(Press-News.org) In the quest to understand how the brain turns sensory input into behavior, Harvard scientists have crossed a major threshold. Using precisely-targeted lasers, researchers have been able to take over an animal's brain, instruct it to turn in any direction they choose, and even to implant false sensory information, fooling the animal into thinking food was nearby.
As described in a September 23 paper published in Nature, a team made up of Sharad Ramanathan, an Assistant Professor of Molecular and Cellular Biology, and of Applied Physics, Askin Kocabas, a Post-Doctoral Fellow in Molecular and Cellular Biology, Ching-Han Shen, a Research Assistant in Molecular and Cellular Biology, and Zengcai V. Guo, from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute were able to take control of Caenorhabditis elegans – tiny, transparent worms – by manipulating neurons in the worms' "brain."
The work, Ramanathan said, is important because, by taking control of complex behaviors in a relatively simple animal - C. elegans have just 302 neurons –we can understand how its nervous system functions..
"If we can understand simple nervous systems to the point of completely controlling them, then it may be a possibility that we can gain a comprehensive understanding of more complex systems," Ramanathan said. "This gives us a framework to think about neural circuits, how to manipulate them, which circuit to manipulate and what activity patterns to produce in them ".
"Extremely important work in the literature has focused on ablating neurons, or studying mutants that affect neuronal function and mapping out the connectivity of the entire nervous system. " he added. "Most of these approaches have discovered neurons necessary for specific behavior by destroying them. The question we were trying to answer was: Instead of breaking the system to understand it, can we essentially hijack the key neurons that are sufficient to control behavior and use these neurons to force the animal to do what we want?"
Before Ramanathan and his team could begin to answer that question, however, they needed to overcome a number of technical challenges.
Using genetic tools, researchers engineered worms whose neurons gave off fluorescent light, allowing them to be tracked during experiments. Researchers also altered genes in the worms which made neurons sensitive to light, meaning they could be activated with pulses of laser light.
The largest challenges, though, came in developing the hardware necessary to track the worms and target the correct neuron in a fraction of a second.
"The goal is to activate only one neuron," he explained. "That's challenging because the animal is moving, and the neurons are densely packed near its head, so the challenge is to acquire an image of the animal, process that image, identify the neuron, track the animal, position your laser and shoot the particularly neuron – and do it all in 20 milliseconds, or about 50 times a second. The engineering challenges involved seemed insurmountable when we started. But Askin Kocabas found ways to overcome these challenges"
The system researchers eventually developed uses a movable table to keep the crawling worm centered beneath a camera and laser. They also custom-built computer hardware and software, Ramanathan said, to ensure the system works at the split-second speeds they need.
The end result, he said, was a system capable of not only controlling the worms' behavior, but their senses as well. In one test described in the paper, researchers were able to use the system to trick a worm's brain into believing food was nearby, causing it to make a beeline toward the imaginary meal.
Going forward, Ramanathan and his team plan to explore what other behaviors the system can control in C. elegans. Other efforts include designing new cameras and computer hardware with the goal of speeding up the system from 20 milliseconds to one. The increased speed would allow them to test the system in more complex animals, like zebrafish.
"By manipulating the neural system of this animal, we can make it turn left, we can make it turn right, we can make it go in a loop, we can make it think there is food nearby," Ramanathan said. "We want to understand the brain of this animal, which has only a few hundred neurons, completely and essentially turn it into a video game, where we can control all of its behaviors."
###Funding for the research was provided by the Human Frontier Science Program, the NIH Pioneer Award and the National Science Foundation.
Understanding the brain by controlling behavior
Using precisely-targeted lasers, researchers manipulate neurons in worms' brains and take control of their behavior
2012-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists predict major shifts in Pacific ecosystems by 2100
2012-09-24
What if you woke up every day to find that the closest grocery store had moved several miles farther away from your home? Over time, you would have to travel hundreds of extra miles to find essential food for yourself and your family. This is potentially a scenario faced by thousands of marine animals affected by climate change.
A new study published in Nature Climate Change examines the distribution of various open ocean animals in the North Pacific and explores how that could change over the next century as global ocean temperatures increase and productivity levels ...
Preterm birth of mother increases risk of pregnancy complications
2012-09-24
Women who were born preterm are at increased risk of complications during pregnancy compared to those born at term, and the risk almost doubles for mothers born before 32 weeks, according to a study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
Pregnancy complications include gestational diabetes, gestational hypertension, and preeclampsia or eclampsia.
