(Press-News.org) The research relates to a family of molecules firstly discovered in Melbourne that applied to blood cell development. One of these, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor or GM-CSF, acts as a messenger between cells acting at a site of inflammation.
Professor John Hamilton has posed the question: could blocking GM-CSF action lead to a new treatment for inflammatory diseases? In experimental models of rheumatoid arthritis, Professor Hamilton and Dr Andrew Cook had previously shown that blocking GM-CSF function with an antibody suppressed the disease leading to clinical trials which are already showing patient benefit.
They have now shown, in a paper that has just appeared in the world's top ranking arthritis journal, Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, that GM-CSF depletion also suppresses pain in such models; they have also noted similar efficacy in an osteoarthritis experimental model.
"Without a doubt, quality of life and to be free from pain are important issues for people suffering with arthritis-related conditions" said Professor Hamilton.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a debilitating condition with the peak incidence being in people in their 30s and 40s. It is more common in women than in men.
"With our ageing population, the more common condition of osteoarthritis impacts more on our community and medical resources. A new therapy that can block such painful conditions would have massive benefits for health providers and governments in the future" said Dr Cook.
### END
New attack on pain
2012-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Viruses with integrated gene switch
2012-08-21
Numerous viruses are used in the service of science today. They serve as gene taxis to transfer therapeutic genes into body cells or as therapeutic viruses targeted to infect and destroy cancer cells. For such applications, the viruses are often equipped with additional genes, such as for immune mediators or for proteins inducing programmed cell death. However, these gene products can harm the body if they are released at the wrong moment or at excessive levels. "Ideally, we want to be able to turn on and off the transferred genes at a specific time," says Dr. Dirk Nettelbeck, ...
New technology to transform blood processing
2012-08-21
A pioneering surgical blood salvage technology developed at the University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, is set to transform the way major surgery is carried out by reducing blood loss in patients.
HemoSep is set to revolutionise the health care sector after gaining the CE mark and receiving Canadian national approval, following highly successful clinical trials in the world leading University of Kirikkale University Hospital in Ankara, Turkey.
The device is designed to recover blood spilled during open-heart and major trauma surgery and concentrate the blood cells for transfusion ...
Dawn of humanity illuminated in special journal edition – 50 years after the Leakeys
2012-08-21
The first systematic, multidisciplinary results to come out of research conducted on the edge of the Serengeti at the rich palaeoanthropological site in the Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania since that produced by Louis and Mary Leakey's team, have recently been published in a special issue of the prestigious Journal of Human Evolution.
Professor Marion Bamford, deputy director of the Bernard Price Institute for Palaeontological Research, and Professor Ron Clarke from the Institute of Human Evolution – both at the University of the Witwatersrand – contributed papers to the 191-page ...
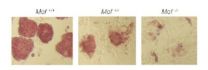
Stem cells can become anything – but not without this protein
2012-08-21
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — How do stem cells preserve their ability to become any type of cell in the body? And how do they "decide" to give up that magical state and start specializing?
If researchers could answer these questions, our ability to harness stem cells to treat disease could explode. Now, a University of Michigan Medical School team has published a key discovery that could help that goal become reality.
In the current issue of the prestigious journal Cell Stem Cell, researcher Yali Dou, Ph.D., and her team show the crucial role of a protein called Mof in preserving ...
Flood risk ranking reveals vulnerable cities
2012-08-21
A new study of nine coastal cities around the world suggests that Shanghai is most vulnerable to serious flooding. European cities top the leader board for their resilience.
These finding are based on a new method to calculate the flood vulnerability of cities, developed by a team of researchers from the Netherlands and the University of Leeds. The work is published in the latest edition of the journal Natural Hazards.
The index does not just look at the likelihood of a city's exposure to a major 'once in a hundred years' flood. The researchers have been careful to ...
Equality laws fail to protect working women from budget cuts
2012-08-21
The UK government has failed to apply laws that protect working women in the wake of the economic crisis, suggests a new study from Queen Mary, University of London.
The article analyses The Fawcett Case, a high-profile legal challenge to the 2010 emergency budget on the grounds that it would have a disproportionately negative impact on women.
The paper also charts how equality legislation has created opportunities for women's rights groups to influence industrial relations; traditionally, trade union territory.
The research was carried out by Dr Hazel Conley, from ...
Language barrier creates legal hurdles for Brits in Turkey
2012-08-21
Many Brits who move to Turkey are failing to grasp local and international laws, leaving them financially at risk when making legal transactions, such as buying property, a study from Queen Mary, University of London has found.
Being unable to speak or read Turkish has made navigating such issues a "legal minefield" for many Brits who emigrate in a quest for the affordable "good life" on the Aegean coast.
Funded by the Nuffield Foundation, the study focuses on British citizens settling in Mugla, a popular tourist spot in Turkey, and their social and legal experiences ...
Catalan researchers identify a key component of cell division
2012-08-21
This press release is available in Spanish and in French
- The Nek9 protein is required for chromosomes to separate into two identical groups.
- Nek9 exerts its action between two molecules of interest for the pharmaceutical industry as anti-tumoral agents, and for which inhibitors are already in advanced stages of clinical trials. Nek9 could be added to the list of candidates.
A study by the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) and the Center for Genomic Regulation (acronym in Catalan CRG) highlights the protein Nek9 as a decisive factor in cell ...
No ordinary forget-me-nots
2012-08-21
Two rare species of forget-me-nots have been added to Flora of New Zealand. These new species were discovered in the mountains of the South Island during an expedition led by Dr. Carlos A. Lehnebach. These new species have been described and illustrated in an article published in the open access journal PhytoKeys.
The expedition was part of a major endeavour by a group of botanists at the Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa in partnership with Landcare Research aiming to describe and list all forget-me-nots (Myosotis) found in New Zealand. Dr. Lehnebach, who is a ...
Research identifies mechanism responsible for eye movement disorder
2012-08-21
A research team from King's College London and the University of Exeter Medical School has identified how a genetic mutation acts during the development of nerves responsible for controlling eye muscles, resulting in movement disorders such as Duane Syndrome, a form of squint.
The findings could provide the key to reversing the condition and unlocking the causes of movement disorders in other parts of the body.
The research is published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
As nerves develop in the womb they respond to signals that tell them in which ...