(Press-News.org) A University of Colorado analysis of state-by-state factors leading to the Electoral College selection of every U.S. president since 1980 forecasts that the 2012 winner will be Mitt Romney.
The key is the economy, say political science professors Kenneth Bickers of CU-Boulder and Michael Berry of CU Denver. Their prediction model stresses economic data from the 50 states and the District of Columbia, including both state and national unemployment figures as well as changes in real per capita income, among other factors.
"Based on our forecasting model, it becomes clear that the president is in electoral trouble," said Bickers, also director of the CU in DC Internship Program.
According to their analysis, President Barack Obama will win 218 votes in the Electoral College, short of the 270 he needs. And though they chiefly focus on the Electoral College, the political scientists predict Romney will win 52.9 percent of the popular vote to Obama's 47.1 percent, when considering only the two major political parties.
"For the last eight presidential elections, this model has correctly predicted the winner," said Berry. "The economy has seen some improvement since President Obama took office. What remains to be seen is whether voters will consider the economy in relative or absolute terms. If it's the former, the president may receive credit for the economy's trajectory and win a second term. In the latter case, Romney should pick up a number of states Obama won in 2008."
Their model correctly predicted all elections since 1980, including two years when independent candidates ran strongly, 1980 and 1992. It also correctly predicted the outcome in 2000, when Al Gore received the most popular vote but George W. Bush won the election.
The study will be published this month in PS: Political Science & Politics, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Political Science Association. It will be among about a dozen election prediction models, but one of only two to focus on the Electoral College.
While many forecast models are based on the popular vote, the Electoral College model developed by Bickers and Berry is the only one of its type to include more than one state-level measure of economic conditions.
In addition to state and national unemployment rates, the authors looked at per capita income, which indicates the extent to which people have more or less disposable income. Research shows that these two factors affect the major parties differently: Voters hold Democrats more responsible for unemployment rates while Republicans are held more responsible for per capita income.
Accordingly -- and depending largely on which party is in the White House at the time -- each factor can either help or hurt the major parties disproportionately.
Their results show that "the apparent advantage of being a Democratic candidate and holding the White House disappears when the national unemployment rate hits 5.6 percent," Berry said. The results indicate, according to Bickers, "that the incumbency advantage enjoyed by President Obama, though statistically significant, is not great enough to offset high rates of unemployment currently experienced in many of the states."
In an examination of other factors, the authors found that none of the following had any statistically significant effect on whether a state ultimately went for a particular candidate: The location of a party's national convention; the home state of the vice president; or the partisanship of state governors.
In 2012, "What is striking about our state-level economic indicator forecast is the expectation that Obama will lose almost all of the states currently considered as swing states, including North Carolina, Virginia, New Hampshire, Colorado, Wisconsin, Minnesota, Pennsylvania, Ohio and Florida," Bickers said.
In Colorado, which went for Obama in 2008, the model predicts that Romney will receive 51.9 percent of the vote to Obama's 48.1 percent, again with only the two major parties considered.
The authors also provided caveats. Factors they said may affect their prediction include the timeframe of the economic data used in the study and close tallies in certain states. The current data was taken five months in advance of the Nov. 6 election and they plan to update it with more current economic data in September. A second factor is that states very close to a 50-50 split may fall an unexpected direction.
"As scholars and pundits well know, each election has unique elements that could lead one or more states to behave in ways in a particular election that the model is unable to correctly predict," Berry said.
Election prediction models "suggest that presidential elections are about big things and the stewardship of the national economy," Bickers said. "It's not about gaffes, political commercials or day-to-day campaign tactics. I find that heartening for our democracy."
###
Contact:
Kenneth Bickers, 303-492-2363
bickers@colorado.edu
Michael Berry, 303-556-6244
michael.berry@ucdenver.edu
Peter Caughey, CU-Boulder media relations, 303-492-4007
David Kelly, CU Denver media relations, 303-315-6374
Editors: For a copy of the complete study email caughey@colorado.edu or david.kelly@ucdenver.edu. Downloadable MP3 files of Kenneth Bickers talking about the forecasting model are available at http://www.colorado.edu/news/media/broadcast-services.
