(Press-News.org) Phosphorus is a vital element not only for plants but also for all living organisms. In recent times, however, farmers have been faced with a growing shortage of this essential mineral, and the price of phosphate-based fertilizers has been steadily increasing. It is therefore high time to start looking for alternatives. This is not an easy task, because phosphorus cannot be replaced by any other substance. But researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology IGB in Stuttgart have found a solution that makes use of locally available resources which, as unlikely as it might seem, are to be found in plentiful supply in the wastewater from sewage treatment plants and in the fermentation residues from biogas plants: a perfect example of the old saying "from muck to riches". The new process was developed by a team of scientists led by Jennifer Bilbao, who manages the nutrient management research group at the IGB. "Our process precipitates out the nutrients in a form that enables them to be directly applied as fertilizer," she explains.
Mobile pilot plant for field tests
The main feature of the patented process, which is currently being tested in a mobile pilot plant, is an electrochemical process that precipitates magnesium-ammonium phosphate – also known as struvite – by means of electrolysis from a solution containing nitrogen and phosphorus. Struvite is precipitated from the process water in the form of tiny crystals that can be used directly as fertilizer, without any further processing. The innovative aspect of this method is that, unlike conventional processes, it does not require the addition of synthetic salts or bases. Bilbao: "It is an entirely chemical-free process."
The 2-meter-high electrolytic cell that forms the centerpiece of the test installation and through which the wastewater is directed contains a sacrificial magnesium anode and a metallic cathode. The electrolytic process splits the water molecules into negatively charged hydroxyl ions at the cathode. At the anode an oxidation takes place: the magnesium ions migrate through the water and react with the phosphate and ammonium molecules in the solution to form struvite.
Energy-saving, chemical-free process
Because the magnesium ions in the process water are highly reactive, this method requires very little energy. The electrochemical process therefore consumes less electricity than conventional methods. For all types of wastewater tested so far, the necessary power never exceeded the extremely low value of 70 watt-hours per cubic meter. Moreover, long-duration tests conducted by the IGB researchers demonstrated that the concentration of phosphorus in the pilot plant's reactor was reduced by 99.7 percent to less than 2 milligrams per liter. This is lower than the maximum concentration permitted by the German Waste Water Ordinance (AbwV) for treatment plants serving communities of up to 100,000 inhabitants. "This means that operators of such plants could generate additional revenue from the production of fertilizer as a sideline to the treatment of wastewater," says Bilbao, citing this as a decisive advantage. Struvite is an attractive product for farmers, because it is valued as a high-quality, slow-release fertilizer. Experiments conducted by the Fraunhofer researchers have confirmed its effectiveness in this respect: crop yields and the uptake of nutrients by the growing plants were up to four times higher with struvite than with commercially available mineral fertilizers.
The scientists intend to spend the next few months testing the mobile pilot plant at a variety of wastewater treatment plants before starting to commercialize the process in collaboration with industrial partners early next year. "Our process is also suitable for wastewaters from the food-industry and from the production of biogas from agricultural wastes," adds Bilbao. The only prerequisite is that the process water should be rich in ammonium and phosphates.
INFORMATION:
Using wastewater as fertilizer
2012-08-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Making it easier to learn to read
2012-08-07
This press release is available in German.
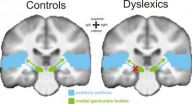
To participate successfully in life, it is important to be able to read and write. Nevertheless, many children and adults have difficulties in acquiring these skills and the reason is not always obvious. They suffer from dyslexia which can have a variety of symptoms. Thanks to research carried out by Begoña Díaz and her colleagues at the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig, a major step forward has been made in understanding the cause of dyslexia. The scientists have discovered an important ...
Lower risk of serious side-effects in trials of new targeted drugs
2012-08-07
Patients in early clinical trials of new-style targeted cancer therapies appear to have a much lower risk of the most serious side-effects than with traditional chemotherapy, according to a new analysis.
Researchers at The Institute of Cancer Research, London, and The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust analysed data from 36 Phase I trials run by the organisations' joint Drug Development Unit.
