(Press-News.org) Most older adults prefer to maintain their independence and remain in their own homes as they age, and robotic technology can help make this a reality. Robots can assist with a variety of everyday living tasks, but limited research exists on seniors' attitudes toward and acceptance of robots as caregivers and aides. Human factors/ergonomics researchers investigated older adults' willingness to receive robot assistance that allows them to age in place, and will present their findings at the upcoming HFES 56th Annual Meeting in Boston.
Changes that occur with aging can make the performance of various tasks of daily living more difficult, such as eating, getting dressed, using the bathroom, bathing, preparing food, using the telephone, and cleaning house. When older adults can no longer perform these tasks, an alternative to moving to a senior living facility or family member's home may someday be to bring in a robot helper.
In their HFES Annual Meeting proceedings paper, "Older Adults' Preferences for and Acceptance of Robot Assistance for Everyday Living Tasks," researchers Cory-Ann Smarr and colleagues at the Georgia Institute of Technology showed groups of adults age 65 to 93 a video of a robot's capabilities and then asked them how they would feel about having a robot in their homes. "Our results indicated that the older adults were generally open to robot assistance in the home, but they preferred it for some daily living tasks and not others," said Smarr.
Participants indicated a willingness for robotic assistance with chores such as housekeeping and laundry, with reminders to take medication and other health-related tasks, and with enrichment activities such as learning new information or skills or participating in hobbies. These older adults preferred human assistance in personal tasks, including eating, dressing, bathing, and grooming, and with social tasks such as phoning family or friends.
"There are many misconceptions about older adults having negative attitudes toward robots," continued Smarr. "The older adults we interviewed were very enthusiastic and optimistic about robots in their everyday lives. Although they were positive, they were still discriminating with their preferences for robot assistance. Their discrimination highlights the need for us to continue our research to understand how robots can support older adults with living independently."
###
To obtain an advance copy of the paper for reporting purposes, or for more information about other research to be presented at the HFES 56th Annual Meeting, contact Lois Smith (lois@hfes.org) or Cara Quinlan (cara@hfes.org; 310/394-1811).
The Human Factors and Ergonomics Society is the world's largest nonprofit individual-member, multidisciplinary scientific association for human factors/ergonomics professionals, with more than 4,600 members globally. HFES members include psychologists and other scientists, designers, and engineers, all of whom have a common interest in designing systems and equipment to be safe and effective for the people who operate and maintain them. Watch science news stories about other HF/E topics at the HFES Web site. "Human Factors and Ergonomics: People-Friendly Design Through Science and Engineering"
Plan to attend the HFES 56th Annual Meeting, October 22-26: https://www.hfes.org//Web/HFESMeetings/2012annualmeeting.html
END
It is commonly assumed that you can "work up an appetite" with a vigorous workout. Turns out that theory may not be completely accurate – at least immediately following exercise.
New research out of BYU shows that 45 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous exercise in the morning actually reduces a person's motivation for food.
Professors James LeCheminant and Michael Larson measured the neural activity of 35 women while they viewed food images, both following a morning of exercise and a morning without exercise. They found their attentional response to the food pictures decreased ...
A paper recently published in the Journal of Animal Science helps researchers further understand how microbials and probiotics affect poultry health.
Researchers at the North Carolina State University and Chung Jen College of Nursing, Health Sciences and Management (Taiwan) conducted a study to investigate the effects of direct fed microbials on energy metabolism in different tissues of broiler chickens. The researchers wanted to learn how consuming microbials and probiotics could change energy use and immune function. Typically, direct fed microbials and probiotics are ...
A new Johns Hopkins study has unraveled the changes in a key cardiac protein that can lead to heart muscle malfunction and precipitate heart failure.
Troponin I, found exclusively in heart muscle, is already used as the gold-standard marker in blood tests to diagnose heart attacks, but the new findings reveal why and how the same protein is also altered in heart failure. Scientists have known for a while that several heart proteins — troponin I is one of them — get "out of tune" in patients with heart failure, but up until now, the precise origin of the "bad notes" remained ...
Abstinence from smoking seems to affect teens differently than adults in a couple ways, but a new study provides evidence that most of the psychological difficulties of quitting are as strong for relatively new, young smokers as they are for adults who have been smoking much longer.
"Adolescents are showing — even relatively early in the dependence process — significant, strong, negative effects just after acute abstinence from smoking," said L. Cinnamon Bidwell, assistant professor (research) in psychiatry and human behavior and the Center for Alcohol and Addiction Studies. ...
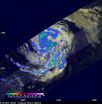
Tropical Depression 14 strengthened into Tropical Storm Nadine while NASA's Hurricane Severe Storm Sentinel Mission, or HS3 mission, was in full-swing and NASA's Global Hawk aircraft captured the event. While the Global Hawk was gathering data over the storm, NASA satellites were also analyzing Nadine from space.
NASA's Global Hawk landed back at Wallops Flight Facility, Wallops Island, Va., after spending a full day gathering data from the 14th Atlantic Tropical Depression that strengthened into Tropical Storm Nadine during the morning hours of Sept. 12.
The Global ...
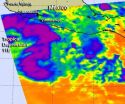
One of NASA's infrared "eyes" is an instrument that flies aboard the Aqua satellite, and it provided data that helped forecasters determine that low pressure "System 90E" strengthened into the eastern Pacific Ocean's eleventh tropical depression.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument onboard Aqua captured an infrared image of System 90E on Sept. 11 at 1947 UTC (3:47 p.m. EDT). That infrared image took the temperatures of the cloud tops and found some strong, high thunderstorms wrapped around the western side of the low pressure area's circulation, from north ...
Chevy Chase, MD—Gestational exposure to ambient urban air pollution, especially during late pregnancy, may contribute to lower vitamin D levels in offspring, according to a recent study accepted for publication in The Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism (JCEM). According to study authors, this could affect the child's risk of developing diseases later in life.
Recent data have demonstrated that maternal vitamin D deficiency during pregnancy may have an influence on the development of asthma and allergic diseases in offspring. A number ...
Chevy Chase, MD—Slow-wave sleep, or 'deep sleep', is intimately involved in the complex control of the onset of puberty, according to a recent study accepted for publication in The Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism (JCEM).
The many changes that occur in boys and girls during puberty are triggered by changes in the brain. Previous studies have shown that the parts of the brain that control puberty first become active during sleep, but the present study shows that it is deep sleep, rather than sleep in general, that is associated with ...
Chevy Chase, MD—There is no evidence to link mildly elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels to an increase in mortality among the elderly, according to a recent study accepted for publication in The Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM). The findings suggest that reflexively treating mild elevations of TSH in those of advanced age is unnecessary.
TSH is a sensitive, commonly measured test to check thyroid function. TSH levels are inversely related to thyroid hormone levels – thyroid hormone levels below a set-point trigger ...
Researchers at Moffitt Cancer Center and colleagues have discovered that changes in the physical characteristics of the effector memory regulatory T cell can predict the progression risk of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) to acute myeloid leukemia. The finding could improve prognostication for patients with MDS and better inform therapeutic decision making.
The study published in the August issue of The Journal of Immunology.
Awareness of the condition increased earlier this year when ABC's "Good Morning America" co-anchor Robin Roberts announced that she is battling ...