(Press-News.org) This press release is available in Spanish.
A U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientist has found a "green" alternative to a type of fertilizer additive that is believed to contribute to the accumulation of heavy metals in waterways.
Ornamental nursery and floral crops require micronutrients like iron, manganese, copper and zinc. But fertilizers that provide these micronutrients often include synthetically produced compounds that bind with the micronutrients so they are available in the root zone.
The most commonly used compounds, known as chelating agents, are not readily biodegradable, and can extract metals from sediments. Their use is believed to add to the amounts of iron and other heavy metals that sometimes flow into or become soluble in waterways. Concerns in Europe about one, called EDTA, have prompted calls there for use of alternative chelating agents.
Joseph Albano, a horticulturalist with the Agricultural Research Service (ARS) U.S. Horticultural Research Laboratory in Fort Pierce, Fla., thinks he has found a "green" alternative for the floral and nursery crop industries. ARS is USDA's principal intramural scientific research agency, and this research supports USDA's commitment to agricultural sustainability.
Albano's alternative chelating agent is known as EDDS. It is a natural compound that is biodegradable and less likely to persist in the environment.
In a series of studies, Albano grew marigolds in standard soil-less potting media using fertilizers formulated with EDDS or one of two commonly used chelating agents: EDTA and DTPA. Each of the three treatments was chelated with iron so Albano could assess the effectiveness of EDDS as a fertilizer iron source.
The results showed that EDDS was a suitable chelating agent for use in fertilizers. There were no differences in plant growth or leaf-tissue iron levels among plants grown with iron-EDDS, those grown with iron-EDTA, or those grown with iron-DTPA fertilizers.
Iron-chelates, like iron-EDTA and iron-DTPA, degrade when exposed to light (photodegradation), so they are often stored in opaque containers that prevent exposure to sunlight. Albano also assessed iron-EDDS photodegradation and discovered that iron-EDDS degraded more quickly than iron-EDTA when exposed to light, which would contribute to its low persistence in the environment. Given how quickly it degrades, Albano recommends that iron-EDDS chelates also be stored in opaque containers.
The report, published in HortScience, was the first peer-reviewed study to evaluate EDDS as a chelating agent in fertilizers used in the production of a floricultural crop, according to Albano. The work is expected to encourage the use of EDDS as an environmentally friendly chelating agent in floral and nursery crop operations.
###Read more about this research in the August 2012 issue of Agricultural Research magazine.
http://www.ars.usda.gov/is/AR/archive/aug12/fertilizer0812.htm
USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer. To file a complaint of discrimination, write: USDA, Office of the Assistant Secretary for Civil Rights, Office of Adjudication, 1400 Independence Ave., SW, Washington, DC 20250-9410 or call (866) 632-9992 (Toll-free Customer Service), (800) 877-8339 (Local or Federal relay), (866) 377-8642 (Relay voice users).
A greener way to fertilize nursery crops
2012-08-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
George Washington University Computational Biology Director solves 200-year-old oceanic mystery
2012-08-28
WASHINGTON — The origin of Cerataspis monstrosa has been a mystery as deep as the ocean waters it hails from for more than 180 years. For nearly two centuries, researchers have tried to track down the larva that has shown up in the guts of other fish over time but found no adult counterpart. Until now.
George Washington University Biology Professor Keith Crandall cracked the code to the elusive crustacean's DNA this summer. His findings were recently published in the journal "Ecology and Evolution," and his research was funded by the National Science Foundation and the ...
NASA sees Typhoon Bolaven dwarf Typhoon Tembin
2012-08-28
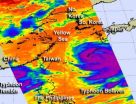
NASA satellites are providing imagery and data on Typhoon Tembin southwest of Taiwan, and Typhoon Bolaven is it barrels northwest through the Yellow Sea. In a stunning image from NASA's Aqua satellite, Bolaven appears twice as large as Tembin.
NASA's Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument that flies onboard the Terra satellite captured a remarkable image of Typhoon Tembin being dwarfed by giant Typhoon Bolaven at 0240 UTC on Aug. 27, 2012. The visible image shows that the island of Taiwan appears to be squeezed between the two typhoons, while ...
