(Press-News.org) Guided press tour
The excavation will be open to the press on Wednesday 15 August from 13.00 to 15.30.The tour starts at Alkenvej 171, 8660 Skanderborg.
Macabre finds in the bog at Alken Enge
A fractured skull and a thigh bone hacked in half -- finds of damaged human bones along with axes, spears, clubs and shields confirm that the bog at Alken Enge was the site of violent conflict
2012-08-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ship-borne measurements show EU policies have improved air quality in harbors
2012-08-14
Sulphur dioxide emissions from shipping have sharply decreased in EU ports thanks to an EU policy which limits sulphur content in fuels for ships at berth or at anchor in ports. Scientists at the European Commission's Joint Research Centre measured key air quality parameters in Mediterranean harbours before and after the entry into force of the low-sulphur requirements in January 2010. In European harbours they found an average decrease of 66% in concentrations of sulphur dioxide, a chemical compound that poses risks to health and the environment. Measurements taken in ...
Feedback can have a negative impact on performance
2012-08-14
People who give positive encouragement and constructive criticism could be wasting their breath according to the latest research from a psychology expert at Queen Mary, University of London.
The study, published in the journal Frontiers in Neuroscience, found that when people received either positive or negative feedback about their performance on complex decision-making tasks, it made their decision making worse.
Study author Dr Magda Osman explained: "The kind of task people had to perform was difficult and demanding. So, when people received positive or negative ...
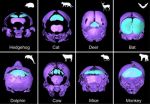
Old skull bone rediscovered
2012-08-14
The mammalian skull, including that of people, is composed of about 20 bones. Fish, reptile and bird skulls, however, have considerably more. After all, when mammals evolved from reptile-like vertebrates 320 million years ago, the skull's structure became simplified during its development and the number of skull bones decreased.
Some bones were lost in the lineage leading to mammals in the course of evolution, especially a number of skull roof bones. The skull's interparietal, which is one of the skull roof bones, particularly puzzled researchers: on the one hand, it ...
UC discoveries could help quiet the world's cities
2012-08-14
They're sleek. They're fast. They're powerful. And, they are deafening. Furthermore, those Top Gun military jets need to be up in the air in the wee hours – over land – to simulate their landings on aircraft carriers. But innovations out of the University of Cincinnati's Gas Dynamics and Propulsion Laboratory are showing promise in reducing the intense noise of these supersonic jets without impacting their power. It's research that can help neighborhoods slumber a little more soundly, keep their windows rattling a little less loudly and also protect the hearing of military ...
If it rolls or flies, UC research is working to keep it quiet
2012-08-14
University of Cincinnati research – from noise reduction in sophisticated military jets to quieter car rides – will be presented at INTER-NOISE 2012, the 41st International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering, to be held Aug. 19-22 in New York City. UC is among only a few universities with a specific focus on vehicle noise control.
The UC research to be presented at INTER-NOISE:
UC innovations to reduce the noise of the nation's most sophisticated military aircraft. Jeff Kastner, research assistant professor in the UC College of Engineering and Applied ...
UC research promises quiet cars -- even when hitting unexpected bumps in the road
2012-08-14
All noise is not necessarily equal – especially when it comes to sound minimization in automobiles.
For instance, automakers have long used sound-absorbing materials (passive control) in the design of cars in order to minimize engine noise and the "routine" noise of tires traveling on smooth pavement at a consistent speed. However, a means to minimize sudden, unexpected noises – like those from an encounter with potholes, bumps or other roadway pavement obstacles – has been more problematic.
A significant step in countering such unexpected roadway noises is the development ...
Marine research in the Brazilian rainforest
2012-08-14
Until recent decades the Atlantic Rainforest covered a large area of today's Brazil from Amazonas to present-day Argentina. In the 1970s, after years of deforestation, this rain forest was almost completely destroyed, mainly replaced by cattle pastures. This study reveals an unexpected aspect of deforestation. Thorsten Dittmar's team and colleagues from Brazil and the USA show that the common practice of slash and burn left huge amounts of charcoal in the soil. This charcoal is washed out by rainfalls and transported by rivers into the Atlantic Ocean. The soluble fraction ...
Girls with ADHD at risk for self-injury, suicide attempts as young adults, says new research
2012-08-14
WASHINGTON – Girls with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder are significantly more likely to attempt suicide or injure themselves as young adults than girls who do not have ADHD, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
Young women diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder as girls, particularly the type with early signs of impulsivity, were three to four times more likely to attempt suicide and two to three times more likely to report injuring themselves than comparable young women in a control group, according to ...
Hope for patients with HIV-associated cognitive impairment
2012-08-14
Current drug therapy for patients with HIV is unable to control the complete replication of the virus in the brain. The drugs therefore do not have any effect against the complications associated with neurocognitive impairment in patients with HIV. New research by Joseph Steiner and colleagues from Johns Hopkins University has discovered that a group of plant polyphenols known as catechins, which naturally occur in green tea and the seed of the cacao tree, may help in the prevention of these neurological complications. Their work is published online in Springer's Journal ...
Scientists uncover strategy able to dramatically reduce chemotherapy's side effects
2012-08-14
Researchers in Leuven (VIB/KU Leuven) have confirmed their hypothesis that normalizing blood vessels by blocking oxygen sensor PHD2 would make chemotherapy more effective. They also demonstrated for the first time that this strategy would reduce the harmful side effects of chemotherapy on healthy organs.
Limited success of chemotherapy
The effectiveness of chemotherapy is first and foremost limited by the difficulties of delivering the anticancer drugs to the actual tumor. Tumors are characterized by abnormally shaped blood vessels – they are irregular in shape, have ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
[Press-News.org] Macabre finds in the bog at Alken EngeA fractured skull and a thigh bone hacked in half -- finds of damaged human bones along with axes, spears, clubs and shields confirm that the bog at Alken Enge was the site of violent conflict