The study, published today in August's Annals of Oncology, found the overall risk to patients of suffering a life-threatening side-effect was around seven times less than for traditional ...
Study questions value of calcium and vitamin D supplements
2012-08-07
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – Aug. 7, 2012 – Prescribing calcium and vitamin D supplements for men at risk of bone loss from hormonal treatment for prostate cancer seems like good medicine.
But new research from epidemiologists at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center showed that this type of supplementation did not prevent bone loss and, in fact, may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and aggressive prostate cancer. The study was published online in the July issue of the journal The Oncologist.
"It wouldn't be so bad if there simply was no obvious benefit," said Gary ...
Children's healthy diets lead to healthier IQ
2012-08-07
Children fed healthy diets in early age may have a slightly higher IQ, while those on heavier junk food diets may have a slightly reduced IQ, according to new research from the University of Adelaide.
The study - led by University of Adelaide Public Health researcher Dr Lisa Smithers - looked at the link between the eating habits of children at six months, 15 months and two years, and their IQ at eight years of age.
The study of more than 7000 children compared a range of dietary patterns, including traditional and contemporary home-prepared food, ready-prepared baby ...
What makes Paris look like Paris? Carnegie Mellon software finds stylistic core
2012-08-07
PITTSBURGH—Paris is one of those cities that has a look all its own, something that goes beyond landmarks such as the Eiffel Tower or Notre Dame. Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University and INRIA/Ecole Normale Supérieure in Paris have developed visual data mining software that can automatically detect these sometimes subtle features, such as street signs, streetlamps and balcony railings, that give Paris and other cities a distinctive look.
The software analyzed more than 250 million visual elements gleaned from 40,000 Google Street View images of Paris, London, New ...
Should young men be vaccinated against human papilloma virus?
2012-08-07
New Rochelle, NY, August 7, 2012 — Vaccination against human papilloma virus (HPV) is recommended for young women to protect them from HPV infection and cervical cancer. Male HPV immunization is increasingly a topic of debate in the medical community. A timely review of the literature published in Viral Immunology, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers (http://www.liebertpub.com), explores whether HPV vaccination of young men is warranted and cost effective. The article is available free online at the Viral Immunology (http://www.liebertpub.com/vim) ...
Study reveals impact of historical domestic cattle hybridization with American bison
2012-08-07
Plains bison are an iconic symbol of America on everything from coins to state flags. Now scientists writing in Conservation Biology are exploring how the cross-breeding of bison with domestic cattle in the late 1800s may still have unwanted effects on modern populations of the species.
"The plains bison are an iconic symbol of rugged individualism and the will to survive," said Professor James Derr from Texas A&M University. "The population crash and the spectacular recovery over the last 125 years is a classic example of the resilience of this species and the success ...
The economic cost of increased temperatures
2012-08-07
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. -- Even temporary rises in local temperatures significantly damage long-term economic growth in the world's developing nations, according to a new study co-authored by an MIT economist.
Looking at weather data over the last half-century, the study finds that every 1-degree-Celsius increase in a poor country, over the course of a given year, reduces its economic growth by about 1.3 percentage points. However, this only applies to the world's developing nations; wealthier countries do not appear to be affected by the variations in temperature.
"Higher ...
A simple way to help cities monitor traffic more accurately
2012-08-07
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Cities count the number of cars on the road in order to plan everything from the timing of stoplights to road repairs. But the in-road metal detectors that do the counting can make errors – most often by registering that a car is present when one isn't.
One common error is called "splashover" because it usually involves an over-sensitive detector picking up the presence a vehicle in the next lane over – as if the signal from the car "splashed over" into the adjacent lane.
Now Ohio State University researchers have developed software to help city managers ...
Greater working memory capacity benefits analytic, but not creative, problem-solving
2012-08-07
Psychological scientists have long known that the amount of information we can actively hold in mind at any given time – known as working memory – is limited. Our working memory capacity reflects our ability to focus and control attention and strongly influences our ability to solve problems.
In a new article in the August issue of Current Directions in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, Jennifer Wiley and Andrew Jarosz of the University of Illinois at Chicago explore the role of working memory capacity in both mathematical ...