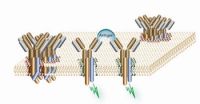
(Press-News.org) In order to track down pathogens and render them harmless, the immune system must be able to recognize myriad different foreign substances and react to them. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and the Centre for Biological Signalling Studies BIOSS at the University of Freiburg have discovered how the immune system's B-cells can be activated by numerous substances from our environment. The receptor molecules on the surface of the B-cells are only activated when the receptor subunits separate following the binding of foreign substances. These findings turn the previous understanding of how B-cell receptors are activated on its head and may contribute to the development of new vaccination strategies and treatments for B-cell tumours. (Nature, September 23, 2010)
Many human diseases, like the increasing number of autoimmune diseases and B-cell tumours such as leukaemia and lymphoma, are triggered by overactive receptors on the surface of white blood cells known as B-lymphocytes or B-cells. Each B-cell has up to 120,000 B-cell receptors on its surface. The activation of these receptors causes the cell to form antibodies. The receptors work on the basis of the lock and key principle, whereby a receptor (the lock) can only be activated by a matching substance (key) and trigger an immune response. If millions of keys can open one lock, the question arises as to how this lock works and how we are protected against the continuing over-activity of our immune response.
Jianying Yang und Michael Reth have now found an answer to this mystery of immune system activation. Using methods from synthetic biology they recreated the mouse B-cell receptor in a fruit-fly cell. Unlike in the previous research carried out in this area, the focus of their attention was the receptor on resting B-cells, the non-activated cells. To their surprise they discovered that the receptor on resting B-cells consists of several different sub-units and forms oligomers. In this form, sectors of the receptors that play an important role in signal transmission are concealed. If a matching binding partner bonds to the receptor, the oligomers disintegrate and the individual sub-units can become active. "The separation process is largely dependent on the structure of the binding partner. This explains why the B-cell receptor can be activated by thousands of different substances," explains Michael Reth from the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology. The discovery that the sub-units of the B-cell receptors form ordered oligomer complexes also leads to the conclusion that the receptors on resting B-cells can only be activated under precisely defined conditions.
Accepted doctrine refuted
The new model for the activation of the receptor is at variance with the hitherto accepted scientific doctrine. Up to now it was believed that the receptors exist in an unordered form in the cell membrane and only aggregate when they make contact with a binding partner. "In contrast, our new model is based on the dissolution and not the formation of a particular receptor structure. This marks a turning point in immunology research and, possibly also, in the field of cell biology," stresses Michael Reth. It appears that other receptor molecules also form oligomers in a resting state which only become active when they disintegrate into subunits or change their conformation.
INFORMATION:
Related links:
[1] BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies
http://www.bioss.uni-freiburg.de/
Original work:
Jianying Yang and Michael Reth
Oligomeric organization of the B cell antigen receptor on resting cells
Nature, 467:465-469: September 23, 2010 (doi: 10.1038/nature09357)
One lock, many keys
2010-10-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
$5 million NSF grant will upgrade and expand NJIT radio telescope array
2010-10-07
A $5 million National Science Foundation (NSF) grant to upgrade and expand a set of radio frequency antennas at Owens Valley Solar Array (OVSA) http://www.ovsa.njit.edu/ has been awarded to NJIT. The new facility is expected to help scientists better understand the nature of solar flares which greatly interest government, industry and the military.
"Space weather incidents such as coronal mass ejections and solar flares can cause problems with cell phone reception, GPS systems, power grids and other technologies," said NJIT Distinguished Professor Dale Gary, a world-renowned ...
Experts advocate realigning type 2 diabetes treatments with disease's natural history
2010-10-07
Chevy Chase, MD— A new consensus statement published in the September, 2010, issue of The Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM) finds that the increasing recognition that beta-cell failure occurs much earlier and severely than commonly believed suggests that regular glycemia screening, early identification of patients at metabolic risk and prompt and aggressive intervention deserves greater emphasis.
The consensus statement is based on the findings of a working group of basic researchers, clinical endocrinologists and primary care ...
New findings pull back curtain on relationship between iron and Alzheimer's disease
2010-10-07
BETHESDA, Md., Oct. 6, 2010 – Massachusetts General Hospital researchers say they have determined how iron contributes to the production of brain-destroying plaques found in Alzheimer's patients.
