(Press-News.org) A new study by researchers at the University of California, San Diego, and Emory University has uncovered fundamental details about the hexamer structures that make up the tiniest droplets of water, the key component of life – and one that scientists still don't fully understand.
The research, recently published in The Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS), provides a new interpretation for experimental measurements as well as a vital test for future studies of our most precious resource. Moreover, understanding the properties of water at the molecular level can ultimately have an impact on many areas of science, including the development of new drugs or advances in climate change research.
"About 60% of our bodies are made of water that effectively mediates all biological processes," said Francesco Paesani, one of the paper's corresponding authors who is an assistant professor in the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry at UC San Diego and a computational researcher with the university's San Diego Supercomputer Center (SDSC). "Without water, proteins don't work and life as we know it wouldn't exist. Understanding the molecular properties of the hydrogen bond network of water is the key to understanding everything else that happens in water. And we still don't have a precise picture of the molecular structure of liquid water in different environments."
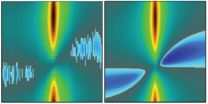
Researchers know that the unique properties of water are due to its capability of forming a highly flexible but still dense hydrogen bond network which adapts according to the surrounding environment. As described in the JACS paper, researchers have determined the relative populations of the different isomers of the water hexamer as they assemble into various configurations called 'cage', 'prism', and 'book'.
The water hexamer is considered the smallest drop of water because it is the smallest water cluster that is three dimensional, i.e., a cluster where the oxygen atoms of the molecules do not lie on the same plane. As such, it is the prototypical system for understanding the properties of the hydrogen bond dynamics in the condensed phases because of its direct connection with ice, as well as with the structural arrangements that occur in liquid water.
This system also allows scientists to better understand the structure and dynamics of water in its liquid state, which plays a central role in many phenomena of relevance to different areas of science, including physics, chemistry, biology, geology, and climate research. For example, the hydration structure around proteins affects their stability and function, water in the active sites of enzymes affects their catalytic power, and the behavior of water adsorbed on atmospheric particles drives the formation of clouds.
"Until now, experiments and calculations on small water clusters have agreed very well up to the pentamer (in chemistry, meaning molecules made of five monomers) but the energetic ordering of the low-lying isomers of the hexamer has always been controversial," said Paesani.
Added corresponding author Joel M. Bowman, with Emory University's Department of Chemistry and the Cherry L. Emerson Center for Scientific Computation: "Ours are the first simulations that use an accurate, full-dimensional representation of the molecular interactions and exact inclusion of nuclear quantum effects through state-of-the-art computational approaches. These allow us to accurately determine the stability of the different isomers over a wide range of temperatures ranging from 0 to 150 Kelvin, (almost minus 460 degrees to about minus 190 degrees Fahrenheit)."
While the prism isomer was identified as the global minimum-energy structure, the quantum simulations predicted that both the cage and prism isomers are present in nearly equal amounts at extremely low temperatures, researchers found. As the temperature increased, more cages, and then book structures, began to appear.
Researchers used SDSC's new data-intensive Gordon supercomputer as well as SDSC's Triton compute cluster to conduct the data-intensive simulations.
"Our simulations took full advantage of Gordon distributing the computations over thousands of processors," said Volodymyr Babin, a researcher with UC San Diego's Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry. "That kind of parallel efficiency would be hardly achievable on a commodity cluster. The scalability of our computational approach stems from the combination of a state-of-the-art simulation technique (replica-exchange) with path-integral molecular dynamics."
Babin said the team is currently working on extending this methodology to study the microscopic origins of the unusual properties of liquid water and ice aiming to assess quantitatively the role played by nuclear quantum effects in the topology of the water phase diagram. This project involves a huge number of data-intensive quantum chemistry computations that are only feasible on supercomputers of the same class as Gordon, he added.
INFORMATION:
The JACS paper is called "The Water Hexamer: Cage, Prism or Both. Full Dimensional Quantum Simulations Say Both," and also included Yimin Wang from Emory University, who developed the potential used in the simulations. The research was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) through grants CHE-1111364 and CHE-1038028, NSF award TG-CHE110009 for computing time on the Extreme Science and Engineering Discovery Environment (XSEDE), and awards from the CCI Center for Aerosol Impacts on Climate and the Environment.
UC San Diego News on the web at: http://ucsdnews.ucsd.edu
A massive galaxy cluster nearly six billion light years from Earth has been discovered with an astounding and unexpected burst of star formation – more prodigious than any galaxy cluster yet observed, an international team of astronomers and NASA announced today.
