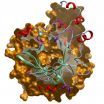
(Press-News.org) The Structural Genomics Consortium (SGC), an international public-private partnership that aims to determine three dimensional structures of medically important proteins, announced today the release into the public domain of its 1000th high resolution protein structure.
The 1000th structure – known as JmjD2C – belongs to a class of proteins involved in epigenetic signalling, a key research area for the SGC. Epigenetics is the study of inherited changes in gene expression caused by proteins such as JmjD2C which 'switch' genes on or off. It is believed that a better understanding of epigenetics could lead to new treatments for a wide variety of diseases including cancer, diabetes, obesity and many psychiatric diseases.
"JmjD2C is already known to play a key a role in the maintenance of self renewal in stem cells as well as roles in cancer," says Professor Udo Oppermann of SGC Oxford, who led the team solving the 1000th structure. "Now that its 3D structure is in the public domain, we hope that this will spur other scientists to investigate its functions more deeply and understand more clearly its role in epigenetics."
"This milestone reinforces the advantages of open-innovation partnerships between the public and private sectors," says Dr Aled Edwards the SGC Chief Executive. "We're extremely proud of this achievement and the efforts of our co-workers and their collaborators around the world."
Formed in 2004, the SGC comprises 180 scientists at labs at the Universities of Oxford and Toronto, and the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm. The international collaboration is supported by public and private sector funding. All research output is made available to the research community free from restriction on use and protein structures are deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB). In 2009, the SGC contributed nearly a third of all new human proteins structures deposited in the PDB, and a similar fraction of protein structures from pathogenic protozoa.
The vast amount of structural information generated by the SGC provides insights into molecular function and is expected to have a great impact on human health by providing a structural framework for the rational chemical design of new or improved drugs that can inhibit or enhance protein function.
"The SGC is providing an incredibly valuable resource to the entire biomedical research community," says Professor Ray Stevens, Department of Molecular Biology and Chemistry at The Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, USA. "Its systematic approach targeting entire protein families, such as protein kinases and other important as well as potential drug target classes, has yielded data that will be very helpful for investigators working to understand further the roles these proteins play in key biological functions. I applaud them for their efforts and accomplishments."
Since its launch, the SGC has identified and deposited in the PDB key protein structures involved in all aspects of cellular function and linked to diseases such as cancer, inflammation, diabetes, neurological disorders and infection. Many of the structures have also been published in scientific articles. Most publications, totalling over 250, are the result of collaborative projects with other scientists utilizing the structural information; the SGC is involved in more than 200 active collaborations with academics around the world.
Dr Alan Schafer, Director of Science Funding at the Wellcome Trust, comments: "The SGC has achieved a remarkable milestone in depositing its thousandth structure in the public domain. This success demonstrates the value of the public-private partnership model avoiding duplication of effort and allowing maximum benefit to the whole research community."
INFORMATION:
Structural Genomics Consortium releases 1,000th protein structure
2010-09-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UH geologists find parts of Northwest Houston sinking rapidly
2010-09-29
HOUSTON, Sept. 28, 2010 – A large section of northwestern Harris County – particularly the Jersey Village area – is sinking rapidly, according to a University of Houston (UH) geologist who has analyzed GPS data measuring ground elevation in the Houston area.
Some points in Jersey Village are subsiding by up to 5.5 centimeters (about 2 inches) a year, said Shuhab Khan, an associate professor of geology at UH. Khan, along with UH geology professor Kevin Burke and former Ph.D. student and UH alumnus Richard Engelkemeir, studied a decade's worth of detailed GPS data measuring ...
AMIA cites concerns about proposed HIPAA modifications
2010-09-29
In comments sent to Secretary Kathleen Sebelius at the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, AMIA (American Medical Informatics Association) called out 10 specific challenges to proposed modifications to HIPAA Privacy and Enforcement Rules. AMIA's comments, sent on behalf of its membership of 4,000 informatics professionals, detail key issues of concern related to the Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (NPRM) on HIPAA modifications, along with suggestions for models of change. The following areas were cited:
Business Associates and Subcontractors
Position: AMIA ...
