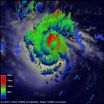
(Press-News.org) The Atlantic Ocean hurricane season spawned two hurricanes this week and NASA satellites have been monitoring them and providing valuable data to forecasters. NASA's TRMM satellite saw very heavy rainfall and powerful towering thunderstorms in Michael when the storm became a hurricane. Michael's wind speeds more than doubled in 24 hours and it is now a major hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson scale.
Tropical Storm Michael became a hurricane on Sept. 5 and NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed by and collected data on rainfall and cloud heights. The TRMM satellite had an outstanding daytime view of intensifying tropical storm Michael on Sept. 5, 2012 at 1459 UTC (10:59 a.m. EDT). Michael was located about 1,125 miles (1,815 km) west-southwest of the Azores at that time moving slowly toward the northeast over open waters of the Atlantic. Rainfall was very intense in the forming eye and the TRMM satellite measured some areas of very heavy rain falling at a rate greater than 3 inches (75 mm) per hour.
TRMM's Precipitation Radar instrument showed that towering thunderstorms called "hot towers" within the forming eye wall were reaching heights of about 9.3 miles (15km). "Hot towers" are towering clouds that emit a tremendous amount of latent heat (thus, called "hot"). NASA research indicates that whenever a hot tower is spotted, a tropical cyclone will likely intensify and that's what happened with Michael.
Over the course of 24 hours, Michael's maximum sustained winds had more than doubled. On Sept. 6 at 11 a.m. EDT, Michael had maximum sustained winds were near 115 mph (185 kmh). Just twenty four hours before, Michael's maximum sustained winds were near 50 mph (85 kmh). Michael's center was about 980 miles (1,580 km) west-southwest of the Azores islands, near latitude 28.3 north and longitude 43.3 west. Michael is moving toward the northeast near 7 mph (11 kmh) and is expected to turn northwest by Sept. 8.
The National Hurricane Center noted that Michael is a category three hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson hurricane wind scale and some gradual weakening is expected beginning Friday, Sept. 7 and continuing through the weekend.
In addition to Michael in the Atlantic Ocean basin today, Leslie is moving toward Bermuda over the weekend, and another low pressure area is being watched in the Gulf of Mexico. That other low pressure area, called System 90L, is located near 29.3 North and 88.3 West over the north central Gulf of Mexico. That broad area of low pressure is drifting southward into the Gulf and has a 40% chance of developing into a tropical depression in the next two days.
INFORMATION:
NASA saw Michael become an Atlantic hurricane, wind speed more than doubled
2012-09-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rice University researchers optimize photoluminescent probes to study DNA and more
2012-09-07
Sorting good data from bad is critical when analyzing microscopic structures like cells and their contents, according to researchers at Rice University. The trick is to find the right window of time through which to look.
A new paper by the Rice lab of Angel Martí, an assistant professor of chemistry and bioengineering, offers a methodology to optimize the sensitivity of photoluminescent probes using time-resolved spectroscopy. Martí and co-author Kewei Huang, a graduate student in his group, found their technique gave results nearly twice as good as standard fluorescence ...
Adding bavituximab to second-line chemotherapy doubles response rate
2012-09-07
Adding the monoclonal antibody bavituximab to docetaxel chemotherapy doubles overall response rate and improves progression-free survival and overall survival in late-stage non-squamous, non-small cell lung cancer (NS-NSCLC) patients who have already received one prior chemotherapy regimen, according to research presented at the 2012 Chicago Multidisciplinary Symposium in Thoracic Oncology. This symposium is sponsored by the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO), the International Association for the Study of Lung ...
Genetic discovery in Montreal for a rare disease in Newfoundland
2012-09-07
This press release is available in French.Researchers from the Guy Rouleau Laboratory affiliated with the CHUM Research Centre and the CHU–Sainte-Justine Research Centre have discovered the genetic cause of a rare disease reported only in patients originating from Newfoundland: hereditary spastic ataxia (HSA).
