prevent up to 80 percent of the injuries related to baby bottles, pacifiers and sippy cups."
This is the first study to use a nationally representative sample to examine injuries associated with bottles, pacifiers and sippy cups that were treated in U.S. emergency departments. Data for this study were obtained from the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System (NEISS), which is operated by the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission. The NEISS provides information on consumer product-related and sports and recreation-related injuries treated in hospital emergency departments across the country.
Both Drs. Keim and McKenzie are faculty members at The Ohio State University College of Medicine.
The Center for Biobehavioral Health of The Research Institute at Nationwide Children's Hospital seeks to improve the health and healthcare of children, adolescents and their families through behavioral research on vulnerable individuals and populations using a multidisciplinary and biopsychosocial approach. The Center focuses its research on the identification of biological, psychological and social factors associated with developmental risk and resiliency in children and families, and the development of innovative interventions that will promote the health and quality of life of children and their families.
The Center for Injury Research and Policy (CIRP) of The Research Institute at Nationwide
Children's Hospital works globally to reduce injury-related pediatric death and disabilities. With innovative research at its core, CIRP works to continually improve the scientific understanding of the epidemiology, biomechanics, prevention, acute treatment and rehabilitation of injuries. CIRP serves as a pioneer by translating cutting edge injury research into education, policy, and advances in clinical care. For related injury prevention materials or to learn more about CIRP, visit http://www.nationwidechildrens.org/injury-research-and-policy.
For more information on Dr. Sarah Keim, visit http://www.nationwidechildrens.org/sarah-a-keim
For more information on the Center for Biobehavioral Health, visit http://www.nationwidechildrens.org/center-for-biobehavioral-health
For more information on the Center for Injury Research and Policy, visit http://www.nationwidechildrens.org/injury-research-and-policy
Study examines injuries with baby bottles, pacifiers and sippy cups in the US
Every 4 hours, a child under 3 years of age is treated in an emergency department for an injury related to these products
2012-05-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
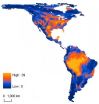
Nearly one-tenth of hemisphere's mammals unlikely to outrun climate change
2012-05-15
A safe haven could be out of reach for 9 percent of the Western Hemisphere's mammals, and as much as 40 percent in certain regions, because the animals just won't move swiftly enough to outpace climate change.
For the past decade scientists have outlined new areas suitable for mammals likely to be displaced as climate change first makes their current habitat inhospitable, then unlivable. For the first time a new study considers whether mammals will actually be able to move to those new areas before they are overrun by climate change. Carrie Schloss, University of Washington ...
Scientists make breakthrough in bile duct cancer with discovery of new gene mutations
2012-05-15
Grand Rapids, Mich. (May 14, 2012) - A team of international scientists has made a significant breakthrough in understanding the cause of bile duct cancer, a deadly type of liver cancer. By identifying several new genes frequently mutated in bile duct cancers, researchers are paving the way for better understanding of how bile duct cancers develop. Their discovery is published online in Nature Genetics.
Bile Duct Cancer, or Cholangiocarcinoma, is a fatal cancer with a poor prognosis. Accounting for 10 to 25 per cent of all primary liver cancers worldwide, bile duct cancer ...
Great recession reflux amounts to more hunger among seniors
2012-05-15
URBANA – A new study that looked at the hunger trends over a 10-year period found that 14.85 percent of seniors in the United States, more than one in seven, face the threat of hunger. This translates into 8.3 million seniors.
"In 2005, we reported that one in nine seniors faced the threat of hunger," said Craig Gundersen, University of Illinois associate professor of agricultural and consumer economics and executive director of the National Soybean Research Laboratory who led the data analysis on the study. "So, unlike the population as a whole, food insecurity among ...
New York Stem Cell Foundation scientist grows bone from human embryonic stem cells
2012-05-15
NEW YORK, NY (May 14, 2012) -- Dr. Darja Marolt, an Investigator at The New York Stem Cell Foundation (NYSCF) Laboratory, is lead author on a study showing that human embryonic stem cells can be used to grow bone tissue grafts for use in research and potential therapeutic application. Dr. Marolt conducted this research as a post-doctoral NYSCF – Druckenmiller Fellow at Columbia University in the laboratory of Dr. Gordana Vunjak-Novakovic.
The study is the first example of using bone cell progenitors derived from human embryonic stem cells to grow compact bone tissue ...
Brain circuitry is different for women with anorexia and obesity
2012-05-15
AURORA, Colo. (May 14, 2012) - Why does one person become anorexic and another obese? A study recently published by a University of Colorado School of Medicine researcher shows that reward circuits in the brain are sensitized in anorexic women and desensitized in obese women. The findings also suggest that eating behavior is related to brain dopamine pathways involved in addictions.
Guido Frank, MD, assistant professor director of the Developmental Brain Research Program at the CU School of Medicine and his colleagues used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) ...
Growing risks from hatchery fish
2012-05-15
Portland, Oregon – May 14, 2012 -- A newly published collection of more than 20 studies by leading university scientists and government fishery researchers in Alaska, British Columbia, Washington, Oregon, California, Russia and Japan provides mounting evidence that salmon raised in man-made hatcheries can harm wild salmon through competition for food and habitat.
"The genetic effects of mixing hatchery fish with wild populations have been well-documented," says journal editor David Noakes from Oregon State University. "But until now the ecological effects were largely ...
Genetic test identifies eye cancer tumors likely to spread
2012-05-15
AUDIO:
The most common form of cancer in the eye can be deadly. New treatments have allowed doctors to preserve vision in patients with ocular melanoma, but sometimes the cancer...
Click here for more information.
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have developed a genetic test that can accurately predict whether the most common form of eye cancer will spread to other parts of the body, particularly the liver.
In 459 patients with ocular ...
Lawrence Livermore work may improve the efficiency of the biofuel production cycle
2012-05-15
By deciphering the makeup of a bacterium found in the soil of a tropical rain forest, scientists may have a better understanding of how to more efficiently produce biofuels.
The production of liquid fuels derived from plant biomass offers a promising technology for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
While sugars stored within the plant cell wall, known as lignocellulose, are plentiful enough to supply most energy needs on the planet, their extraction is difficult and requires chemical pretreatment followed by enzymatic digestion using ...
Microbe that can handle ionic liquids
2012-05-15
In the search for technology by which economically competitive biofuels can be produced from cellulosic biomass, the combination of sugar-fermenting microbes and ionic liquid solvents looks to be a winner save for one major problem: the ionic liquids used to make cellulosic biomass more digestible for microbes can also be toxic to them. A solution to this conundrum, however, may be in the offing.
Researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Joint BioEnergy Institute (JBEI), a multi-institutional partnership led by Berkeley Lab, have identified a tropical rainforest ...
Religion replenishes self-control
2012-05-15
There are many theories about why religion exists, most of them unproven. Now, in an article published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, psychologist Kevin Rounding of Queen's University, Ontario, offers a new idea, and some preliminary evidence to back it up. The primary purpose of religious belief is to enhance the basic cognitive process of self-control, says Rounding, which in turn promotes any number of valuable social behaviors. He ran four experiments in which he primed volunteers to think about religious matters. Those ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
[Press-News.org] Study examines injuries with baby bottles, pacifiers and sippy cups in the USEvery 4 hours, a child under 3 years of age is treated in an emergency department for an injury related to these products