The team, whose study results appear in this week's Journal of Biological Chemistry, report that there is a very close link between elevated levels of iron in the brain and the enhanced production of the amyloid precursor protein, which in Alzheimer's disease breaks down into a peptide that makes up the destructive plaques.
Dr. Jack T. Rogers, the head of the hospital's neurochemistry ...
Long-extinct passenger pigeon finds a place in the family tree
2010-10-07
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — With bits of DNA extracted from century-old museum specimens, researchers have found a place for the extinct passenger pigeon in the family tree of pigeons and doves, identifying for the first time this unique bird's closest living avian relatives.
The new analysis, which appears this month in Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, reveals that the passenger pigeon was most closely related to other North and South American pigeons, and not to the mourning dove, as was once suspected.
Naturalists have long lamented that one of North America's most ...
Wistar researchers discover new class of objects encoded within the genome
2010-10-07
Despite progress in decoding the genome, scientists estimate that fully 95 percent of our DNA represents dark, unknown territory. In the October 1 issue of the journal Cell researchers at The Wistar Institute shed new light on the genetic unknown with the discovery of the ability of long non-coding RNA (ncRNA) to promote gene expression. The researchers believe these long ncRNA molecules may represent so-called gene enhancer elements—short regions of DNA that can increase gene transcription. While scientists have known about gene enhancers for decades, there has been no ...
UF study: Emotional effects of heavy combat can be lifelong for veterans
2010-10-07
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — The trauma from hard combat can devastate veterans until old age, even as it influences others to be wiser, gentler and more accepting in their twilight years, a new University of Florida study finds.
The findings are ominous with the exposure of today's men and women to heavy combat in the ongoing Iraq and Afghanistan wars on terror at a rate that probably exceeds the length of time for U.S. veterans during World War II, said UF sociologist Monika Ardelt.
"The study shows that we really need to take care of our veterans when they arrive home, because ...
New soy-based natural S-equol supplement reduces menopausal hot flashes, muscle and joint pain in first study among US women
2010-10-07
CHICAGO, IL (Oct. 6, 2010) – A new women’s health, whole soy germ-based nutritional supplement containing Natural S-equol reduced the frequency of moderate to severe hot flashes and reduced muscle and joint pain in the first study of its kind among postmenopausal U.S. women, according to peer-reviewed data presented as a poster presentation at the North American Menopause Society (NAMS) Annual Meeting. Also, the first study to report Natural S-equol contributions to bone health and a study of Natural S-equol safety were presented at NAMS.
“These data from U.S. women ...
Tip sheet: Soy-based natural S-equol supplement data presented from 4 studies at the North American Menopause Society Annual Meeting
2010-10-07
Four clinical studies that add to the evidence about the use of a new nutritional supplement containing the whole soy germ-based ingredient Natural S-equol to improve health were presented at the North American Menopause Society (NAMS) Annual Meeting. These studies include a poster about a first-of-its-kind study in U.S. women that documents the effectiveness of Natural S-equol in reducing the frequency of moderate to severe hot flashes and reducing muscle and joint pain. A second poster reported the first clinical study about Natural S-equol contributions to bone health. ...
Family ties bind desert lizards in social groups
2010-10-07
SANTA CRUZ, CA-- Researchers at the University of California, Santa Cruz, have found that a species of lizard in the Mojave Desert lives in family groups and shows patterns of social behavior more commonly associated with mammals and birds. Their investigation of the formation and stability of family groups in desert night lizards (Xantusia vigilis) provides new insights into the evolution of cooperative behavior.
The researchers reported the results of a five-year study of desert night lizards in a paper published in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological ...
GOES-13 on top of new seventeenth Atlantic (sub) tropical depression
2010-10-07
The GOES-13 satellite keeps a vigilant eye on the Atlantic Ocean and eastern U.S. and this morning at 5 a.m. EDT it saw System 97L organize into the seventeenth tropical depression of the Atlantic Ocean season. The only catch is that it is actually a subtropical depression, so it is currently known as Subtropical Depression 17 (TD17).
A subtropical storm is one where central convection (rapidly rising air that forms thunderstorms) is fairly near the center and it has a warming core in the mid-levels of the troposphere. Subtropical cyclones differ from tropical cyclones ...