(Press-News.org) People who bear the genetic mutation for Huntington's disease learn faster than healthy people. The more pronounced the mutation was, the more quickly they learned. This is reported by researchers from the Ruhr-Universität Bochum and from Dortmund in the journal Current Biology. The team has thus demonstrated for the first time that neurodegenerative diseases can go hand in hand with increased learning efficiency. "It is possible that the same mechanisms that lead to the degenerative changes in the central nervous system also cause the considerably better learning efficiency" says Dr. Christian Beste, head of the Emmy Noether Junior Research Group "Neuronal Mechanisms of Action Control" at the RUB.
Passive learning through repeated stimulus presentation
In a previous study, the Bochum psychologists reported that the human sense of vision can be changed in the long term by repeatedly exposing subjects to certain visual stimuli for short periods (we reported in May 2011, http://aktuell.ruhr-uni-bochum.de/pm2011/pm00136.html.de). The task of the participants was to detect changes in the brightness of stimuli. They performed better if they had viewed the stimuli passively for a while first. In the current study, the researchers presented the same task to 29 subjects with the genetic mutation for Huntington's disease, who, however, did not yet show any symptoms. They also tested 45 control subjects without such mutations in the genome. In both groups, the learning efficiency was better after passive stimulus presentation than without the passive training. Subjects with the Huntington's mutation, however, increased their performance twice as fast as those without the mutation.
Glutamate may have paradoxical effect
Degenerative diseases of the nervous system are based on complex changes. A key mechanism is an increased release of the neurotransmitter glutamate. However, since glutamate is also important for learning, in some cases it could lead to the paradoxical effect: better learning efficiency despite degeneration of the nerve cells.
Detecting differences in brightness under aggravated conditions
In each experimental run, the subjects saw two consecutive small bars on a computer screen that either had the same or different brightness. Sometimes, however, not only the brightness changed from bar one to bar two, but also the orientation of the bar (vertical or horizontal). "Normally, the distraction stimulus, i.e. the change in orientation, draws all the attention" Christian Beste explains. "But after the passive training with the visual stimuli, the distraction stimulus has no effect at all." The shift of attention from the non-relevant to the relevant properties of the stimulus was also visible in the electroencephalogram (EEG) in brain areas for early visual processing.
Better performance with stronger mutation
In Huntington's disease, a short segment of a gene is repeated. The number of repetitions determines when the disease breaks out. In the present study, a greater number of repetitions was, however, also associated with higher learning efficiency. "This shows that neurodegenerative changes can cause paradoxical effects" says Christian Beste. "The everyday view that neurodegenerative changes fundamentally entail deterioration of various functions can no longer be maintained in this dogmatic form."
###Bibliographic record
C. Beste, E. Wascher, H.R. Dinse, C. Saft (2012): Faster perceptual learning through excitotoxic neurodegeneration, Current Biology, doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.08.012
Further information
Dr. Christian Beste, Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience, Department of Biological Psychology, Faculty of Psychology at the Ruhr-Universität, 44780 Bochum, Germany, Tel.
+49/234/32-24323
Christian.Beste@rub.de
Click for more
Previous press release on the subject
http://aktuell.ruhr-uni-bochum.de/pm2011/pm00136.html.en
Editor: Dr. Julia Weiler
Learning faster with neurodegenerative disease
Huntington's gene mutation carriers: Severity of the genetic mutation related to learning efficiency
2012-09-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Whole-genome scan helps select best treatment for childhood cancer
2012-09-14
A whole-genome scan to identify large-scale chromosomal damage can help doctors choose the best treatment option for children with neuroblastoma, one of the most common types of childhood cancer, finds an international collaboration jointly led by The Institute of Cancer Research, London.
The researchers called for all children diagnosed with neuroblastoma worldwide to have a whole-genome scan as a standard part of their treatment.
Neuroblastoma, a cancer of the developing nervous system, is sometimes very treatable but other forms are highly aggressive, making the ...
New test to crack down on sporting drugs-cheat test
2012-09-14
Scientists from three UK universities have developed a new test to catch drugs-cheats in sport.
Over the last 10 years, the GH-2004 team, which is based the University of Southampton, has been developing a test for Growth Hormone misuse in sport with funding from the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) and US Anti-Doping Agency and with support from UK Anti-Doping.
The test, developed by scientists at the University of Southampton, King's College London and University of Kent at Canterbury, is based on the measurement of two proteins in the blood, insulin-like growth factor-I ...
Researchers find our inner reptile hearts
2012-09-14
Since the early 1900s, scientists have been wondering how birds and mammals could have developed almost identical conduction systems independently of each other when their common ancestor was a cold-blooded reptile with a sponge-like inner heart that has virtually no conduction bundles.
The studies show that it is simply the spongy inner tissue in the foetal heart that gets stretched out to become a fine network of conductive tissue in adult birds and mammals. And this knowledge can be put to use in the future.
### END ...
Environment: Speaking the same language on noise exposure
2012-09-14
Quantifying noise exposure will be significantly easier thanks to a new set of common noise assessment methods published today. Comparable data on noise exposure in Europe is a prerequisite to set up EU policies to reduce noise pollution, a growing health and economic concern all over Europe. The new methods – known as Common Noise Assessment Methods in Europe (CNOSSOS-EU) – were drawn up by the European Commission's in-house science service, the Joint Research Centre. They assess noise from road, rail and air traffic and from industry, and will provide consistent and comparable ...
