(Press-News.org) DALLAS – Sept. 29, 2010 – More people are drinking than 20 years ago, according to a UT Southwestern Medical Center analysis of national alcohol consumption patterns. Gathered from more than 85,000 respondents, the data suggests that a variety of factors, including social, economic and ethnic influences and pressures, are involved in the increase.
"The reasons for the uptick vary and may involve complex sociodemographic changes in the population, but the findings are clear: More people are consuming alcohol now than in the early 1990s," said Dr. Raul Caetano, dean of the UT Southwestern School of Health Professions and lead author of the paper available online and in the October issue of Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research.
The findings, Dr. Caetano said, suggest that continuous monitoring of alcohol consumption levels is needed to understand better the factors that affect consumption. Monitoring also would help to detect as early as possible signs that rates of risky drinking behaviors such as binge drinking or drinking to intoxication may be increasing, said Dr. Caetano, who also is regional dean of the UT School of Public Health's campus in Dallas.
"Changes in the population due to aging, the influx of immigrant groups, and a decline in mean income level because of economic recessions can all impact trends in drinking and problems associated with drinking," he said.
While more Caucasians, Hispanics and African-Americans reported drinking between 1992 and 2002, only Caucasian women consumed more drinks per person. The number of drinks that African-Americans and Hispanics consumed leveled out over the 10-year time period.
In addition to an increase in the number of both male and female drinkers within all three ethnic groups, the researchers also found that among women, Caucasians were more likely than Hispanics or African-Americans to consume five or more drinks a day or drink to intoxication. An increase in drinking five or more drinks a day was also detected among the heavier drinkers in the population, suggesting a potential polarization of drinking practices.
Dr. Caetano said the team also identified several sociodemographic predictors for whether someone was more likely to drink to intoxication. They found that males younger than 60 who did not have a college degree were likely to consume more drinks per month. Being unemployed or unmarried also were identified as risk factors for males getting intoxicated more than once a month, he said.
For the study, the researchers culled data from the 1991-92 National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey and the 2001-02 National Epidemiologic Study on Alcohol and Related Conditions. The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism conducted both surveys, in which trained interviewers spoke with individuals 18 or older in the respondents' homes. The interviewers used a standardized questionnaire, so both surveys used the same overall methodology. Each study included about 43,000 participants.
Both studies defined drinkers as individuals who had consumed at least 12 drinks that contained at least 0.6 ounces of any kind of alcohol within the past year. Those who hadn't imbibed that much alcohol within the past year or who had never had any kind of alcohol were classified as nondrinkers.
While many uncontrolled variables could skew the results, Dr. Caetano said the overall trend is clear – the proportion of men and women who drink alcohol has risen in all three ethnic groups.
"This suggests to us that a variety of public-health policies such as restrictions on alcohol advertising, regulating high-alcohol-content beverages, increasing taxes on alcohol, as well as treatment and brief interventions may be needed to reduce alcohol-related problems," he said.
Researchers from the University of North Texas Health Science Center in Fort Worth also contributed to the study.
The study was supported by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism.
INFORMATION:
This news release is available on our World Wide Web home page at
http://www.utsouthwestern.edu/home/news/index.html
To automatically receive news releases from UT Southwestern via e-mail,
subscribe at www.utsouthwestern.edu/receivenews
Media Contact: Kristen Holland Shear
214-648-3404
Kristen.hollandshear@utsouthwestern.edu
Alcohol consumers are becoming the norm, UT Southwestern analysis finds
2010-09-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Milky Way sidelined in galactic tug-of-war
2010-09-30
The Magellanic Stream is an arc of hydrogen gas spanning more than 100 degrees of the sky as it trails behind the Milky Way's neighbor galaxies, the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds. Our home galaxy, the Milky Way, has long been thought to be the dominant gravitational force in forming the Stream by pulling gas from the Clouds. A new computer simulation by Gurtina Besla (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics) and her colleagues now shows, however, that the Magellanic Stream resulted from a past close encounter between these dwarf galaxies rather than effects of the ...
Hepatitis C virus faces new weapon from Florida State scientists
2010-09-30
In recent human trials for a promising new class of drug designed to target the hepatitis C virus (HCV) without shutting down the immune system, some of the HCV strains being treated exhibited signs of drug resistance.
In response, an interdisciplinary team of Florida State University biologists, chemists and biomedical researchers devised a novel genetic screening method that can identify the drug-resistant HCV strains and the molecular-level mechanisms that make them that way –– helping drug developers to tailor specific therapies to circumvent them.
