(Press-News.org) This press release is available in German.
Hot summer days cause in large cities very seldom great happiness among inhabitants. On those days the air is highly polluted with automobile and industrial emissions what makes breathing difficult and unhealthy. According to the latest calculations of Max Planck scientist Andrea Pozzer this scenario could become true for most of world population in 2050 if no counteractive measures are taken. Especially China, North India and the Middle East are expected to be affected by a drastic decrease in air quality.
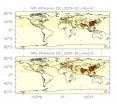
In 2050, the air quality worldwide will be as bad as it already is nowadays in urban areas of Southeast Asia. This is the result of a simulation of the atmosphere done by scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, the Institute of Atmospheric Physics and the Joint Research Centre of the European Commission. The chemical atmospheric model EMAC used by the researchers for their current study is the first to include all five major air pollutants known to negatively impact human health: nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide, ozone, carbon monoxide and particulate matter smaller than 2.5 micrometres which are regarded as particularly harmful.
Air pollution is one of the major current health risks of humanity. At present, urban outdoor air pollution causes 1.3 million estimated deaths per year worldwide, according to the World Health Organisation. That number will increase in coming years. Therefor Andrea Pozzer and his colleagues studied the impact of man-made emissions on air quality in different regions of the earth. They show, what could happen if no further action is taken to reduce pollutants.
"Our study shows that further legislation to control and reduce man-made emissions is needed, in particular for eastern China and northern India, to avoid hot-spots of elevated air pollution," says Andrea Pozzer of the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry in Mainz, whose latest research findings are published in the current issue of 'Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics', a journal of the European Geosciences Union. According to the results of this study eastern China and northern India are the places that are struggling with the highest pollution levels.
East Asia will be exposed to high levels of pollutants, such as nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide and fine particulate matter (PM2.5). Northern India and the Arabian Gulf region, on the other hand, will suffer a marked increase in ozone levels. This is primarily due to population density and the expected increase in industrial production and transport in these areas. Air pollution in Europe and North America would also increase, but due to the effect of mitigation policies – that have been in place for over two decades now – to a much lesser extent than in Asia.
Pozzer and his colleagues studied the impact of man-made emissions on air quality, assuming past emission trends continue and no additional climate change and air pollution reduction measures beyond what is in place since 2005 are implemented. While pessimistic, the global emissions trends indicate such continuation.
Subsequent to these results the researchers want to broaden the analyses. In the near future they want to calculate how many people would actually be affected by the harmful effects of deteriorating air quality.
INFORMATION:
Original publication
A. Pozzer, P. Zimmermann, U.M. Doering, J. van Aardenne, H. Tost, F. Dentener, G. Janssens-Maenhout & J. Lelieveld
Effects of business-as-usual anthropogenic emissions on air quality
Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss., 12, 8617-8676, doi:10.5194/acpd-12-8617-2012, 2012
Worldwide increase of air pollution
Atmospheric model calculates changes in air quality over the coming decades
2012-08-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Spouses of breast cancer survivors hold on to hope
2012-08-01
(Edmonton) Male partners of breast cancer patients are likely to take a pass on spousal support groups in favour of exercise or an evening out with friends to cope with stresses associated with the disease, according to new research from the University of Alberta.
Faculty of Nursing professor Wendy Duggleby said spouses of women with breast cancer have unique needs when it comes to retaining a sense of hope at a time when they provide important physical and emotional support for their partners.
"There are many programs out there for women, but for men a lot of support ...
Black gay men worldwide 15 times more likely to have HIV and racial disparity
2012-08-01
ATLANTA – An international team of researchers, including a scientist at Georgia State University, found that black men who have sex with men (MSM) are more likely to have HIV than other MSM, and that social inequalities play a major role.
Examining data from nearly 200 studies in the U.S., the United Kingdom and Canada, the researchers found that stigma, poverty and inadequate access to health care were major factors in the disparities. The term "MSM" was used in the study, as some men who have sex with men do not identify with the terms gay or bisexual.
The results ...
