An economical, effective and biocompatible gene therapy strategy promotes cardiac repair
2012-07-07
(Press-News.org) Dr Changfa Guo, Professor Chunsheng Wang and their co-investigators from Zhongshan hospital Fudan University, Shanghai, China have established a novel hyperbranched poly(amidoamine) (hPAMAM) nanoparticle based hypoxia regulated vascular endothelial growth factor (HRE-VEGF) gene therapy strategy which is an excellent substitute for the current expensive and uncontrollable VEGF gene delivery system. This discovery, reported in the June 2012 issue of Experimental Biology and Medicine, provides an economical, feasible and biocompatible gene therapy strategy for cardiac repair.
Transplantation of VEGF gene manipulated mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) has been proposed as a promising therapeutic method for cardiac repair after myocardium infarction. However, the gene delivery system, including the VEGF gene and delivery vehicle, needs to be optimized. On one hand, long-term and uncontrollable VEGF over-expression in vivo has been observed to lead to hemangioma formation instead of functional vessels in animal models. On the other hand, though non-viral gene vector can circumvent the limitations of virus, drawbacks of the current non-viral vectors, such as complex synthesis procedure, limited transfection efficiency and high cytotoxicity, still needs to be overcome.
Co-investigators, Drs. Kai Zhu and Hao Lai, said "Hypoxia response elements were inserted into the promoter region of VEGF gene to form HRE-VEGF, which provided a safer alternative to the conventionally available VEGF gene". "The HRE-VEGF up-regulates gene expression under hypoxic conditions caused by ischemic myocardium and turns it off under normoxia condition when the regional oxygen supply is adequate."
The hPAMAM nanoparticles, which exhibit high gene transfection efficiency and low cytotoxicity during the gene delivery process, can be synthesized by a simpler and more economical one-step/pot polymerization technique. Drs. Zhu and Lai, said "Using the hPAMAM based gene delivery approach, our published and unpublished results explicitly demonstrated that it was an economical, effective and biocompatible gene delivery vehicle".
Dr Guo concluded that "Treatment with hPAMAM-HRE-VEGF transfected MSCs after myocardium infarction improved the myocardial VEGF level, which improved graft MSC survival, increased neovascularization and ultimately improved heart function. And this novel VEGF gene delivery system may have clinical relevance for tissue repair in other ischemic diseases".
Dr. Steve Goodman, Editor-in-Chief of Experimental Biology and Medicine said "Guo and colleagues have provided an exciting new nanoparticle based gene therapy for cardiac repair. This novel approach has great promise for repair of the heart after myocardial infarction."
INFORMATION:
Experimental Biology and Medicine is the journal of the Society of Experimental Biology and Medicine. To learn about the benefits of society membership visit www.sebm.org. If you are interested in publishing in the journal please visit http://ebm.rsmjournals.com/
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-07-07
Patients look up their illnesses online to become better informed and prepared to play an active role in their care — not because they mistrust their doctors, a new University of California, Davis, study suggests.
The study surveyed more than 500 people who were members of online support groups and had scheduled appointments with a physician.
"We found that mistrust was not a significant predictor of people going online for health information prior to their visit," said Xinyi Hu, who co-authored the study as part of her master's thesis in communication. "This was somewhat ...
2012-07-07
AMHERST, Mass. – Physicists Benjamin Brau, Carlo Dallapiccola and Stephane Willocq at the University of Massachusetts Amherst were instrumental in this week's preliminary observation of a new particle, possibly the long-sought Higgs boson, announced by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) particle physics laboratory.
The Standard Model of particle physics can correctly explain the elementary particles and forces of nature after more than four decades of experiments. But it cannot, without the Higgs boson, explain how most of these particles acquire their ...
2012-07-07
Detroit - A Wayne State University researcher has found that an extract from algae could become a key to regulating cardiovascular disease.
In a study funded by Health Enhancement Products of Bloomfield Hills, Mich., Smiti Gupta, Ph.D., assistant professor in the department of nutrition and food science in the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, has found that dietary intake of ProAlgaZyme increased the level of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) in an animal model.
While medications for the control of high plasma cholesterol levels such as statins and numerous dietary ...
2012-07-07
BETHESDA, MD – July 6, 2012 – Yona Goldshmit, Ph.D., is a former physical therapist who worked in rehabilitation centers with spinal cord injury patients for many years before deciding to switch her focus to the underlying science.
"After a few years in the clinic, I realized that we don't really know what's going on," she said.
Now a scientist working with Peter Currie, Ph.D., at Monash University in Australia, Dr. Goldshmit is studying the mechanisms of spinal cord repair in zebrafish, which, unlike humans and other mammals, can regenerate their spinal cord following ...
2012-07-07
BETHESDA, MD – July 6, 2012 – Zebrafish, popular as aquarium fish, now have an important place in research labs as a model organism for studying human diseases.
At the 2012 International Zebrafish Development Conference, held June 20-24 in Madison, Wisconsin, numerous presentations highlighted the utility of the zebrafish for examining the basic biological mechanisms underlying human disorders and identifying potential treatment approaches for an impressive array of organ and systemic diseases.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), while rarely ...
2012-07-07
Real-time data that will be used in everything from weather forecasts to disaster response is now being beamed down to Earth from a cone-shaped appendage aboard the nation's newest Earth-observing satellite.
The High Rate Data (HRD) link is an antenna aboard the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (NPP) satellite that provides 'direct broadcast' data to users in real-time. Researchers world-wide are then able to use customized algorithms, or mathematical formulas, turning raw data into images to help manage quickly changing regional events, such as rapidly spreading ...
2012-07-07
On July 11, NASA scientists will launch into space the highest resolution solar telescope ever to observe the solar corona, the million degree outer solar atmosphere. The instrument, called HI-C for High Resolution Coronal Imager, will fly aboard a Black Brant sounding rocket to be launched from the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico. The mission will have just 620 seconds for its flight, spending about half of that time high enough that Earth's atmosphere will not block ultraviolet rays from the sun. By looking at a specific range of UV light, HI-C scientists hope ...
2012-07-07
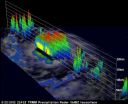
NASA's TRMM satellite revealed that Tropical Storm Daniel's most concentrated rainfall is occurring around the storm's center.
When the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed over Tropical Storm Daniel on July 6, 2012 at 0034 UTC, data revealed heavy rain falling around the southern periphery of the center of circulation. The heavy rain was falling at a rate of more than 2 inches/50 mm per hour. TRMM is jointly managed by both NASA and the Japanese Space Agency, JAXA.
Daniel remains no threat to land, however, as the storm is expected to continue ...
2012-07-07
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — An evaluation of national data by UC Davis researchers has found that extra weight is not necessarily linked with a higher risk of death.
When compared to those with normal weight, people who were overweight or obese had no increased risk of death during a follow-up period of six years. People who were severely obese did have a higher risk, but only if they also had diabetes or hypertension.
The findings, which appear in the July-August issue of The Journal of American Board of Family Medicine, call into question previous studies -- using data ...
2012-07-07
Richmond, Va. (July 6, 2012) – Researchers have created the first mouse model demonstrating the role of a cancer promoting gene, Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1), in hepatocellular carcinoma, or liver cancer. The mouse model represents a critical step in understanding the molecular mechanisms of liver cancer progression and could lead to novel therapies for the disease.
Insights from the mouse model were recently published in the journal Hepatology by a team of researchers led by Devanand Sarkar, M.B.B.S., Ph.D., Harrison Scholar at Virginia Commonwealth University (VCU) ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] An economical, effective and biocompatible gene therapy strategy promotes cardiac repair