June 2012 story tips from Oak Ridge National Laboratory
2012-06-05
(Press-News.org) MATERIALS – Transparent performance . . .
Windshields, windows, solar panels, eyeglasses, heart stents and hundreds of other products representing a multi-billion-dollar market are potential targets for Oak Ridge National Laboratory's thin-film superhydrophobic technology. Conventional commercially available products tend to lack transparency, suitable bonding capability or both, making them largely impractical, said Tolga Aytug, one of the developers. The ORNL product, based on glass, can be produced with manufacturing processes that are cost effective and easily scaled up. In addition to the inherent self-cleaning properties, these coatings result in energy savings by reducing the need for washing and chemically treating windows and other optical coatings exposed to weather. [Contact: Ron Walli, (865) 576-0226; wallira@ornl.gov]
COMPUTING – Decoding the materials genome . . .
A hybrid supercomputer capable of 10 to 100 petaflops, or a quadrillion calculations per second, can support the Materials Genome Initiative, says Jeongnim Kim of Oak Ridge National Laboratory. The initiative aims to accelerate understanding of the fundamentals of materials, providing practical information that innovators can use to develop new products and processes. Kim is the principal author of QMCPACK, an application code widely used for large-scale simulations of molecules, solids and nanostructures. The code uses a technique called Quantum Monte Carlo to predict electronic structures. [Contact: Dawn Levy, (865) 576-6448; levyd@ornl.gov]
ENERGY -- Industrial strength savings . . .
Wireless sensors that could help the steel industry save money and reduce energy use and emissions are being put to the test at Commercial Metals Co. in Cayce, S.C. A team led by Glenn Allgood of Oak Ridge National Laboratory recently installed wireless sensors designed to withstand harsh conditions and provide instantaneous information to improve monitoring and control of a steel mill's equipment. Allgood noted that the melting, refining, casting and rolling process consume a significant amount of electrical and chemical energy. While steel mill operators have traditionally measured and monitored energy inputs, they have not attempted to measure and quantify energy losses. CMC is expecting a measurable improvement in efficiency and corresponding production cost savings as a result of using the information as feedback into the process. [Contact: Ron Walli, (865) 576-0226; wallira@ornl.gov]
SUPERCOMPUTING -- Lower costs, less toxicity . . .
Discovery of new drugs requires the screening of thousands of compounds to identify hundreds of candidates that are winnowed to dozens of effective agents. A few go on to preclinical development, the stage at which most drugs fail, and fewer still make it further to become the subjects of expensive and time-consuming clinical trials. Oak Ridge National Laboratory researcher Jeremy Smith, working with University of Tennessee assistant professor Jerome Baudry, is using supercomputers to speed the process. "If drug candidates are going to fail, you want them to fail fast, fail cheap," Smith said. In one day, a petaflop supercomputer -- which executes 1 quadrillion calculations per second -- can analyze 10 million drug candidates binding to a protein. Within a decade, exaflop machines are expected to handle the interactions of 10 million drugs with 1,000 different proteins, allowing predictions of effectiveness and side effects. [Contact: Dawn Levy, (865) 576-6448; levyd@ornl.gov]
ENGINEERING – Ceramics put to the test . . .
Researchers from Corning Inc. used the VULCAN Engineering Materials Diffractometer at Oak Ridge National Laboratory's Spallation Neutron Source to investigate the mechanical properties of ceramic materials used in car emission control and filtration devices. The instrument helps researchers understand the performance of the materials at the high temperatures required in car engines, and researchers plan to continue their relationship with VULCAN and its instrument scientists on other relevant materials, extending their study to performance at low temperatures. [Contact: Agatha Bardoel, bardoelaa@ornl.gov]
INFORMATION: END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-06-05
DURHAM, N.C. -- Treating adolescents for major depression can also reduce their chances of abusing drugs later on, a secondary benefit found in a five-year study of nearly 200 youths at 11 sites across the United States.
Only 10 percent of 192 adolescents whose depression receded after 12 weeks of treatment later abused drugs, compared to 25 percent of those for whom treatment did not work, according to research led by John Curry, a professor of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University.
"It turned out that whatever they responded to -- cognitive behavioral therapy, ...
2012-06-05
Reston, Va. (June 4, 2012) – For those with esophageal cancer, initial staging of the disease is of particular importance as it determines whether to opt for a curative treatment or palliative treatment. Research presented in the June issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine shows that physicians using positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT) can discern incremental staging information about the cancer, which can significantly impact management plans.