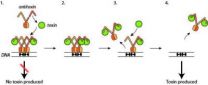
X-rays reveal the self-defence mechanisms of bacteria
2012-09-14
Many pathogenic bacteria are able to go into a dormant state by producing persister cells that are not susceptible to conventional antibiotics. This causes serious problems in the treatment of life-threatening diseases such as tuberculosis, where the presence of persister cells often leads to a resurgence of infection following medical treatment.
At the molecular level, the formation of persister cells is due to the presence of toxins that are produced by the bacteria themselves, and which enable them to enter the dormant state. During this hibernation period, the bacteria ...
Radar measurements of highest precision
2012-09-14
This press release is available in German.
Precise determination of distances is of increasing importance in fabrication technology, for instance, when actuating robots, producing micromechanical components, or controlling machine tools. Frequently, glass scales, inductive sensors, or laser measurement systems are used for distance measurements. Glass scales are very precise and reach micrometer precision. However, they are too inflexible and expensive for daily use. Inductive sensors measuring distances with a coil, magnetic field, and movement work in a contact-free ...
Passive smoking also affects neurodevelopment in babies
2012-09-14
A new study shows that newborns that have been exposed to nicotine from both active and passive smoking mothers show poor physiological, sensory, motor and attention responses.
Smoking during pregnancy has been linked to many different problems in infants like learning difficulties, attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity and even obesity.
However, although the paediatric and obstetric disorders linked to tobacco during this stage are well defined, the effects on neonatal behaviour have not yet been studied in depth.
A new study headed by experts at the ...
New insights on cell competition
2012-09-14
Scientists from the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) describe how natural selection also occurs at the cellular level, and how our body's tissues and organs strive to retain the best cells in their ranks in order to fend off disease processes. These results appear this week in the new issue of Cell Reports. The research, carried out in the CNIO, is led by Eduardo Moreno, who is currently working at the University of Bern in Switzerland.
Recent studies suggest that natural selection described by Charles Darwin also occurs at the cellular level, as our body's ...
Trade unions still fail to lure women leaders, study finds
2012-09-14
There is little doubt that Frances O'Grady has made history as the first woman to be elected General Secretary of the Trades Union Congress in September 2012. A recent study from Queen Mary, University of London casts some light on the level of O'Grady's achievement in the wider union landscape.
This cross-national study found that in both the UK and the US, women still have fewer top positions in trade unions despite growth in overall female membership.
The paper, Lift as You Rise: Union Women's Leadership Talk, discusses the lack of women at union leadership level, ...
Getting (drugs) under your skin
2012-09-14
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Using ultrasound waves, MIT engineers have found a way to enhance the permeability of skin to drugs, making transdermal drug delivery more efficient. This technology could pave the way for noninvasive drug delivery or needle-free vaccinations, according to the researchers.
"This could be used for topical drugs such as steroids — cortisol, for example — systemic drugs and proteins such as insulin, as well as antigens for vaccination, among many other things," says Carl Schoellhammer, an MIT graduate student in chemical engineering and one of the lead authors ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ACES marks 150 years of the Morrow Plots, our nation's oldest research field
Physicists open door to future, hyper-efficient ‘orbitronic’ devices
$80 million supports research into exceptional longevity
Why the planet doesn’t dry out together: scientists solve a global climate puzzle
Global greening: The Earth’s green wave is shifting
You don't need to be very altruistic to stop an epidemic
Signs on Stone Age objects: Precursor to written language dates back 40,000 years
MIT study reveals climatic fingerprints of wildfires and volcanic eruptions
A shift from the sandlot to the travel team for youth sports
Hair-width LEDs could replace lasers
The hidden infections that refuse to go away: how household practices can stop deadly diseases
Ochsner MD Anderson uses groundbreaking TIL therapy to treat advanced melanoma in adults
A heatshield for ‘never-wet’ surfaces: Rice engineering team repels even near-boiling water with low-cost, scalable coating
Skills from being a birder may change—and benefit—your brain
Waterloo researchers turning plastic waste into vinegar
Measuring the expansion of the universe with cosmic fireworks
How horses whinny: Whistling while singing
US newborn hepatitis B virus vaccination rates
When influencers raise a glass, young viewers want to join them
Exposure to alcohol-related social media content and desire to drink among young adults
Access to dialysis facilities in socioeconomically advantaged and disadvantaged communities
Dietary patterns and indicators of cognitive function
New study shows dry powder inhalers can improve patient outcomes and lower environmental impact
Plant hormone therapy could improve global food security
A new Johns Hopkins Medicine study finds sex and menopause-based differences in presentation of early Lyme disease
Students run ‘bee hotels’ across Canada - DNA reveals who’s checking in
SwRI grows capacity to support manufacture of antidotes to combat nerve agent, pesticide exposure in the U.S.
University of Miami business technology department ranked No. 1 in the nation for research productivity
Researchers build ultra-efficient optical sensors shrinking light to a chip
Why laws named after tragedies win public support
[Press-News.org] Learning faster with neurodegenerative diseaseHuntington's gene mutation carriers: Severity of the genetic mutation related to learning efficiency