(Press-News.org) Toronto – Tax collectors and insurance agencies trying to boost honest reporting could improve compliance simply by asking people to sign their forms at the beginning instead of at the end.
That's because attesting to the truthfulness of the information before a form is filled out tends to activate people's moral sense, making it harder for them to fudge their numbers after, says a new paper.
"Based on our previous research we knew that an honour code is useful, but we were wondering how much the location mattered," says Nina Mazar, an assistant professor of marketing at the University of Toronto's Rotman School of Management. Prof. Mazar co-wrote the paper with Lisa L. Shu of the Kellogg School of Management, Francesca Gino and Max H. Bazerman of Harvard Business School, and Dan Ariely of the Fuqua School of Business.
Their conclusions were supported in three separate experiments. The largest, involving more than 13,000 U.S. auto insurance policy forms with over 20,000 cars, showed customers who signed at the beginning on average revealed a 2,428 miles higher usage (3907 km) than those who signed at the end – more than a 10% difference. The researchers calculated that added up to a $48 or more differential in the two groups of customers' annual insurance premium per car.
Previous research has shown that people can use various forms of self-deception to avoid facing up to their own dishonest behaviour. But if their self-awareness is triggered before they are presented with an opportunity to lie, they are less likely to do it. Asking people to sign an honour code afterwards comes "too late," says the paper.
Where the signature is placed likely won't make a difference to individuals who have no intention of being honest, says Prof. Mazar. But given that in the U.S. there is a $345-billion gap between what people should be paying in taxes and what they claim, it's "unlikely" the gap is caused "by a few bad apples," she says.
"There are so many temptations around us," says Prof. Mazar. "Sometimes we do give in."
The paper was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, one of the world's most-cited multidisciplinary scientific serials.
###
For the latest thinking on business, management and economics from the Rotman School of Management, visit www.rotman.utoronto.ca/FacultyAndResearch/NewThinking.aspx.
The Rotman School of Management at the University of Toronto is redesigning business education for the 21st century with a curriculum based on Integrative Thinking. Located in the world's most diverse city, the Rotman School fosters a new way to think that enables the design of creative business solutions. The School is currently raising $200 million to ensure Canada has the world-class business school it deserves. For more information, visit www.rotman.utoronto.ca.
For more information:
Ken McGuffin
Manager, Media Relations
Rotman School of Management
University of Toronto
Voice 416.946.3818
E-mail mcguffin@rotman.utoronto.ca
Follow Rotman on Twitter @rotmanschool
Watch Rotman on You Tube www.youtube.com/rotmanschool
Honestly? Just sign here -- first
Joint study by Rotman School researcher shows signature placement curbs cheating
2012-09-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA sees Sanba become a super typhoon
2012-09-14
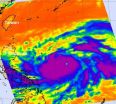
Tropical Storm Sanba exploded in intensity between Sept. 12 and 13, becoming a major Category 4 Typhoon on the Saffir-Simpson Scale. NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared data that showed a large area of powerful thunderstorms around the center of circulation, dropping heavy rain over the western North Pacific Ocean.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Super Typhoon Sanba on Sept. 13 at 0447 UTC (12:47 a.m. EDT). The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of Sanba and found an eye about 20 nautical miles (23 miles/37 km) wide, surrounded ...
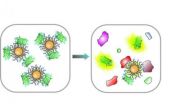
UMass Amherst chemists develop nose-like sensor array to 'smell' cancer diagnoses
2012-09-14
AMHERST, Mass. – In the fight against cancer, knowing the enemy's exact identity is crucial for diagnosis and treatment, especially in metastatic cancers, those that spread between organs and tissues. Now chemists led by Vincent Rotello at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have developed a rapid, sensitive way to detect microscopic levels of many different metastatic cell types in living tissue. Findings appear in the current issue of the journal ACS Nano.
In a pre-clinical non-small-cell lung cancer metastasis model in mice developed by Frank Jirik and colleagues ...
'Smart growth' strategies curb car use, greenhouse gas emissions, SF State study suggests
2012-09-14
A new study finds that smart growth approaches to urban planning could substantially reduce the number of miles that residents drive in a year. The research was published this week in The B.E. Journal of Economic Analysis and Policy.
