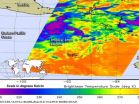
(Press-News.org) Bitter cold cloud tops tell forecasters that a storm has a lot of uplift, and the colder the cloud tops, the higher they are in the atmosphere, and the stronger the thunderstorms. NASA's Aqua satellite data showed that the cloud top temperatures in newborn Tropical Storm Carlotta became colder overnight and continue to grow colder as the low pressure area formely known as System 94E strengthened into a tropical storm. Carlotta is even expected to strengthen further and become a hurricane.
Because Carlotta is expected to continue strengthening, the government of Mexico has issued a hurricane warning for the Pacific coast of Mexico From Salina Cruz to Punta Maldonado. A hurricane watch is also in effect for the Pacific coast of Mexico west of Punta Maldonado to Acapulco and east of Salina Cruz to Barra De Tonala.
Forecasters look at data from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite. When cloud temperatures get colder, it means that clouds are getting higher. The lowest temperatures in Carlotta were as cold as or colder than 220 degrees Kelvin or minus 63 degrees Fahrenheit (-52 Celsius). The data from AIRS is also used to create an accurate 3-D map of atmospheric temperature, water vapor and clouds, all of which are helpful to forecasters.
At 11 a.m. EDT (8 a.m. PDT) Tropical Storm Carlotta's maximum sustained winds were near 45 mph (75 kph), and further strengthening is expected in the warm waters along the western coast of Mexico. Carlotta is expected to become a hurricane on June 15, according to the National Hurricane Center. Currently, Carlotta is located about 385 miles (620 km) south-southeast of Puerto Angel and 590 miles (950 km) southeast of Acapulco, Mexico. Carlotta is moving northwest near 9 mph (15 kph) and is expected to continue for the next couple of days. The storm should be near the Pacific coast of Mexico on Friday and move near the coast Friday night and Saturday, according to the National Hurricane Center.
That means that hurricane conditions are expected in the warning area by Friday night, June 15 and those conditions will continue on June 16, Saturday. Storm surge, heavy rainfall, flooding and mudslides are also possible. Isolated rainfall totals can reach 10-12 inches (250-300 mm) over the Mexican states of Guerrero, Oaxaca, Chiapas and southern Guatemala.
INFORMATION:
NASA sees bitter cold cloud tops in newborn Tropical Storm Carlotta
2012-06-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Chance alignment between galaxies mimics a cosmic collision
2012-06-15
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope shows a rare view of a pair of overlapping galaxies, called NGC 3314. The two galaxies look as if they are colliding, but they are actually separated by tens of millions of light-years, or about ten times the distance between our Milky Way and the neighboring Andromeda galaxy. The chance alignment of the two galaxies, as seen from Earth, gives a unique look at the silhouetted spiral arms in the closer face-on spiral, NGC 3314A.
The motion of the two galaxies indicates that they are both relatively undisturbed and that they are moving in markedly ...
First flight instrument delivered for James Webb
2012-06-15
The first of four instruments to fly aboard NASA's James Webb Space Telescope (Webb) has been delivered to NASA. The Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) will allow scientists to study cold and distant objects in greater detail than ever before.
MIRI arrived at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., May 29. It has been undergoing inspection before being integrated into Webb's science instrument payload known as the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM).
Assembled at and shipped from the Science and Technology Facilities Council's Rutherford Appleton Laboratory ...
New solar active region spitting out flares
2012-06-15
An active region on the sun, numbered AR 1504, rotated into view over the left side of the sun on June 10, 2012. The region fired off two M-class flares and two coronal mass ejections (CMEs) on June 13 and June 14, 2012. The first flare lasted for a relatively long three hours, peaking on June 13, 2012 at 9:17 AM EDT. The associated CME traveled at approximately 375 miles per second and is directed toward Earth, though due to its slow speed, the effect on Earth is expected to be minimal.
The second M-class flare was also a long-duration flare, and it peaked on June 14, ...
Unexpected discovery highlights new role for cell death regulator
2012-06-15
An unexpected discovery of how the body controls cell death has revealed a potential new therapeutic target.
A research team based at Cardiff University's School of Biosciences has already revealed the mechanism by which high alcohol intake can induce pancreatitis and its progression to pancreatic cancer. Now a new study, published in Current Biology, reveals a hitherto unknown interaction between two well known molecules, which has important implications for our understanding of inflammation and cancer in the pancreas as well as other organs.
The Cardiff team studied ...
Vitamin D with calcium shown to reduce mortality in elderly
2012-06-15
A study recently published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism (JCEM) suggests that vitamin D—when taken with calcium—can reduce the rate of mortality in seniors, therefore providing a possible means of increasing life expectancy.
During the last decade, there has been increasing recognition of the potential health effects of vitamin D. It is well known that calcium with vitamin D supplements reduces the risk of fractures. The present study assessed mortality among patients randomized to either vitamin D alone or vitamin D with ...
Researchers identify need to sample multiple tumor zones in breast cancer
2012-06-15
Philadelphia, PA, June 15, 2012 – Certain short strands of RNA, known as microRNAs (miRNAs), have been linked to the progression and metastasis of breast cancer and may provide information about prognosis. However, studies of miRNA expression profiles often report conflicting findings. While the potential for using miRNAs in breast cancer diagnosis is promising, scientists report in a new study published online today in The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics that differences in the amount and types of miRNA within breast tumors can be misleading.
"Personalized medicine ...
Obstructive sleep apnea is associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy
2012-06-15
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is independently associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), according to a new study from researchers in the UK. The severity of DPN is also correlated with the degree of OSA and the severity of nocturnal hypoxemia.
"OSA is known to be associated with inflammation and oxidative stress, so we hypothesized that it would be associated with peripheral neuropathy in patients with T2DM," said lead author Abd Tahrani, MD, clinical lecturer in endocrinology and diabetes at the University ...
Antioxidant shown to reduce blindness risk in extremely premature babies
2012-06-15
BOSTON, MA—Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) is the second most common cause of childhood blindness in the United States, occurring in half of premature infants born earlier than or at 28 weeks gestational age. The condition is caused by abnormal blood vessel development in the retina of the eye. ROP risk increases with decreasing gestational age.
A study by researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) suggests that the antioxidant, rhSOD (recombinant human Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase), reduces the risk of developing ROP in extremely low gestational age newborns. ...
Graphic warning labels improve smokers' recall of warning and health risks related to smoking
2012-06-15
PHILADELPHIA – In a first of its kind study in the U.S., researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania have shown that the addition of graphic warning labels on cigarette packaging can improve smokers' recall of the warning and health risks associated with smoking. The new findings are published online-first in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
In past studies in Europe and Canada, graphic warning labels have proven to be effective in eliciting negative responses to smoking, increasing reported intention to quit smoking ...
Persistence is learned from fathers, study shows
2012-06-15
When the going gets tough, the tough ought to thank their fathers.
New research from Brigham Young University shows that dads are in a unique position to help their adolescent children develop persistence.
BYU professors Laura Padilla-Walker and Randal Day arrived at these findings after following 325 families over several years. And over time, the persistence gained through fathers lead to higher engagement in school and lower rates of delinquency.
"In our research we ask 'Can your child stick with a task? Can they finish a project? Can they make a goal and complete ...