The potentially ...
Surgery offers long-term survival for early stage prostate cancer patients
2010-09-30
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- In the largest, most modern, single-institution study of its kind, Mayo Clinic urologists mined a long-term data registry for survival rates of patients who underwent radical prostatectomy (http://www.mayoclinic.org/radical-prostatectomy/) for localized prostate cancer. The findings are being presented at the North Central Section of the American Urological Association's 84th Annual Meeting in Chicago.
A radical prostatectomy is an operation to remove the prostate gland and some of the tissue around it. In this study, Mayo Clinic researchers discovered ...
Correction: Abatacept found ineffective in treatment of non-life threatening lupus
2010-09-30
Results from a 12-month multi-center clinical trial did not show therapeutic benefit of abatacept over placebo in patients with non-life threatening systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Abatacept failed to prevent new disease flares in SLE patients tapered from corticosteroids in an analysis where mild, moderate and severe disease flares were evaluated together. Full details of the phase IIb clinical trial are published in the October issue of Arthritis & Rheumatism, a journal of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
The ACR estimates that 161,000 to 322,000 adults ...
NASA uses 3 satellites to see strengthening Tropical Storm Nicole
2010-09-30
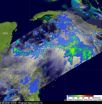
NASA is providing data from three satellites to give forecasters valuable information on newly strengthened Tropical Storm Nicole. Nicole was Tropical Depression 16 until 11 a.m. EDT, Sept. 29 and NASA data helped confirm her new designation. Satellite data from NASA showed frigid thunderstorm cloud top temperatures, heavy rainfall, and extensive cloud cover as Nicole strengthened.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument uses infrared technology to take a tropical cyclone's temperature. AIRS sits on NASA's Aqua satellite and captured an image of those cloud ...
Penn biologists say species accumulate on Earth at slower rates than in the past
2010-09-30
PHILADELPHIA –- Computational biologists at the University of Pennsylvania say that species are still accumulating on Earth but at a slower rate than in the past.
In the study, published in the journal PLoS Biology, Penn researchers developed a novel computational approach to infer the dynamics of species diversification using the family trees of present-day species. Using nine patterns of diversification as alternative models, they examined 289 phylogenies, or evolutionary trees, representing amphibians, arthropods, birds, mammals, mollusks and flowering plants.
The ...
Resource restoration planning process begins for BP/Deepwater Horizon oil spill
2010-09-30
The Department of the Interior, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the co-trustees for natural resources affected by the BP/Deepwater Horizon oil spill announced today they have started the injury assessment and restoration planning phase of the Natural Resource Damage Assessment, a legal process to determine the type and amount of restoration needed to compensate the public for harm to natural resources and their human uses as a result of the spill.
This is the second phase of the NRDA process. Much of the initial "preassessment" phase has already ...
California's leadership in tobacco control results in lower lung cancer rate
2010-09-30
A study led by researchers at the University of California, San Diego shows that California's 40 year-long tobacco control program has resulted in lung cancer rates that are nearly 25 percent lower than other states.
"The consistency in the trends from cigarette sales and population surveys was reassuring" said John P. Pierce, PhD, Sam M. Walton Professor of Cancer Research in the Department of Family and Preventive Medicine at UCSD School of Medicine and director of the Population Sciences Division at Moores UCSD Cancer Center. "What is really important is that the widening ...
Less than half of essential workers willing to report to work during a serious pandemic
2010-09-30
September 28, 2010 – Although first responders willingly put themselves in harm's way during disasters, new research indicates that they may not be as willing— if the disaster is a potentially lethal pandemic.
In a recent study, researchers at Columbia University's Mailman School of Public Health found that more than 50% of the first responders and other essential workers they surveyed might be absent from work during a serious pandemic, even if they were healthy.
The study, reported online in the October issue of the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, ...
Dirty hands, dirty mouths: U-M study finds a need to clean the body part that lies
2010-09-30
ANN ARBOR, Mich.---Apparently your mom had it right when she threatened to wash your mouth out with soap if you talked dirty. Lying really does create a desire to clean the "dirty" body part, according to a University of Michigan study.
"The references to 'dirty hands' or 'dirty mouths' in everyday language suggest that people think about abstract issues of moral purity in terms of more concrete experiences with physical purity," said Spike W.S. Lee, a U-M doctoral candidate in psychology, who conducted the study with Norbert Schwarz, a psychologist at the U-M Institute ...