(Press-News.org) Ann Arbor, Mich. — Significantly more children get health insurance coverage after increases in federal matching funds to states for Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP), according to new research from the University of Michigan.
The research, published Monday in the journal Health Affairs, showed that a 10-percentage-point increase in the federal match for Medicaid and CHIP, similar to the increase that occurred with the American Reinvestment and Recovery Act, is associated with an increase of 1.9 percent in the number of children enrolled in Medicaid nationwide, or approximately 500,000 additional children.
"Throughout the past decade, Medicaid and CHIP enrollment for children has increased, while the level of uninsurance has decreased. Our study suggests that these combined federal and state programs have succeeded in providing health insurance coverage for children, even as the number of children in poor and low-income families has increased," says Stephen Patrick, M.D., M.P.H., M.S., the study's lead author and a neonatal-perinatal medicine fellow in the Department of Pediatrics and Communicable Diseases at C.S. Mott Children's Hospital at the University of Michigan.
Patrick is a 2010-12 Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Clinical Scholar at the University of Michigan.
"Medicaid and CHIP work as a partnership between states and the federal government that benefits children," says Matthew M. Davis, M.D., M.A.P.P., associate professor in the Child Health Evaluation and Research Unit and the Division of General Medicine at the U-M Medical School and associate professor of public policy at the Gerald R. Ford School of Public Policy.
"We found a strong relationship between the federal share of funding, called the Federal Medical Assistance Percentage, and Medicaid enrollment for children over the past decade," says Davis, who is senior author on the paper.
"Congress can change the federal match at any time, and they have increased the match to help states during tough economic times," explains Davis. "The match was increased during our recent recession, but returned to previous levels in June 2011. We found that changes in FMAP are associated with significant changes in children's health care coverage through Medicaid and CHIP, even after accounting for state-level factors such as government revenues and proportion of children living in poverty."
It is not yet clear what effect the federal match decrease in 2011 will have on children's health care coverage.
"When states receive reduced federal funds for Medicaid, they may be forced to limit their outreach to enroll eligible children, restrict optional benefits, or otherwise reduce activities in their Medicaid programs that they might pursue," Patrick says. "It is clear from decades of research that children with coverage have better access to timely health care than children without coverage.
"The fact that it requires an act of Congress to respond to states' economic downturns through the federal match mechanism suggests that the match needs to be modernized," says Patrick.
The researchers analyzed publicly available data from all 50 states from 1999 to 2009.
INFORMATION:Journal citation: doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2011.0988 HEALTH AFFAIRS 31,
NO. 8 (2012)
Funding: This work was supported by a grant from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Clinical Scholars Program.
Additional author: From the University of Michigan: Hwajung Choi, research analyst, Department of Internal Medicine.
About the University of Michigan Health System:
For more than 160 years, the University of Michigan Health System has been a national leader in advanced patient care, innovative research to improve human health and comprehensive education of physicians and medical scientists. UMHS includes the U-M Hospitals & Health Centers, with its three hospitals and dozens of outpatient health centers and clinics throughout Michigan; the U-M Medical School with its Faculty Group Practice and research laboratories; and the Michigan Health Corporation.
The three U-M hospitals -- University Hospital, C.S. Mott Children's Hospital, and Von Voigtlander Women's Hospital – have been recognized numerous times for excellence in patient care, including 17 years on the U.S. News & World Report honor roll of "America's Best Hospitals."
Learn more at www.mottchildren.org
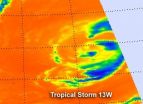
Infrared satellite imagery from shows how cold cloud top temperatures are in a tropical cyclone, and recent imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite shows the cloud-top temperatures have been warming in Tropical Storm 13W. Warming cloud top temperatures indicate less strength, and Tropical Storm 13W is weakening.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm 13W on August 7 at 0253 UTC. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies onboard Aqua captured an infrared image of the storm's cloud temperatures that showed very limited strong thunderstorms make ...