Research: Men respond negatively to depictions of 'ideal masculinity' in ads
2012-08-01
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. – The male response to depictions of ideal masculinity in advertising is typically negative, which has implications for advertisers and marketers targeting the increasingly fragmented consumer demographic, according to research from a University of Illinois marketing expert.
Cele Otnes, a professor of advertising and of business administration who studies how marketing and advertising shapes consumption, says that men who compare themselves to the hyper-masculine or over-exaggerated male stereotypes in advertising and popular culture experience a range ...
New research reveals extent of poor-quality antimalarial medicines in South American countries
2012-08-01
Rockville, Md., August 1, 2012 — Two articles recently published in Malaria Journal shed new light on the quality of antimalarial medicines circulating in countries in the Amazon Basin in South America. Researchers from the Promoting the Quality of Medicines (PQM) program, a cooperative agreement between the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) and the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention (USP), in conjunction with country partners, coordinated these studies in the context of the Amazon Malaria Initiative (AMI).
"Though several studies in recent years have assessed ...
Obese donors increase risk of death for pediatric liver transplant recipients
2012-08-01
Children undergoing liver transplantation are at greater risk of graft loss and death from adult organ donors who are severely obese according to research published in the August issue of Liver Transplantation, a journal of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. The study, funded in part by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), found that pediatric donor body mass index (BMI) did not increase mortality risk in this pediatric population.
Obesity is a global health concern. A 2008 report from the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates ...
13-year Cascadia study complete – and Northwest earthquake risk looms large
2012-08-01
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A comprehensive analysis of the Cascadia Subduction Zone off the Pacific Northwest coast confirms that the region has had numerous earthquakes over the past 10,000 years, and suggests that the southern Oregon coast may be most vulnerable based on recurrence frequency.
Written by researchers at Oregon State University, and published online by the U.S. Geological Survey, the study concludes that there is a 40 percent chance of a major earthquake in the Coos Bay, Ore., region during the next 50 years. And that earthquake could approach the intensity of ...
Researchers find potential cancer roadblock
2012-08-01
EAST LANSING, Mich. — By identifying a key protein that tells certain breast cancer cells when and how to move, researchers at Michigan State University hope to better understand the process by which breast cancer spreads, or metastasizes.
When breast cancer metastasizes, cancer cells break away from a primary tumor and move to other organs in the body, including the lungs, liver and brain. In work published recently in the journal Cancer Research, MSU researchers Kathy Gallo and Jian Chen show a protein called MLK3 (mixed lineage kinase 3) is a critical driver of breast ...
More code cracking
2012-08-01
A trio of groundbreaking publications from researchers in Northwestern University's Physical Sciences-Oncology Center (PS-OC) report important methodological advances that will enable a better understanding of how gene expression is regulated, both in normal cells and in cancer cells. This knowledge could lead to the development of more effective therapeutic agents to treat cancer patients.
The three papers, published recently in the journals Nature Genetics, Nature Biotechnology and Nature, focus on nucleosomes, a basic unit of DNA packaging, and may help to uncover ...
New study: Running mechanics, not metabolism, are the key to performance for elite sprinters
2012-08-01
Sprinters competing in the 2012 Olympics might assume their championship performance is the result of their fuel-efficient physiology.
But a new study disproves the classic scientific view that conserving energy maximizes performance in a sprinting event.
The study by biomechanics researchers Matthew W. Bundle at the University of Montana and Peter G. Weyand at Southern Methodist University, Dallas, demonstrates that metabolic economy is not an important factor for performance in events lasting 60 seconds or less.
In fact, just the opposite is true.
"That prevailing ...
In fly DNA, the footprint of a fly virus
2012-08-01
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- In a curious evolutionary twist, several species of a commonly studied fruit fly appear to have incorporated genetic material from a virus into their genomes, according to new research by University at Buffalo biologists.
The study found that several types of fruit fly -- scientific name Drosophila -- harbored genes similar to those that code for the sigma virus, a fly virus in the same family as rabies. The authors believe the genetic information was acquired during past viral infections and passed on from fruit fly parent to offspring through many generations.
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
[Press-News.org] Worldwide increase of air pollutionAtmospheric model calculates changes in air quality over the coming decades