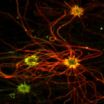
(Press-News.org) A team of scientists from Johns Hopkins and other institutions report that restoring tiny, hair-like structures to defective cells in the olfactory system of mice is enough to restore a lost sense of smell. The results of the experiments were published online this week in Nature Medicine, and are believed to represent the first successful application of gene therapy to restore this function in live mammals.
An expert in olfaction, Randall Reed, Ph.D., professor of molecular biology and genetics and co-director of the Center for Sensory Biology at the Johns Hopkins Institute for Basic Biomedical Sciences, cautions that researchers are still years away from applying the same therapy in people, and that if and when it comes, it will likely be most effective for those who suffer from anosmia (lack of smell) due to inherited genetic disorders. "But our work has already contributed to a better understanding of the cellular factors involved in anosmia, and that will give us insights into other neurological disorders, as well," he says.
The mice used in the current study carried a genetic mutation that destroyed the production of a protein critical for the functioning of cilia in the cells responsible for smell, called olfactory sensory neurons. These specialized cells each display several of the protruding, hair-like structures that contain receptors for odorants. Without functional cilia, the cells become a broken link in the chain of events necessary for proper odor detection in the environment, the researchers explained.
Beginning with a common cold virus, which readily infects the cells of the nasal cavity, researchers replaced some of the viral genes with a corrected version of the defective cilia gene. They then infected smelling-impaired mice with the altered virus, delivering the corrected gene to the olfactory neural cells that needed it.
At the cellular level, scientists saw a restoration of proper chemical signaling between nerve cells after the treated mice were stimulated with various odorants. Perhaps even more indicative of their success, Reed says, was the 60 percent increase in body weight that the mice experienced once they could smell their meals, leading to increased appetite. Many people with anosmia lose weight because aromas play a significant part in creating appetite and food enjoyment.
Researchers are optimistic about the broader implications of this work, Reed notes, because cilia are not only important to olfactory cells, but also to cells all over the body, from the kidney to the eye. The fact that they were able to treat live mice with a therapy that restored cilia function in one sensory system suggests that similar techniques could be used to treat cilia disorders elsewhere.
"We also hope this stimulates the olfactory research community to look at anosmia caused by other factors, such as head trauma and degenerative diseases," says senior author Jeffrey Martens, Ph.D., an associate professor of pharmacology at the University of Michigan. "We know a lot about how this system works – now have to look at how to fix it when it malfunctions."
INFORMATION:
In addition to Randall Reed from Johns Hopkins, the paper's authors include Jeffrey Martens, Jeremy McIntyre, Ariell Joiner, Corey Williams, Paul Jenkins, Dyke McEwen, Lian Zhang and John Escobado from the Martens Lab at the University of Michigan; Erica Davis, I-Chun Tsai and Nicholas Katsanis from Duke University; Aniko Sabo, Donna Muzny and Richard Gibbs from the Baylor College of Medicine; Eric Green and James Mullikin from the National Institutes of Health Intramural Sequencing Center; Bradley Yoder from the University of Alabama-Birmingham; Sophie Thomas and Tania Attié-Bitach from L'Université Paris Descartes; Katarzyna Szymanska and Colin A. Johnson from St. James's University Hospital in Leeds, UK; and Philip Beales from University College London, UK.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health: National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (#R01DC009606, F32DC011990, R01DC004553, R01DC008295), National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (#R01DK75996, R01DK072301, R01DK075972, DK074083), National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (#R01HD042601), and National Eye Institute (#R01EY021872). Additional funding sources included L'Agence Nationale de la Recherche and the European Community's Seventh Framework Programme.
On the Web:
Article in Nature Medicine: http://www.nature.com/nm/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nm.2860.html
Q&A with Randy Reed: http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/institute_basic_biomedical_sciences/about_us/scientists/Randall_Reed.html
Reed Lab: http://www.mbg.jhmi.edu/Pages/people/profile.aspx?PID=16
The nose knows: Gene therapy restores sense of smell in mice
2012-09-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Coping skills, marital satisfaction help pregnant moms manage stress when fetus has heart defect
2012-09-08
Expectant mothers who learn from prenatal diagnosis that they are carrying a fetus with a congenital heart defect (CHD) commonly suffer post-traumatic stress, depression and anxiety. However, a healthy relationship with one's partner and positive coping mechanisms can reduce this intense stress, according to new research from the Cardiac Center of The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
The study is published in the September 2012 issue of The Journal of Pediatrics.
"Receiving the news of carrying a fetus with a CHD is a stressful event which can potentially influence ...
UC Santa Cruz study shows how sea otters can reduce CO2 in the atmosphere
2012-09-08
Can an abundance of sea otters help reverse a principal cause of global warming?
A new study by two UC Santa Cruz researchers suggest that a thriving sea otter population that keeps sea urchins in check will in turn allow kelp forests to prosper. The spreading kelp can absorb as much as 12 times the amount of CO2 from the atmosphere than if it were subject to ravenous sea urchins, the study finds.
