(Press-News.org) Everyone knows the adage: "If something sounds too good to be true, then it probably is." Why, then, do some people fall for scams and why are older folks especially prone to being duped?
An answer, it seems, is because a specific area of the brain has deteriorated or is damaged, according to researchers at the University of Iowa. By examining patients with various forms of brain damage, the researchers report they've pinpointed the precise location in the human brain, called the ventromedial prefrontal cortex, that controls belief and doubt, and which explains why some of us are more gullible than others.
"The current study provides the first direct evidence beyond anecdotal reports that damage to the vmPFC (ventromedial prefrontal cortex) increases credulity. Indeed, this specific deficit may explain why highly intelligent vmPFC patients can fall victim to seemingly obvious fraud schemes," the researchers wrote in the paper published in a special issue of the journal Frontiers in Neuroscience.
A study conducted for the National Institute of Justice in 2009 concluded that nearly 12 percent of Americans 60 and older had been exploited financially by a family member or a stranger. And, a report last year by insurer MetLife Inc. estimated the annual loss by victims of elder financial abuse at $2.9 billion.
The authors point out their research can explain why the elderly are vulnerable.
"In our theory, the more effortful process of disbelief (to items initially believed) is mediated by the vmPFC, which, in old age, tends to disproportionately lose structural integrity and associated functionality," they wrote. "Thus, we suggest that vulnerability to misleading information, outright deception and fraud in older adults is the specific result of a deficit in the doubt process that is mediated by the vmPFC."
The ventromedial prefrontal cortex is an oval-shaped lobe about the size of a softball lodged in the front of the human head, right above the eyes. It's part of a larger area known to scientists since the extraordinary case of Phineas Gage that controls a range of emotions and behaviors, from impulsivity to poor planning. But brain scientists have struggled to identify which regions of the prefrontal cortex govern specific emotions and behaviors, including the cognitive seesaw between belief and doubt.
The UI team drew from its Neurological Patient Registry, which was established in 1982 and has more than 500 active members with various forms of damage to one or more regions in the brain. From that pool, the researchers chose 18 patients with damage to the ventromedial prefrontal cortex and 21 patients with damage outside the prefrontal cortex. Those patients, along with people with no brain damage, were shown advertisements mimicking ones flagged as misleading by the Federal Trade Commission to test how much they believed or doubted the ads. The deception in the ads was subtle; for example, an ad for "Legacy Luggage" that trumpets the gear as "American Quality" turned on the consumer's ability to distinguish whether the luggage was manufactured in the United States versus inspected in the country.
Each participant was asked to gauge how much he or she believed the deceptive ad and how likely he or she would buy the item if it were available. The researchers found that the patients with damage to the ventromedial prefrontal cortex were roughly twice as likely to believe a given ad, even when given disclaimer information pointing out it was misleading. And, they were more likely to buy the item, regardless of whether misleading information had been corrected.
"Behaviorally, they fail the test to the greatest extent," says Natalie Denburg, assistant professor in neurology who devised the ad tests. "They believe the ads the most, and they demonstrate the highest purchase intention. Taken together, it makes them the most vulnerable to being deceived." She added the sample size is small and further studies are warranted.
Apart from being damaged, the ventromedial prefrontal cortex begins to deteriorate as people reach age 60 and older, although the onset and the pace of deterioration varies, says Daniel Tranel, neurology and psychology professor at the UI and corresponding author on the paper. He thinks the finding will enable doctors, caregivers, and relatives to be more understanding of decision making by the elderly.
"And maybe protective," Tranel adds. "Instead of saying, 'How would you do something silly and transparently stupid,' people may have a better appreciation of the fact that older people have lost the biological mechanism that allows them to see the disadvantageous nature of their decisions."
The finding corroborates an idea studied by the paper's first author, Erik Asp, who wondered why damage to the prefrontal cortex would impair the ability to doubt but not the initial belief as well. Asp created a model, which he called the False Tagging Theory, to separate the two notions and confirm that doubt is housed in the prefrontal cortex.
"This study is strong empirical evidence suggesting that the False Tagging Theory is correct," says Asp, who earned his doctorate in neuroscience from the UI in May and is now at the University of Chicago.
INFORMATION:
Kenneth Manzel, Bryan Koestner, and Catherine Cole from the UI are contributing authors on the paper. The National Institute on Aging and the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke funded the research.
Why are elderly duped? UI researchers explain why
2012-08-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Danes frequently confronted by religion
2012-08-16
Ramadan dinners in the Danish Parliament, staff parties without either pork or alcohol and prayer rooms at the airport are all examples of how religion is becoming more visible in public spaces.