Plants unpack winter coats when days get shorter
2012-08-28
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Mechanisms that protect plants from freezing are placed in storage during the summer and wisely unpacked when days get shorter.
In the current issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Michael Thomashow, University Distinguished Professor of molecular genetics, demonstrates how the CBF (C-repeat binding factor) cold response pathway is inactive during warmer months when days are long, and how it's triggered by waning sunlight to prepare plants for freezing temperatures.
The CBF cold response pathway was discovered by Thomashow's ...
Parents and readers beware of stereotypes in young adult literature
2012-08-28
COLUMBIA, Mo. — A newly defined genre of literature, "teen sick-lit," features tear-jerking stories of ill adolescents developing romantic relationships. Although "teen sick-lit" tends to adhere to negative stereotypes of the ill and traditional gender roles, it also explores the taboo realm of sexuality, sickness and youth, says the University of Missouri researcher who named the genre in a recent study. Readers and their parents should be aware of how the presentation of disease and disability in these stories can instill prejudices and enforce societal norms in young ...
Divorced parents in hostile relationships use technology to sabotage communication, MU study finds
2012-08-28
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Separated and divorced couples are increasingly using emails, texting and social media to communicate with their ex-partners about their children. However, when ex-spouses use that technology to withhold or manipulate information, the children are the ones who suffer most, according to a University of Missouri family studies expert. A new study suggests divorce counselors should teach separated parents effective ways to use communication technology in order to maintain healthy environments for their children.
Lawrence Ganong, a professor of human development ...
Speaking 2 languages also benefits low-income children
2012-08-28
Living in poverty is often accompanied by conditions that can negatively influence cognitive development. Is it possible that being bilingual might counteract these effects? Although previous research has shown that being bilingual enhances executive functioning in middle-class children, less is known about how it affects lower income populations.
In a study forthcoming in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, psychological scientist Pascale Engel de Abreu of the University of Luxembourg and colleagues examine the effects of speaking ...
ASGE initiative examines real-time imaging of Barrett's esophagus
2012-08-28
OAK BROOK, Ill. – August 27, 2012 – The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy's (ASGE) Preservation and Incorporation of Valuable Endoscopic Innovations (PIVI) initiative examines real-time imaging of Barrett's esophagus in an article appearing in the August issue of GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, ASGE's monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal. This PIVI is one in a series of statements defining the diagnostic or therapeutic threshold that must be met for a technique or device to become considered appropriate for incorporation into clinical practice.
Barrett's ...
Working moms spend less time daily on kids' diet, exercise, study finds
2012-08-28
When it comes to cooking, grocery shopping and playing with children, American moms with full-time jobs spend roughly three-and-half fewer hours per day on these and other chores related to their children's diet and exercise compared to stay-at-home and unemployed mothers, reports a new paper by a Cornell University health economist.
Male partners do little to make up the deficit: Employed fathers devote just 13 minutes daily to such activities and non-working fathers contribute 41 minutes, finds the study, which will be printed in the December issue of Economics and ...
Accuracy of narrow band imaging with colonoscopy allows for distal non-cancerous polyps to be left in place
2012-08-28
OAK BROOK, Ill. – August 27, 2012 – According to a new study, the use of narrow band imaging (NBI) during colonoscopy is sufficiently accurate to allow distal hyperplastic (non-cancerous) polyps to be left in place without removal and small, distal adenomas (pre-cancerous polyps) to be removed and discarded without pathologic assessment. These findings validate NBI criteria based on color, vessels and pit characteristics for predicting real-time colorectal polyp histology. The study appears in the August issue of GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, the monthly peer-reviewed ...
Scientists find oldest occurrence of arthropods preserved in amber
2012-08-28
An international team of scientists has discovered the oldest record of arthropods—invertebrate animals that include insects, arachnids, and crustaceans—preserved in amber. The specimens, one fly and two mites found in millimeter-scale droplets of amber from northeastern Italy, are about 100 million years older than any other amber arthropod ever collected. The group's findings, which are published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, pave the way for a better evolutionary understanding of the most diverse group of organisms in the world.
"Amber ...