The theory is outlined in a paper released online today (September 7, 2012) in Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment by lead authors UC Santa Cruz professors Chris Wilmers ...
Subsidies change incentives for adoption of foster children: Study
2012-09-08
The structure of a federal program that provides monthly subsidies to promote the adoptions of special needs children in foster care may actually be delaying some adoptions, according to a new study by University of Notre Dame economist Kasey Buckles.
The Adoption Assistance and Child Welfare Act (AACWA), passed in 1980, provides an average of $670 per month for foster parents of special needs children, while adoptive parents of special needs children receive an average of $571 per month. "Special needs" refers to foster children who may be harder to place ...
Turf study to monitor runoff, establish fertilizer management practices
2012-09-08
COLLEGE STATION – Improperly applied fertilizer to newly placed sod may result in nutrient runoff into the water supply, but just when is the best time to apply fertilizer and what kind is the best for new turf?
Aiming to answer those questions is a team of scientists from Texas A&M AgriLife Research: Dr. Jacqui Aitkenhead-Peterson, assistant professor of urban nutrient and water management; Dr. Ben Wherley, assistant professor of turfgrass science and ecology; Dr. Richard White, professor of turfgrass physiology and management; and Jim Thomas, senior research associate, ...
Tension on gut muscles induces cell invasion in zebrafish intestine, mimicking cancer metastasis
2012-09-08
VIDEO:
The movie shows a segment of the mutant intestine (3.5 day old fish, lateral view of the intestine). The time lapse images were taken over about six to eight hours....
Click here for more information.
PHILADELPHIA — The stiffness of breast tissue is increasingly recognized as an important factor explaining the onset of breast cancer. Stiffening induces molecular changes that promote cancerous behavior in cells. Bioengineering studies have found that breast cancer ...
NASA's Global Hawk Mission Begins with Flight to Hurricane Leslie
2012-09-08
NASA has begun its latest hurricane science field campaign by flying an unmanned Global Hawk aircraft over Hurricane Leslie in the Atlantic Ocean during a day-long flight from California to Virginia. With the Hurricane and Severe Storm Sentinel (HS3) mission, NASA for the first time will be flying Global Hawks from the U.S. East Coast.
The Global Hawk took off from NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., Thursday and landed at the agency's Wallops Flight Facility on Wallops Island, Va., today at 11:37 a.m. EDT after spending 10 hours collecting ...
Treatment with fungi makes a modern violin sound like a Stradiavarius
2012-09-08
A good violin depends not only on the expertise of the violin maker, but also on the quality of the wood that is used. The Swiss wood researcher Professor Francis W. M. R. Schwarze (Empa, Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology, St. Gallen, Switzerland) has succeeded in modifying the wood for a violin through treatment with special fungi. This treatment alters the acoustic properties of the instrument, making it sound indistinguishably similar to a Stradivarius. In his dinner talk at the 1st ECRC "Franz-Volhard" Symposium of the Max Delbrück Center ...
Health-care costs at end of life exceed total assets for 25 percent of Medicare population
2012-09-08
As many as a quarter of Medicare recipients spend more than the total value of their assets on out-of-pocket health care expenses during the last five years of their lives, according to researchers at Mount Sinai School of Medicine. They found that 43 percent of Medicare recipients spend more than their total assets minus the value of their primary residences. The findings appear online in the current issue of the Journal of General Internal Medicine.
The amount of spending varied with the patient's illness. Those with dementia or Alzheimer's disease spent the most for ...
On 9/13, Lifestyle and Entertainment Magazine Nine Thirteen Goes Live
2012-09-08
Set to officially launch its website at the apex of Mercedes-Benz Fashion Week, NINE THIRTEEN is a refreshingly bold, new magazine poised to take the lifestyle and entertainment worlds by storm Thursday, September 13th.
The well-known president, founder and Editor-In-Chief of NINE THIRTEEN, Catrina Cha'Ron, will be pulling out all the stops for this can't be missed media frenzy and fashionable event. With over 20 years of experience in top level management which includes launching mayoral initiatives and philanthropic service, for Cha'Ron NINE THIRTEEN is a dream realized. ...
Lilburn Back Pain Chiropractor, Dr. Matthew Loop, Offers Locals Fast and Safe Relief
2012-09-08
Dr. Matthew Loop, who created and runs All-Pro Chiropractic and Pain Specialists helps several patients on a daily basis who suffer from back pain. Back pain is one of the most common ailments amongst adults, affecting hundreds of thousands each year. It can be related to muscle problems, a herniated disc or a simple misalignment of the spine.
Dr. Loop observes, "Most back pain typically originates from a particular mechanical issue, as when someone lifts a heavy box improperly or someone sits for an extended period of time on a poorly designed chair or simply using ...