The findings are based on a study of 7405 women born preterm and 16 714 women born at term between 1976 and 1995 in the province of Quebec. Of the preterm women, 554 were less than 32 weeks at birth and 6851 were at ...
What does the feminization of family medicine mean?
2012-09-24
With more women in family medicine in Canada, what does this mean for the specialty and the profession, for patients and for society, asks a Salon opinion piece in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
Female family physicians (FPs) now outnumber males, with 50.6% of the profession now female; this trend will continue as older, mainly male, physicians retire. These changing demographics will have implications for the way medicine is practised and for patients. Female FPs practise differently than men, working fewer hours (47 v. 52), seeing fewer patients but with ...
Eunuchs outlive other men
2012-09-24
Castrated men living in Korea centuries ago outlived other men by a significant margin. The findings, reported in the September 25 issue of Current Biology, a Cell Press publication, suggest that male sex hormones are responsible for shortening the lives of men, the researchers say.
The evidence comes after careful study of genealogy records of noble members of the Imperial court of the Korean Chosun dynasty (AD 1392-1910).
"This discovery adds an important clue for understanding why there is a difference in the expected life span between men and women," said Kyung-Jin ...
JCI early table of contents for September 24, 2012
2012-09-24
Small proteins in the cornea protect against bacterial infection
Exposed tissue surfaces, including skin and mucous membranes, are under constant threat of attack by microorganisms in the environment. The layer of cells that line these areas, known as epithelial cells, are the first line of defense against these pathogens, but the underlying molecular mechanisms that allow them to repel microbes are unknown. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, report that epithelial cells in the cornea, which ...
Small proteins in the cornea protect against bacterial infection
2012-09-24
Exposed tissue surfaces, including skin and mucous membranes, are under constant threat of attack by microorganisms in the environment. The layer of cells that line these areas, known as epithelial cells, are the first line of defense against these pathogens, but the underlying molecular mechanisms that allow them to repel microbes are unknown. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, report that epithelial cells in the cornea, which is highly resistant to bacterial infection, express small antimicrobial ...
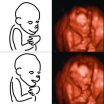
Human brains outpace chimp brains in the womb
2012-09-24
VIDEO:
This movie shows a pregnant chimpanzee undergoing an ultrasound imaging procedure to explore brain growth in her fetus.
Click here for more information.
Humans' superior brain size in comparison to their chimpanzee cousins traces all the way back to the womb. That's according to a study reported in the September 25 issue of Current Biology, a Cell Press publication, that is the first to track and compare brain growth in chimpanzee and human fetuses.
"Nobody knew ...
Pregnancy complications up to twice higher in women born preterm
2012-09-24
This press release is available in French. Women who were born premature are more likely to have pregnancy complications than women who weren't, according to data analyzed by a team lead by Dr. Anne Monique Nuyt, a neonatal specialist and researcher at the Sainte-Justine Mother and Child University Hospital Center and University of Montreal. This is the first study to clearly show the impact of preterm birth (i.e. before 37 weeks of gestation) itself on pregnancy risks. "We knew that to be born with a low birth weight could be associated with increased risk of pregnancy ...
Research shows ants share decision-making, lessen vulnerability to 'information overload'
2012-09-24
TEMPE, Ariz. – Scientists at Arizona State University have discovered that ants utilize a strategy to handle "information overload." Temnothorax rugatulus ants, commonly found living in rock crevices in the Southwest, place the burden of making complicated decisions on the backs of the entire colony, rather than on an individual ant.
In a study published in the early, online version of scientific journal Current Biology, Stephen Pratt, an associate professor in ASU's School of Life Sciences in the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, and Takao Sasaki, a graduate student ...
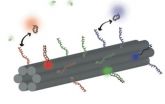
Researchers at Harvard's Wyss Institute engineer novel DNA barcode
2012-09-24
VIDEO:
DNA origami is a process that can be used to self-assemble shapes that are of nanometer dimensions -- 100 nanometers is about 1,000 times shorter than the width of an...
Click here for more information.
BOSTON, September 24, 2012—Much like the checkout clerk uses a machine that scans the barcodes on packages to identify what customers bought at the store, scientists use powerful microscopes and their own kinds of barcodes to help them identify various parts of a cell, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
[Press-News.org] Understanding the brain by controlling behaviorUsing precisely-targeted lasers, researchers manipulate neurons in worms' brains and take control of their behavior