In 2012, an estimated 17,500 people will be diagnosed with esophageal cancer and 15,000 will die from ...
2012-06-05
Researchers at the University of Toronto Scarborough (UTSC) used an innovative technique to examine chemical interactions that are implicated in Parkinson's Disease.
The work details how a protein called alpha-synuclein interacting with the brain chemical dopamine can lead to protein misfolding and neuronal death.
Parkinson's Disease is a neurodegenerative disease which results in loss of motor control and cognitive function. Although the cause isn't known precisely, the disease involves the death of brain cells that produce dopamine, a chemical important in neuronal ...
2012-06-05
Tampa, Fla. (June 4, 2012) – After carrying out a study comparing the repopulation efficiency of immature hepatic stem/progenitor cells and mature hepatocytes transplanted into liver-injured rats, a research team from Sapporo, Japan concluded that mature hepatocytes offered better repopulation efficiency than stem/progenitor cells.
Until day 14 post-transplantation, the growth of the stem/progenitor cells was faster than the mature hepatocytes, but after two weeks most of the stem/progenitor cells had died. However, the mature hepatocytes continued to survive and proliferate ...
2012-06-05
Tampa, Fla. (June 4, 2012) – When autologous (self-donated) lung-derived mensenchymal stem cells (LMSCs) were transplanted endoscopically into 13 adult female sheep modeled with emphysema, post-transplant evaluation showed evidence of tissue regeneration with increased blood perfusion and extra cellular matrix content. Researchers concluded that their approach could represent a practical alternative to conventional stem cell-based therapy for treating emphysema.
The study is published in Cell Transplantation (21:1), now freely available on-line at http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/cog/ct/.
...
2012-06-05
The mosquito is possibly summer's biggest nuisance. Sprays, pesticides, citronella candles, bug zappers — nothing seems to totally deter the blood-sucking insect. And neither can rain apparently.
Even though a single raindrop can weigh 50 times more than a mosquito, the insect is still able to fly through a downpour.
Georgia Tech researchers used high-speed videography to determine how this is possible. They found the mosquito's strong exoskeleton and low mass render it impervious to falling raindrops.
The research team, led by Assistant Professor of Mechanical Engineering ...
2012-06-05
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - A new Purdue University-developed process for creating biofuels has shown potential to be cost-effective for production scale, opening the door for moving beyond the laboratory setting.
A Purdue economic analysis shows that the cost of the thermo-chemical H2Bioil method is competitive when crude oil is about $100 per barrel when using certain energy methods to create hydrogen needed for the process. If a federal carbon tax were implemented, the biofuel would become even more economical.
H2Bioil is created when biomass, such as switchgrass or corn ...
2012-06-05
As voters increasingly rely on websites of presidential primary candidates for news, they run a risk because candidates' online attacks are not vetted through traditional "watchdog journalists" and other gatekeepers to determine accuracy or fairness, according to a study by Baylor University researchers.
"The primary danger is that constituents often use this one-sided information to decide how to vote," said Mia Moody, Ph.D., study co-author and an assistant professor of journalism, public relations and new media in Baylor's College of Arts & Sciences.
The study — "Not ...
2012-06-05
AUDIO:
Drugs that are used to treat Type 2 diabetes also can contribute to unwanted side effects. But now, working with mice, researchers, led by scientists at Washington University School of...
Click here for more information.
Drugs for type 2 diabetes can contribute to weight gain, bone fractures and cardiovascular problems, but in mice, an investigational drug appears to improve insulin sensitivity without those troublesome side effects, researchers at Washington University ...
2012-06-05
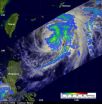
Over the weekend of June 2 and 3, Typhoon Mawar skirted the east coast of the Philippines bringing heavy surf, heavy rainfall and gusty winds that led to several missing and injured people. NASA's TRMM satellite and Aqua satellite showed heavy rainfall and cloud extent of the storm.
On June 1, Mawar (known as Ambo in the Philippines) had maximum sustained winds near 45 knots and it was about 245 miles east-northeast of Manila, Philippines. On that day, as Mawar continued north, some warnings were posted for the Philippines: Public storm warning signal #1 was up in the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] June 2012 story tips from Oak Ridge National Laboratory