END
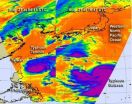
Typhoon Tembin and Typhoon Bolaven continue to churn in the Philippine Sea, and infrared satellite data from NASA showed the power within both storms.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies onboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured imagery of both storms on Aug. 21 in two different overpasses. Aqua flies over the same locations during early morning and early afternoon (local time) as it orbits the Earth. Aqua passed over the Philippine Sea on Aug. 21 at 04:41 UTC (12:41 a.m. EDT) and 16:47 UTC (12:47 p.m. EDT). The two satellite passes were combined ...
Scientists at UCLA and the Technion, Israel's Institute of Technology, have unraveled how our brain cells encode the pronunciation of individual vowels in speech.
Published in the Aug. 21 edition of the journal Nature Communications, the discovery could lead to new technology that verbalizes the unspoken words of people paralyzed by injury or disease.
"We know that brain cells fire in a predictable way before we move our bodies," said Dr. Itzhak Fried, a professor of neurosurgery at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA. "We hypothesized that neurons would ...
Using bioluminescent proteins from a jellyfish, a team of scientists has lit up the inside of a neuron, capturing spectacular video footage that shows the movement of proteins throughout the cell.
The video offers a rare peek at how proteins, the brain's building blocks, are directed through neurons to renew its structure. It can be viewed online here: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=baI9q2--q7s&feature=youtu.be
"Your brain is being disassembled and reassembled every day," said Don Arnold, associate professor of molecular and computational biology at the USC Dornsife ...
Knowing the position of missing oxygen atoms could be the key to cheaper solid oxide fuel cells with longer lifetimes. New microscopy research from the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory is enabling scientists to map these vacancies at an atomic scale.
Although fuel cells hold promise as an efficient energy conversion technology, they have yet to reach mainstream markets because of their high price tag and limited lifespans. Overcoming these barriers requires a fundamental understanding of fuel cells, which produce electricity through a chemical reaction ...
Augusta, GA—Researchers at the Georgia Health Sciences University Cancer Center have identified a gene that disrupts the inflammatory process implicated in liver cancer.
Laboratory mice bred without the gene lacked a pro-inflammatory protein called TREM-1 and protected them from developing liver cancer after exposure to carcinogens.
The study, published in Cancer Research, a journal for the American Association for Cancer Research, could lead to drug therapies to target TREM-1, said Dr. Anatolij Horuzsko, an immunologist at the GHSU Cancer Center and principal investigator ...
Washington, D.C.—Carnegie scientists are the first to discover the conditions under which nickel oxide can turn into an electricity-conducting metal. Nickel oxide is one of the first compounds to be studied for its electronic properties, but until now scientists have not been able to induce a metallic state. The compound becomes metallic at enormous pressures of 2.4 million times the atmospheric pressure (240 gigapascals). The finding is published in Physical Review Letters.
"Physicists have predicted for decades that the nickel oxide would transition from an insulator—a ...
Northwestern University scientists have connected 250 years of organic chemical knowledge into one giant computer network -- a chemical Google on steroids. This "immortal chemist" will never retire and take away its knowledge but instead will continue to learn, grow and share.
A decade in the making, the software optimizes syntheses of drug molecules and other important compounds, combines long (and expensive) syntheses of compounds into shorter and more economical routes and identifies suspicious chemical recipes that could lead to chemical weapons.
"I realized that ...
Enzymes involved in breaking down fat can now be manipulated to work three times harder by turning on a molecular switch recently observed by chemists at the University of Copenhagen. Being able to control this chemical on/off button could have massive implications for curing diseases related to obesity including diabetes, cardio vascular disease, stroke and even skin problems like acne. But the implications may be wider.
The results suggest that the switch may be a common characteristic of many more enzymes. Since enzymes are miniscule worker-molecules that control a ...
AUDIO:
This is a gibbon call without helium.
Click here for more information.
Have you ever heard an opera singing ape? Researchers in Japan have discovered that singing gibbons use the same vocal techniques as professional soprano singers. The study, published in the American Journal of Physical Anthropology, explains how recording gibbons singing under the influence of helium gas reveals a physiological similarity to human voices.
The research was led by Dr Takeshi Nishimura ...
Philadelphia, PA, August 23, 2012 – The routine use of prostate specific antigen (PSA) testing for screening and monitoring prostate cancer has led to early and more sensitive detection of the disease. A new study published in The Journal of Urology® reports that in the "PSA era," survival has improved for patients with newly diagnosed prostate cancer that has spread to the bones or other parts of the body and the disparity between African American and Caucasian men has been resolved.
"Our analysis indicates an overall improvement in risk adjusted survival rates for ...