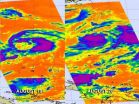
(Press-News.org) NASA's Terra and Aqua satellite have captured Hurricane Gordon over three days as it neared the Azores Islands in the eastern Atlantic Ocean. Gordon weakened to a tropical storm on August 20.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS, is an instrument that flies onboard NASA's Terra and Aqua satellites and provides high-resolution imagery to users. When NASA's Terra satellite flew over Gordon on August 17 at 9:30 a.m. EDT it was a tropical storm and did not have a visible eye. It was followed up by a fly over of NASA's Aqua satellite on August 18 at 11:50 a.m. EDT, it had strengthened into a hurricane and had a clear and visible eye. On August 19, Gordon was still a hurricane at 10:55 a.m. EDT when NASA's Aqua satellite again passed over the storm. At that time, Gordon was affecting the Azores Islands. Ocean swells in the eastern Azores generated by Gordon are expected to start subsiding today, August 20, as Gordon moves east and toward Portugal.
At 8 a.m. EDT (1200 UTC) on August 20, Gordon weakened back to tropical storm status with maximum sustained winds near 70 mph (110 kmh). The center of Tropical Storm Gordon was located about 115 miles (180 km) east-northeast of Santa Maria Island in the Azores, near latitude 37.7 north and longitude 23.2 west. The National Hurricane Center noted that Gordon is moving toward the east-northeast near 15 mph (24 kmh) and is expected to slow and turn east.
The National Hurricane Center expects Tropical Storm Gordon to become extra-tropical later in the day on August 20.
INFORMATION:
NASA satellites capture 3 days of Hurricane Gordon's Atlantic track
2012-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
First evidence discovered of planet's destruction by its star
2012-08-21
The first evidence of a planet's destruction by its aging star has been discovered by an international team of astronomers. The evidence indicates that the missing planet was devoured as the star began expanding into a "red giant" -- the stellar equivalent of advanced age. "A similar fate may await the inner planets in our solar system, when the Sun becomes a red giant and expands all the way out to Earth's orbit some five-billion years from now," said Alexander Wolszczan, Evan Pugh Professor of Astronomy and Astrophysics at Penn State University, who is one of the members ...
NASA watches as Tropical Storm Bolaven develops
2012-08-21
Tropical Storm Bolaven was born over the weekend of August 18-19 in the western North Pacific, and NASA captured infrared satellite imagery of its birth and growth.
NASA's Aqua satellite has been monitoring the birth and progress of Tropical Storm Bolaven in the western North Pacific from Aug 19-20, 2012. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument has provided infrared satellite imagery that shows the development of colder thunderstorm cloud-top temperatures, that were indicative of strengthening storms. Tropical Storm Bolaven also took more of a rounded shape ...
Infants' avoidance of drop-off reflects specific motor ability, not fear
2012-08-21
Researchers have long studied infants' perceptions of safe and risky ground by observing their willingness to cross a visual cliff, a large drop-off covered with a solid glass surface. In crawling, infants grow more likely to avoid the apparent drop-off, leading researchers to conclude that they have a fear of heights. Now a new study has found that although infants learn to avoid the drop-off while crawling, this knowledge doesn't transfer to walking. This suggests that what infants learn is to perceive the limits of their ability to crawl or walk, not a generalized fear ...
Ethnic and political violence increases children's aggressive behavior
2012-08-21
Ethnic and political violence in the Middle East can increase violence in families, schools, and communities, which can in turn boost children's aggressiveness, especially among 8-year-olds. Those are the findings of a new study that examined children and their parents in the Middle East.
"The study has important implications for understanding how political struggles can spill over into the everyday lives of families and children, and suggests that intervention might be necessary in a number of different social areas to protect children from the adverse impacts of exposure ...
For poorer children, living in a high-cost area hurts development
2012-08-21
Young children in lower-income families who live in high-cost areas don't do as well academically as their counterparts in low-cost areas, according to a new study.
The study, by researchers at Child Trends and the University of California (UCLA), appears in the journal Child Development.
"Among families with incomes below 300 percent of the federal poverty threshold—that's below $66,339 for a family of four—living in a region with a higher cost of living was related to lower academic achievement in first grade," according to Nina Chien, a research scientist with Child ...
Sacrificing sleep to study can lead to academic problems
2012-08-21
Regardless of how much a high school student generally studies each day, if that student sacrifices sleep in order to study more than usual, he or she is more likely to have academic problems the following day. Because students tend to increasingly sacrifice sleep time for studying in the latter years of high school, this negative dynamic becomes more and more prevalent over time.
Those are the findings of a new longitudinal study that focused on daily and yearly variations of students who sacrifice sleep to study. The research was conducted at the University of California, ...
Time with parents is important for teens' well-being
2012-08-21
It's thought that children grow increasingly distant and independent from their parents during their teen years. But a new longitudinal study has found that spending time with parents is important to teens' well-being.
The study, conducted at the Pennsylvania State University, appears in the journal Child Development.
Researchers studied whether the stereotype of teens growing apart from their parents and spending less time with them captured the everyday experiences of families by examining changes in the amount of time youths spent with their parents from early to ...
Chain of violence
2012-08-21
ANN ARBOR, Mich.---Children exposed to ethnic and political violence in the Middle East are more aggressive than other children, a new study shows. And the younger children are, the more strongly they are affected, in a "chain of violence" that goes from political and ethnic strife, to violence in communities, schools, and families, and ends with their own aggressive behavior.
"Our results have important implications for understanding how political struggles spill over into the everyday lives of families and children," says psychologist Paul Boxer, lead author of the ...
New survey: Women want to SEE breast reconstruction results before cancer surgery
2012-08-21
VIDEO:
A new survey by the American Society of Plastic Surgeons shows that 89 percent of women want to see what breast reconstruction surgery results would look like before undergoing treatment...
Click here for more information.
A new survey released today by the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) shows that 89 percent of women want to see what breast reconstruction surgery results would look like before undergoing treatment for breast cancer,* prompting the world's ...
MRI findings shed light on multiple sclerosis
2012-08-21
OAK BROOK, Ill. – New magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) research shows that changes in brain blood flow associated with vein abnormalities are not specific for multiple sclerosis (MS) and do not contribute to its severity, despite what some researchers have speculated. Results of the research are published online in the journal Radiology.
"MRI allowed an accurate evaluation of cerebral blood flow that was crucial for our results," said Simone Marziali, M.D., from the Department of Diagnostic Imaging at the University of Rome Tor Vergata in Rome.
MS is a disease of the ...