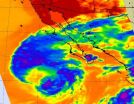
(Press-News.org) NASA infrared satellite imagery showed Tropical Storm Miriam had strong convection and thunderstorm activity in all quadrants of the storm on Sept. 26, except the western quadrant. That activity waned dramatically in 24 hours because of strong wind shear and cooler sea surface temperatures.
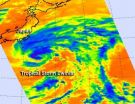
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared data on Tropical Storm Miriam on Sept. 26 at 2047 UTC, when it was off the coast of Baja California. Strongest thunderstorms with very cold cloud top temperatures appear to surround north, east and south of the center of circulation. By Sept. 27, only the northern quadrant of the storm appeared to have those strong thunderstorms.
Miriam appears to be weakening quickly because of strong wind shear and cooler waters.
At 11 a.m. EDT on Sept. 27, Miriam's maximum sustained winds had decreased to near 40 mph (65 kmh) and further weakening is expected. The National Hurricane Center noted that Miriam could become a remnant low later today or tomorrow, Sept. 28.
The center of Tropical Storm Miriam was located near latitude 22.2 north and longitude 116.3 west. Miriam is moving northwest near 6 mph (9 kmh) and is expected to turn west.
Regardless of the weakening condition of the storm, Miriam is still generating dangerous ocean swells along the south and west coasts of the southern and central Baja peninsula today but those will begin to gradually subside by Sept. 28.
INFORMATION:
NASA sees a western weakness in Tropical Storm Miriam
2012-09-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA sees a wide-eyed Super Typhoon Jelawat
2012-09-28
One day ago, Super Typhoon Jelawat's eye was about 25 nautical miles in diameter, today, Sept. 27, NASA satellite data indicated that eye has grown to 36 nautical miles!
The latest infrared image from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite shows a clear eye in Typhoon Jelawat on Sept. 25. The cloud top temperatures of the thunderstorms surrounding the eye exceed -63 Fahrenheit (-52 Celsius) indicating that they are very powerful and heavy rainmakers.. Jelawat also has a rounded shape indicating that circulation is strong ...
NASA sees Tropical Storm Ewiniar embedded in low pressure
2012-09-28
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Ewiniar and noticed strong convection still persists in the storm, despite now being embedded in a subtropical area of low pressure off the coast of Japan.
As Tropical Storm Ewiniar continues to move northward it wound up in an elongated area of low pressure (called a trough) off Japan's east coast. The trough is bringing a strong westerly flow of air into Ewiniar. Despite being battered by those winds, infrared data from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite is showing ...
Study shows the MDHearingAid to be an effective low cost solution to hearing loss
2012-09-28
Washington, D.C. - A study presented at the American Academy of Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery Foundation Annual Meeting in Washington, D.C. shows that the MD Hearing Aid line offers a reasonable low-cost solution to those who are not using hearing aids or other amplification devices because of cost concerns.
In the study, researchers at the Michigan Ear Institute sought to evaluate a novel, inexpensive (under $200.) over- the-counter hearing aid regarding to its acoustic properties and also to test the hearing aid on patients with varying levels of hearing loss ...
Major genetic discovery explains 10 percent of aortic valve disease
2012-09-28
This press release is available in French and German.MONTREAL, Canada, September 28, 2012 - Researchers at the Sainte-Justine University Hospital Center and University of Montreal have identified genetic origins in 10% of an important form of congenital heart diseases by studying the genetic variability within families. "This is more than the sum of the genes found to date in all previous studies, which explained only 1% of the disease, says Dr. Marc-Phillip Hitz, lead author of the study published in PLOS Genetics, under the direction of Dr. Gregor Andelfinger, pediatric ...
Making headway on beta-blockers and sleep
2012-09-28
Boston, MA—Over 20 million people in the United States take beta-blockers, a medication commonly prescribed for cardiovascular issues, anxiety, hypertension and more. Many of these same people also have trouble sleeping, a side effect possibly related to the fact that these medications suppress night-time melatonin production. Researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) have found that melatonin supplementation significantly improved sleep in hypertensive patients taking beta-blockers.
The study will be electronically published on September 28, 2012 and will be ...
Effective HIV care benefited all HIV patients, regardless of demographics and behavioral risk
2012-09-28
Improved treatment options, a multi-pronged treatment model, and federal funding from the Ryan White Program have helped an inner city Baltimore clinic improve outcomes for HIV patients across all groups, including those most often hardest hit by the disease. Published in Clinical Infectious Diseases, the results from the 15-year analysis of patients at a clinic serving a primarily poor, African-American patient population with high rates of injection drug use demonstrate what state-of-the-art HIV care can achieve, given appropriate support.
Current antiretroviral therapy ...
Eliminating invasive cervical cancer possible, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers report
2012-09-28
Researchers at Moffitt Cancer Center and colleagues at the University of South Florida and The Ohio State University have published a paper in the September issue of Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention that provides an overview on preventing invasive cervical cancer.
"The good news is that over the past several decades, the incidence of invasive cervical cancer has declined dramatically," said senior author Anna R. Giuliano, Ph.D., director of Moffitt's Center for Infection Research in Cancer and senior member of the Cancer Epidemiology Department. "The bad ...
Gout guidelines arm patients and physicians with tools to fight painful disease
2012-09-28
Gout is one of the most common forms of inflammatory arthritis, affecting nearly 4% of adult Americans. Newly approved guidelines that educate patients in effective methods to prevent gout attacks and provide physicians with recommended therapies for long-term management of this painful disease are published in Arthritis Care & Research, a peer-reviewed journal of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
Uric acid is produced by the metabolism of purines, which are found in foods and human tissue. When uric acid levels increase, crystals can form and deposit in joints, ...
Eating cherries lowers risk of gout attacks by 35%
2012-09-28
A new study found that patients with gout who consumed cherries over a two-day period showed a 35% lower risk of gout attacks compared to those who did not eat the fruit. Findings from this case-crossover study published in Arthritis & Rheumatism, a journal of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), also suggest that risk of gout flares was 75% lower when cherry intake was combined with the uric-acid reducing drug, allopurinol, than in periods without exposure to cherries or treatment.
Previous research reports that 8.3 million adults in the U.S. suffer with gout, ...
Learning to live on mars
2012-09-28
Boston, MA—Since the beginning of August, NASA's Mars rover, Curiosity, has been roaming all over the distant planet learning as much as it can about the Martian terrain. The mission control team back on Earth has also learned what it may be like on Mars by trying to live and work on a Martian day, which is about 40 minutes longer than an Earth day. This 'day' length causes havoc with the internal 24-hour body clock but researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) have developed and tested a fatigue management program which is successful at controlling this space-age ...