Smart growth focuses on the development of compact, walkable cities with houses and jobs located close together. By shortening residents' commutes, this form of urban design aims to cut transportation-related energy use and greenhouse gas emissions. California is already pursuing smart growth in order to meet emissions reductions set by the ...
NASA sees wind shear battering Tropical Storm Nadine
2012-09-14
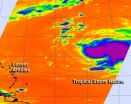
Tropical Storm Nadine is struggling against wind shear and some dry air. Infrared satellite imagery from NASA showed that Nadine's most powerful thunderstorms were being pushed east of the center.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Nadine early on Sept. 13 and saw several factors that indicated the storm was still struggling to achieve hurricane status.
Infrared data from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) that flies aboard Aqua found the strongest thunderstorms with very cold cloud temperatures (colder than -63F/-52C) were being pushed east of Nadine's ...
Warmer temperatures make new USDA plant zone map obsolete
2012-09-14
Gardeners and landscapers may want to rethink their fall tree plantings. Warming temperatures have already made the U.S. Department of Agriculture's new cold-weather planting guidelines obsolete, according to Dr. Nir Krakauer, assistant professor of civil engineering in The City College of New York's Grove School of Engineering.
Professor Krakauer developed a new method to map cold-weather zones in the United States that takes rapidly rising temperatures into account. Analyzing recent weather data, he overhauled the Department of Agriculture's latest plant zone map released ...
Researchers develop rapid method to measure carbon footprints
2012-09-14
Researchers have developed new software that can rapidly calculate the carbon footprints of thousands of products simultaneously, a process that up to now has been time consuming and expensive. The methodology should help companies to accurately label products, and to design ways to reduce their environmental impacts, said Christoph Meinrenken, the project's leader and associate research scientist at Columbia University's Earth Institute and Columbia Engineering. A new study, published online in the Journal of Industrial Ecology, describes the methodology.
The project ...
Home sweet lab: Computerized house to generate as much energy as it uses
2012-09-14
In a ribbon-cutting ceremony on Sept. 12, 2012, the U.S. Commerce Department's National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) unveiled a new laboratory designed to demonstrate that a typical-looking suburban home for a family of four can generate as much energy as it uses in a year. Following an initial year-long experiment, the facility will be used to improve test methods for energy-efficient technologies and develop cost-effective design standards for energy-efficient homes that could reduce overall energy consumption and harmful pollution, and save families money ...
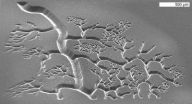
Nanoengineers can print 3D microstructures in mere seconds
2012-09-14
Nanoengineers at the University of California, San Diego have developed a novel technology that can fabricate, in mere seconds, microscale three dimensional (3D) structures out of soft, biocompatible hydrogels. Near term, the technology could lead to better systems for growing and studying cells, including stem cells, in the laboratory. Long-term, the goal is to be able to print biological tissues for regenerative medicine. For example, in the future, doctors may repair the damage caused by heart attack by replacing it with tissue that rolled off of a printer.
Reported ...
Childrem of immigrants come out ahead of peers
2012-09-14
Children of immigrants are outperforming children whose family trees have deeper roots in the United States, learning more in school and then making smoother transitions into adulthood, according to sociologists at The Johns Hopkins University.
Researchers Lingxin Hao and Han S. Woo tracked nearly 11,000 children from as young as age 13 into their early 30s, coming from families with diverse backgrounds. When comparing children with similar socioeconomic status and school conditions, Hao and Woo found that the best students, and later the most successful young adults, ...
Surviving without ice
2012-09-14
With sea ice in the Arctic melting to record lows in summer months, marine animals living there face dramatic changes to their environment. Yet some crustaceans, previously thought to spend their entire lives on the underside of sea ice, were recently discovered to migrate deep underwater and follow ocean currents back to colder areas when ice disappears.
"Our findings provide a basic new understanding of the adaptations and biology of the ice-associated organisms within the Arctic Ocean," said Mark Moline, director of the University of Delaware's School of Marine Science ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] Honestly? Just sign here -- firstJoint study by Rotman School researcher shows signature placement curbs cheating