This condition is characterized by lower-limb spasticity (or stiffness) and ataxia (lack of coordination), the latter leading to speech and swallowing problems, and eye movement abnormalities. The disease is not deadly, but people start developing gait problems ...
Stage I NSCLC patients who receive radiation therapy are surviving longer
2012-09-07
Stage I, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients who received radiation therapy have an increased median survival of 21 months compared to 16 months, and the percentage of patients who receive no treatment declined from 20 percent to 16 percent, respectively, when comparing the two eras evaluated, 1999-2003 and 2004-2008, according to detailed analysis of the SEER-17 (Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results, National Cancer Institute) national database presented at the 2012 Chicago Multidisciplinary Symposium in Thoracic Oncology. This symposium is sponsored by the ...
Brain radiation after lung cancer treatment reduces risk of cancer spreading
2012-09-07
Stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with surgery and/or radiation therapy have a significantly reduced risk of developing brain metastases if they also receive prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI); however, this study did not show an improvement in overall survival with PCI, according to research presented at the 2012 Chicago Multidisciplinary Symposium in Thoracic Oncology. This symposium is sponsored by the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO), the International Association for the ...
Changes in water chemistry leave lake critters defenseless
2012-09-07
TORONTO, Sept. 6, 2012 – Imagine that the players on your favourite football team were smaller than their opponents, and had to play without helmets or pads. Left defenseless, they would become easy prey for other teams. Similarly, changes in Canadian lake water chemistry have left small water organisms vulnerable to their predators, which may pose a serious environmental threat, according to a new study.
"At low calcium levels the organisms grow slower and cannot build their armour," says study lead author Howard Riessen, professor of biology, SUNY College at Buffalo. ...
Standard chemotherapy provides higher survival rate than experimental in lung cancer patients
2012-09-07
Treatment with pemetrexed, carboplatin and bevacizumab followed by maintenance pemetrexed and bevacizumab (Pem+Cb+B) is no better than standard therapy with paclitaxel, carboplatin and bevacizumab followed by bevacizumab (Pac+Cb+B) in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NS-NSCLC), according to research presented at the 2012 Chicago Multidisciplinary Symposium in Thoracic Oncology. This symposium is sponsored by the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO), the International Association ...
Childhood virus RSV shows promise against adult cancer
2012-09-07
SAN ANTONIO (Sept. 6, 2012) — RSV, a virus that causes respiratory infections in infants and young children, selectively kills cancer cells while leaving healthy cells alone, researchers from the School of Medicine at The University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio said.
Santanu Bose, Ph.D., of the School of Medicine, is the inventor on a pending U.S. patent of RSV as an oncolytic therapy. This represents a new use for the virus. Bandana Chatterjee, Ph.D., of the School of Medicine and the South Texas Veterans Health Care System, is the co-inventor. Oncolytic ...
Social psychologists espouse tolerance and diversity -- do they walk the walk?
2012-09-07
Every ten years or so, someone will make the observation that there is a lack of political diversity among psychological scientists and a discussion about what ought to be done ensues. The notion that the field discriminates against and is skewed toward a liberal political perspective is worthy of concern; scholars, both within and outside the field, have offered various solutions to this diversity problem.
As psychological scientists Yoel Inbar and Joris Lammers point out, however, we have few of the relevant facts necessary to understand and address the issue.
In ...
Parents' skin cancer concern doesn't keep kids inside
2012-09-07
Pick your poison: sun exposure that leads to skin cancer or low physical activity that leads to obesity? In fact, a University of Colorado Cancer Center study published this week in the journal Preventing Chronic Disease shows that parents' concern about skin cancer doesn't make them keep their kids indoors.
"Actually, our hypothesis was the opposite – that if parents were concerned about skin cancer they wouldn't let their children go out as much," says Alexander Tran, summer fellow working with Lori Crane, PhD, CU Cancer Center investigator and chair of the Department ...