Tropical Storm Haikui is headed for landfall in southeastern China, and NASA's Aqua satellite caught a stunning image of its size and its ragged, but wide eye when it was a typhoon earlier today, August 7. As a result of interaction with land, Haikui has weakened to a tropical storm.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Typhoon Haikui on August 6, 2012 at 12:35 a.m. EDT the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument onboard captured an image of the storm as it was approaching China. The MODIS image clearly showed Haikui's ragged and elongated eye ...
Satellite data helps forecasters see where the strongest part of a tropical cyclone is located, and NASA's Aqua satellite noticed Ernesto's strongest storms were on the eastern side yesterday. Today, strong storms surround Ernesto's center.
A visible image of Tropical Storm Ernesto approaching Central America was captured by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument that flies onboard NASA's Aqua satellite. In an image captured on August 6, 2012 at 1840 UTC (2:40 p.m. EDT), the strongest thunderstorms appeared to be on the northern and eastern ...
Conflict-of-interest statements made by physicians and scientists in their medical journal articles after they had been allegedly paid by pharmaceutical manufacturers as part of off-label marketing programs are often inadequate, highlighting the deficiencies in relying on author candidness and the weaknesses in some journal practices in ensuring proper disclosure, according to a study by international researchers published in this week's PLOS Medicine. Off-label marketing is the promotion by a manufacturer of a drug for use in a condition or age group, or in a dose or form ...
NJIT Distinguished Research Professor and former Bell Labs scientist Louis J. Lanzerotti, will see his 50-year quest to better understand space weather and Earth's Van Allen Radiation Belts rocket, once again, into space on Aug. 23, 2012. This is when NASA's twin Radiation Belt Storm Probes (RBSP) begin their mission to study the extremes of space weather. Lanzerotti, today one of the most respected and valued scientists behind space exploration, was the principal investigator to build one of five instruments aboard each of the two spacecraft that comprise the RBSP mission. ...
A research article by Katharina Kranzer from the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine and colleagues describe the feasibility and costs of an active tuberculosis case finding project in Cape Town, South Africa.
The study describes the integration of tuberculosis testing into a mobile HIV testing service for HIV-negative individuals with symptoms suggestive of tuberculosis and all HIV-positive individuals.
The mobile testing clinic, named the Tutu Tester after Archbishop Emeritus Desmond Tutu, visits underserviced areas in greater Cape Town and provides testing ...
PISCATAWAY, NJ – Heavy drinking is known to affect teenagers' developing brains, but certain patterns of brain activity may also help predict which kids are at risk of becoming problem drinkers, according to a study in the September issue of the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
Using special MRI scans, researchers looked at 40 12- to 16-year-olds who had not started drinking yet, then followed them for about 3 years and scanned them again. Half of the teens started to drink alcohol fairly heavily during this interval. The investigators found that kids who had ...
New research confirms no significant difference in the rates of death among patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who were exposed to one of several TNF inhibitors used to treat RA, adalimumab (Humira), etanercept (Enbrel), and infliximab (Remicade). This population-based study of RA patients in Sweden—the first to compare mortality rates among patients treated with individual TNF inhibitors—is now available in Arthritis & Rheumatism, a journal published by Wiley on behalf of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
RA is a chronic, autoimmune disease characterized ...
VANCOUVER, Wash. — Washington State University researchers have documented an underappreciated suite of players in global warming: dams, the water reservoirs behind them, and surges of greenhouse gases as water levels go up and down.
Bridget Deemer, a doctoral student at Washington State University-Vancouver, measured dissolved gases in the water column of Lacamas Lake in Clark County and found methane emissions jumped 20-fold when the water level was drawn down. A fellow WSU-Vancouver student, Maria Glavin, sampled bubbles rising from the lake mud and measured a 36-fold ...
The new website incorporates the previous site's branding and a new industry standard user experience. X & D Supply is leveraging the Magento Open Commerce Platform along with Thoughtrend 's product data warehouse. The aims of the site are to allow visitors a means to quickly find the items they're looking for while allowing X & D Supply to maximize its growth through a new sales channel.
"Our new site offers end users a means to more efficiently purchase industrial tools and related MRO equipment online", says Mike Graven of X & D Supply. The new ...