Smithsonian researchers find differences between Galapagos and mainland frigatebirds
2010-09-29
Although the magnificent frigatebird may be the least likely animal on the Galapagos Islands to be unique to the area, it turns out the Galapagos population of this tropical seabird may be its own genetically distinct species warranting a new conservation status, according to a paper by researchers at the Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute, the Smithsonian's National Museum of Natural History and the University of Missouri-St. Louis published last week in the scientific journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
The Galapagos Islands, which once served as a scientific ...
The dual nature of dew
2010-09-29
When the scientific and spiritual worlds collide, they do so in the most surprising ways. Classical meteorological and plant science has, in the last century, insisted that dew negatively affects plant life, leading to rot and fungus. But in the Judeo-Christian tradition, dew is most welcomed as an important source of vegetative and plant life, celebrated in poetry and prayer.
Now Prof. Pinhas Alpert of Tel Aviv University's Department of Geophysics and Planetary Sciences has developed an explanation for the perplexing paradox with his colleagues. According to scientific ...
Noise and chemicals: Workers are losing their hearing
2010-09-29
A study carried out by Spanish researchers has shown that the presence of chemical contaminants can interact with noise and modify, for good or for bad, the way in which work-related "deafness" – which is increasingly common among young people – manifests itself. Noise-related hearing loss is the most common occupational disease in Europe.
"Workers exposed to noise in the presence of metalworking fluids exhibit a delay in hearing alteration in comparison with those exposed only to noise at the same intensity. However, those exposed to noise in the presence of welding ...
Truthy.indiana.edu to search, identify smear tactics, Twitter-bombs through election runup
2010-09-29
Astroturfers, Twitter-bombers and smear campaigners need beware this election season as a group of leading Indiana University information and computer scientists today unleashed Truthy.indiana.edu, a sophisticated new Twitter-based research tool that combines data mining, social network analysis and crowdsourcing to uncover deceptive tactics and misinformation leading up to the Nov. 2 elections.
Combing through thousands of tweets per hour in search of political keywords, the team based out of IU's School of Informatics and Computing will isolate patterns of interest ...
Immunization coverage key to good health locally, globally
2010-09-29
FORT WORTH, TEXAS, USA, September 28, 2010—The outbreak of whooping cough in Texas, California, and other states this year underscores the critical importance of widespread vaccination coverage, both locally as well as around the world, said a leading global health official attending conferences on world affairs and immunization in Fort Worth this week.
Alex Palacios, a special representative of the GAVI Alliance, a public-private partnership aimed at increasing immunisation rates in poor countries, said that despite public health advances in the US and other wealthy countries ...
Tracking down pathogenic yeasts
2010-09-29
More than half of all people are hosts to Candida albicans in their bodies. This species might be located on their skin or mucous membranes or in the intestines – frequently without causing any symptoms. However, it can be dangerous to patients whose immunological system has been weakened such as after organ transplants or chemotherapy with cancer. Then, this fungus penetrates into deeper layers of tissue and uses the blood system to spread throughout the body. In Germany alone, several thousand people die from systemic candida infections every year.
But why does Candida ...
Understanding Missouri River's sediment dynamics key to protecting endangered species
2010-09-29
Sept. 28, 2010 -- A new report from the National Research Council says that more organized and systematic procedures for gathering and evaluating data on Missouri River sediment are required to improve decisions and better manage the river's ecosystem, including protecting endangered species and developing water quality standards. In addition, the report finds that the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers' projects to restore habitats along the Missouri River are not significantly changing the size of the oxygen-depleted "dead zone" in the Gulf of Mexico, nor will options for ...
Wheel in a corset
2010-09-29
Just imagine your car suddenly comes to a halt on a quiet country road, and it's only four years old. This is not a pleasant thought. A breakdown is expensive. Not to mention the safety risk to the occupants – because the breakdown was caused by the extremely light plastic wheels so highly praised by the car salesman. One of them has broken. »Such a scenario must, of course, never happen in reality,« states Prof. Dr.-Ing. Andreas Büter from the Fraunhofer Institute for Structural Durability and System Reliability LBF in Darmstadt. The experts there specialize in operational ...