"Prior to the mass migration of the '60s, '70s and '80s, almost all Danes shared similar values and were members of the national Christian church, so religion was not an issue in everyday life. There was no need to discuss neither one's own nor another person's religious viewpoint, and secularisation was a matter of course. Today, it is difficult to be in a public place, read ...
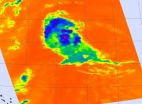
NASA sees System 93L explode into Tropical Storm Gordon
2012-08-16
VIDEO:
An animation of satellite observations from Aug. 13-16, 2012 shows the birth of the Atlantic Ocean hurricane season's eighth tropical depression that strengthens into Tropical Storm Gordon. This visualization was...
Click here for more information.
NASA has been watching the low pressure system called System 93L for the last week, and late on August 15 it organized into Tropical Depression 8, then Tropical Storm Gordon. NOAA's GOES-13 satellite captured a visible ...
Hubble watches star clusters on a collision course
2012-08-16
Astronomers using data from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope have caught two clusters full of massive stars that may be in the early stages of merging. The clusters are 170,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a small satellite galaxy to our Milky Way.
What at first was thought to be only one cluster in the core of the massive star-forming region 30 Doradus (also known as the Tarantula Nebula) has been found to be a composite of two clusters that differ in age by about one million years.
The entire 30 Doradus complex has been an active star-forming region ...
NASA is tracking electron beams from the sun
2012-08-16
In the quest to understand how the world's weather moves around the globe, scientists have had to tease apart different kinds of atmospheric movement, such as the great jet streams that can move across a whole hemisphere versus more intricate, localized flows. Much the same must currently be done to understand the various motions at work in the great space weather system that links the sun and Earth as the sun shoots material out in all directions, creating its own version of a particle sea to fill up the solar system.
"People think of the sun as giving out light and ...
Metabolic protein wields phosphate group to activate cancer-promoting genes
2012-08-16
HOUSTON - A metabolic protein that nourishes cancer cells also activates tumor-promoting genes by loosening part of the packaging that entwines DNA to make up chromosomes, a team led by scientists at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center reports in the Aug. 16 issue of Cell.
Working in cell lines and mouse models of glioblastoma multiforme, the most lethal form of brain tumor, senior author Zhimin Lu, Ph.D., associate professor of Neuro-Oncology at MD Anderson, and colleagues show that pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) fuels tumor growth by influencing a histone protein.
DNA ...
Annals of Internal Medicine publishes new CDC recommendations on hepatitis C screening
2012-08-16
PHILADELPHIA, August 16, 2012 – Without other risk factors, all Americans born between 1945 and 1965 should have a one-time screening for the hepatitis C virus (HCV) according to new recommendations being published early online today in Annals of Internal Medicine, the flagship journal of the American College of Physicians. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) also recommends that all persons identified with HCV should receive a brief alcohol screening and intervention and be referred to appropriate care and treatment services for HCV and related conditions.
Up ...
Thermafiber Releases RainBarrier HD
2012-08-16
Thermafiber has officially announced the release of a new continuous insulation product. RainBarrier HD (Heavy Density) is a rigid insulation board with a consistent 6.0pcf density throughout the entire thickness. The consistent density from top to bottom simplifies installation by eliminating the need to orient the insulation in a certain direction like other mixed-density products. The increased density enhances the rigidity and ease of fabrication. The mineral wool board is non-combustible and provides exceptional R-values of 4.2 per inch of thickness. In addition to ...
Resistance to dementia may run in the family
2012-08-16
MINNEAPOLIS – People who are free of dementia and have high levels of a protein that indicates the presence of inflammation have relatives who are more likely to avoid the disease as well, according to a new study published in the August 15, 2012, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
"In very elderly people with good cognition, higher levels of C-reactive protein, which is related to inflammation, are associated with better memory," said study author Jeremy M. Silverman, PhD, with Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New ...
Both early alcohol use and early intoxication can herald trouble for college students
2012-08-16
An early age at first drink (AFD) has been linked to later alcohol-related problems, which is one of the reasons behind the legal drinking age of 21 in the U.S. It is unclear, however, if increased risk is primarily due to initiation of any drinking, or initiation of heavier drinking. A comparison of the influence of these potential risk factors among college undergraduates found that both an early AFD as well as a quick progression from the first drink to drinking to intoxication independently predicted later problems.
Results will be published in the November 2012 ...
Examining alcohol + energy drink consumption among the Australian public
2012-08-16
Not only have energy drinks become increasingly popular among adolescents and young adults in recent years, so too has mixing and drinking them with alcohol. However, research on the subjective psychological, physiological, and behavioral risk-taking outcomes of alcohol/energy drinks has had mixed results. A first-of-its-kind study compares the outcomes of alcohol/energy drinks with alcohol-only drinks among members of the Australian public.
Results will be published in the November 2012 issue of Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research and are currently available ...