In a wide-ranging discussion on the eve of the announcement, two of the leading astronomers on the project talked about the record-breaking galaxy cluster, called Phoenix, and how its surprising properties are prompting astronomers to re-think how galaxy clusters – among the largest structures in the universe ...
A long-time staple of science fiction is the tractor beam, a technology in which light is used to move massive objects – recall the tractor beam in the movie Star Wars that captured the Millennium Falcon and pulled it into the Death Star. While tractor beams of this sort remain science fiction, beams of light today are being used to mechanically manipulate atoms or tiny glass beads, with rapid progress being made to control increasingly larger objects. Those who see major roles for optomechanical systems in a host of future technologies will take heart in the latest results ...
JUPITER, FL, August 15, 2012 – Working with a national team of researchers, a scientist from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute has shown for the first time a link between low levels of a specific hormone and increased risk of metabolic disease in humans.
The study, published online ahead of print in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, focuses on the hormone adropin, which was previously identified by Scripps Research Associate Professor Andrew Butler's laboratory during an investigation of obese and insulin-resistant mice. Adropin is ...
Astronomers have found an extraordinary galaxy cluster — one of the largest objects in the universe — that is breaking several important cosmic records. The discovery of this cluster, known as the Phoenix Cluster, made with the National Science Foundation's South Pole Telescope, may force astronomers to rethink how these colossal structures, and the galaxies that inhabit them, evolve.
Follow-up observations made in ultraviolet, optical and infrared wavelengths show that stars are forming in this object at the highest rate ever seen in the middle of a galaxy cluster. The ...
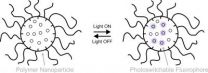
CORAL GABLES, FL (August, 15, 2012)--University of Miami scientists have developed a way to switch fluorescent molecules on and off within aqueous environments, by strategically trapping the molecules inside water-soluble particles and controlling them with ultraviolet light. The new system can be used to develop better fluorescent probes for biomedical research.
Previous studies have used water-soluble particles to bring organic molecules into water. What is novel about this system is the use of a photoswitching mechanism in combination with these particles.
The findings ...
A National Science Foundation-funded radio telescope in Antarctica has found an extraordinary galaxy cluster that may force astronomers to rethink how galaxy clusters and the galaxies that inhabit them evolve.
The galaxy cluster was discovered some 5.7 billion light years from Earth by the 10-meter wide South Pole Telescope (SPT) located at NSF's Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station in Antarctica, which is funded by NSF's Office of Polar Programs.
NSF manages the U.S. Antarctic Program, through which it coordinates all U.S research and required logistical support on the ...
Scientists using the Lyman Alpha Mapping Project (LAMP) spectrometer aboard NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) have made the first spectroscopic observations of the noble gas helium in the tenuous atmosphere surrounding the Moon.
These remote-sensing observations complement in situ measurements taken in 1972 by the Lunar Atmosphere Composition Experiment (LACE) deployed by Apollo 17.
Although designed to map the lunar surface, the LAMP team expanded its science investigation to examine the far ultraviolet emissions visible in the tenuous atmosphere above the ...
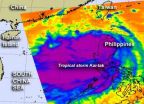
Warnings are still in effect in the northern Philippines and now in Hong Kong, as Tropical Storm Kai-tak continues to drop heavy rainfall and move toward a landfall in China. NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared data that shows a large area of strong thunderstorms that make up Kai-tak.
NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared data on Kai-tak when it passed overhead on August 15 at 0517 UTC (1:17 a.m. EDT/1:17 p.m. local time, Hong Kong). Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted that infrared satellite imagery shows the organization near the center of Kai-tak's ...
Scientists using the Lyman Alpha Mapping Project (LAMP) aboard NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter have made the first spectroscopic observations of the noble gas helium in the tenuous atmosphere surrounding the Moon. These remote-sensing observations complement in-situ measurements taken in 1972 by the Lunar Atmosphere Composition Experiment (LACE) deployed by Apollo 17.
Although LAMP was designed to map the lunar surface, the team expanded its science investigation to examine the far ultraviolet emissions visible in the tenuous atmosphere above the lunar surface, detecting ...
Two tropical cyclones were spotted from NOAA's GOES-15 satellite today, August 15. Tropical Storm Hector continues to weaken in the Eastern Pacific Ocean, while the remnants of the Atlantic Ocean's Tropical Depression 7 are moving over Central America. NASA's GOES Project, located at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md., uses the GOES-15 satellite data to create images and animations from the satellite. The NOAA GOES-15 satellite sits in a fixed orbit over the eastern U.S. and provides infrared and visible imagery of the Eastern Pacific Ocean basin continuously. ...